
In the intricate tapestry of the human brain, each structure has its unique significance, playing a vital role in our cognitive and emotional lives. Among these, the habenula, a tiny but crucial region, emerges as a fascinating subject, especially in the realm of emotional processing. This diminutive area, nestled deep within the brain’s epithalamus, serves as a critical hub in the neural network that governs our emotions, influencing everything from our mood swings to our stress responses. Despite its small size, the habenula’s impact on our emotional health is immense. It operates in concert with the limbic system, the brain’s emotional center, modulating our feelings and reactions in ways that researchers are only beginning to understand.
Contents
Introduction to the Habenula and Emotions
In the vast and complex universe of the human brain, where each component plays a pivotal role, the habenula stands out for its unique contribution to emotional processing. Often overshadowed by larger and more famous brain regions, this diminutive structure holds keys to understanding how we process emotions, respond to stress, and regulate mood.
Definition and Importance of the Habenula
The habenula, a tiny structure located in the epithalamus, may not be as well-known as the amygdala or hippocampus, but its impact on emotional regulation is significant. This small area of the brain acts as a critical relay station, processing information between various neural regions. It plays a vital role in our emotional and behavioral responses, especially in how we process negative experiences and learn from them. Understanding the habenula not only offers insights into the basic workings of the brain but also sheds light on potential treatments for emotional disorders.
Overview of Emotional Processing in the Brain
Emotional processing in the brain is a complex and multifaceted operation, involving numerous structures and pathways. The brain’s limbic system, often referred to as the emotional brain, includes key players like the amygdala, hippocampus, and thalamus, which work together to process and regulate our emotions. The habenula’s interaction with these regions is crucial, as it influences our emotional responses and plays a role in mood regulation, reward processing, and avoidance behaviors.
Anatomy of the Habenula
The habenula may be a tiny component of the brain, but its anatomical structure and connections are complex and significant.
Location of the Habenula in the Brain
Situated in the epithalamus, near the center of the brain, the habenula is part of the diencephalon, which also includes the thalamus and hypothalamus. This strategic location places it at a crossroads of neural pathways, allowing it to interact with multiple brain regions. The habenula is actually composed of two small nuclei, the lateral and medial habenular nuclei, each with distinct connections and functions. Its central position in the brain’s anatomy is key to its role as a relay station in neural networks [1].
Structural Components of the Habenula
The habenula’s structure is intricate, with each of its nuclei playing different roles. The lateral habenula is primarily involved in processing negative emotional stimuli and is connected to regions of the brain responsible for mood regulation and stress response. Meanwhile, the medial habenula is linked to the regulation of several neurotransmitters, such as acetylcholine and serotonin, which are crucial in mood and emotional responses. The unique architecture of the habenula allows it to modulate a wide range of neural activities and emotional behaviors.
Habenula Connections to Other Brain Regions
The habenula’s extensive connections to other brain regions underscore its importance in emotional processing. It receives inputs from the limbic system, particularly the amygdala and hippocampus, which are central to emotion and memory. Furthermore, it connects to the dopamine and serotonin systems, influencing mood and reward-related behaviors.
The habenula also sends signals to the brainstem, impacting physiological responses to emotional stimuli. These connections enable the habenula to play a central role in coordinating emotional responses across different brain systems [2].
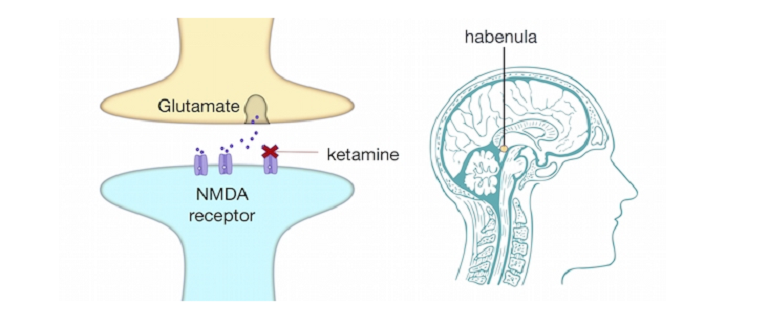
The Habenula’s Role in Emotional Processing
As we move deeper into the mysteries of the human brain, the habenula emerges as a crucial player in the complex domain of emotional processing. This small structure, intricately woven into the brain’s fabric, plays a pivotal role in how we experience, interpret, and respond to a myriad of emotional stimuli.
Interaction of the Habenula with the Limbic System
The habenula’s intimate relationship with the limbic system, the brain’s emotional powerhouse, is fundamental to its role in emotional processing. The limbic system, encompassing structures like the amygdala and hippocampus, is central to the formation and processing of emotions.
The habenula acts as a conduit, relaying information between these structures and other brain regions. This interaction allows the habenula to influence our emotional responses, particularly in situations involving negative feedback, disappointment, or stress. It’s this ability to modulate the limbic system’s activity that underscores the habenula’s vital role in emotional regulation [3].
Influence of the Habenula on Mood and Motivation
The habenula’s impact extends beyond mere emotional processing; it plays a significant role in regulating mood and motivation. By modulating neurotransmitter systems, including dopamine and serotonin, the habenula can influence our feelings of pleasure and pain, reward and punishment.
When the habenula is activated, especially in response to negative events or unmet expectations, it can contribute to feelings of sadness or pessimism. Conversely, its inhibition can lead to increased motivation and a more positive mood. Thus, the habenula serves as a critical balancing mechanism in our emotional and motivational landscape.
The Habenula and Stress Response
Another crucial aspect of the habenula’s function is its involvement in the body’s stress response. When faced with stress, the habenula interacts with the hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal (HPA) axis, a central part of the body’s response system to stress. By influencing this axis, the habenula helps regulate the release of stress hormones like cortisol.
Additionally, it affects the autonomic nervous system, which controls bodily functions such as heart rate and digestion, further underscoring its role in responding to stressful situations. This connection between the habenula and the stress response system highlights its importance in both emotional and physiological aspects of stress management [4].
The habenula’s intricate involvement in emotional processing, mood regulation, and stress response illustrates its significance in the broader context of brain function and mental health. This deeper understanding of the habenula’s role opens new avenues for exploring how the brain processes emotions and responds to various stimuli.
Research on the Habenula
The habenula, though small in size, has become a significant focus in contemporary neuroscience research. The growing body of work surrounding this structure is revealing its intricate role in emotional processing and its potential implications for mental health.
Historical Perspective of the Habenula
The study of the habenula has evolved significantly over time. Initially, this tiny brain region was somewhat overlooked due to its size and the complexity of studying its deep-seated location. Early research, primarily in animal models, began to unravel its basic functions, hinting at its role in emotional and behavioral responses.
However, it wasn’t until the advent of more sophisticated imaging and neuroscientific techniques that the habenula’s true significance began to emerge. These advancements allowed researchers to observe the habenula’s activity in real-time and in more nuanced ways, leading to a deeper understanding of its functions and importance in the neural circuitry of emotions.
Recent Studies and Findings Involving the Habenula
Recent research has brought the habenula into the spotlight, highlighting its role in various aspects of emotional processing. Studies using advanced neuroimaging techniques have shown that the habenula is hyperactive in individuals experiencing depression, suggesting a link between habenula activity and mood disorders.
Furthermore, research on animal models has indicated that the habenula plays a role in behavioral responses to negative stimuli, such as disappointment or failure. These studies have begun to map the complex neural pathways involving the habenula, shedding light on how this region influences not only emotional responses but also decision-making and behavioral outcomes.
The Habenula in Various Emotional Disorders
The implications of habenula research are particularly relevant in the context of emotional disorders. The link between habenula activity and depressive states opens new avenues for potential treatments targeting this brain region. Additionally, understanding the habenula’s role in stress responses and negative emotional processing can provide insights into anxiety disorders and phobias [5].
The ongoing research is also exploring the habenula’s involvement in addiction and its potential role in substance abuse disorders, given its connection to the brain’s reward system. This growing body of research is not only enhancing our understanding of these disorders but also paving the way for new therapeutic approaches.
Clinical Implications of the Habenula and Emotional Disorders
The emerging research on the habenula not only advances our understanding of brain function but also holds significant implications for clinical practice, particularly in the realm of mental health. The insights gained from studying this small brain region are opening new pathways for the treatment and understanding of various emotional disorders.
Potential of the Habenula in Treating Emotional Disorders
One of the most promising aspects of habenula research lies in its potential for developing new treatments for emotional disorders. Given its role in mood regulation and stress response, the habenula could be a target for innovative therapeutic approaches.
For instance, treatments that modulate habenula activity might offer relief for patients with depression, especially those who have not responded to traditional antidepressants. Similarly, therapies aimed at altering habenula function could provide new ways to manage anxiety disorders, PTSD, and other conditions linked to stress and emotional regulation.
Habenula and Psychiatric Medications
The habenula’s involvement in the brain’s neurotransmitter systems also makes it a point of interest for the development of psychiatric medications. Current research is exploring how medications can influence habenula activity, potentially leading to more effective treatments with fewer side effects.
This line of inquiry is particularly relevant for medications that target the serotonin and dopamine systems, both of which are closely linked to the habenula. Understanding how these drugs interact with the habenula could lead to more precise and personalized medication regimens for patients with mood and anxiety disorders.
Future Research Directions Involving the Habenula
Looking forward, the habenula is a rich field for future research, with many avenues yet to be explored. Potential areas of focus include the habenula’s role in chronic pain management, its impact on sleep regulation, and its involvement in neurodegenerative diseases.
Additionally, further research is needed to fully understand the habenula’s complex interactions with other brain regions and its role in various neuropsychiatric conditions. As our understanding of the habenula expands, so too will the opportunities for clinical applications that could significantly improve the lives of individuals suffering from a range of emotional and mental health issues.
References
[1] Understanding the habenula: A major node in circuits regulating emotion and motivation
[2] Lateral Habenula Beyond Avoidance: Roles in Stress, Memory, and Decision-Making
[3] Reward processing by the lateral habenula in normal and depressive behaviors
[4] The lateral habenula nucleus regulates pruritic sensation and emotion
[5] Smells and Emotions Tug on the Brain’s Habenula

