
In the fast-paced digital world, adults are spending more time than ever before in front of screens. From smartphones and computers to televisions and gaming consoles, screens have become an integral part of our daily lives. While technology offers numerous benefits, excessive screen time may have detrimental effects on cognitive health in adults. Here we explore the impact of prolonged screen exposure on various aspects of cognitive functioning, including memory, attention, language, and problem-solving.
Contents
- Understanding Screen Time
- Cognitive Health in Adults
- The Impact of Excessive Screen Time on Cognitive Health
- Role of Sleep in Screen Time and Cognitive Health
- Strategies to Minimize Screen Time
- References
Understanding Screen Time
As we begin our exploration of the impact of excessive screen time on cognitive health, it is essential to first understand what screen time entails and the different types of screens and activities that contribute to our daily screen exposure.
Definition of Screen Time
Screen time refers to the amount of time spent engaging with electronic devices that have display screens. This includes activities such as watching television, browsing the internet, using social media, playing video games, and working on computers. With the increasing use of digital devices in both our personal and professional lives, screen time has become a significant aspect of our daily routines.
Types of Screens and Activities
There are several types of screens that contribute to our overall screen time. Let’s take a closer look at each of these and the common activities associated with them.
Television
Television remains a popular source of entertainment for many adults. Activities contributing to screen time include watching live broadcasts, streaming services, and recorded shows or movies.
Computers
Computers play a crucial role in both personal and professional settings. Screen time on computers includes work-related tasks, checking emails, browsing the internet, watching videos, and engaging in video conferences.
Smartphones
Smartphones have become an indispensable part of our lives, and their convenience contributes significantly to screen time. Common activities include texting, using social media, browsing the internet, watching videos, and playing games.
Tablets
Tablets, similar to smartphones, are portable devices that contribute to screen time. They are often used for reading e-books, browsing the internet, watching videos, playing games, and completing work-related tasks.
Gaming Consoles
Gaming consoles are another source of screen time for many adults. These devices are primarily used for playing video games, which can consume hours of time in immersive virtual environments.
Average Screen Time for Adults
According to a report by Nielsen, American adults spend an average of over 11 hours per day interacting with media, with a significant portion of this time spent in front of screens. As technology continues to advance and permeate every aspect of our lives, it is crucial to understand the potential implications of excessive screen time on cognitive health in adults.

Cognitive Health in Adults
Before delving into the effects of excessive screen time on cognitive health, it is vital to understand the concept of cognitive health and the key cognitive functions that contribute to our daily lives.
Definition of Cognitive Health
Cognitive health refers to the ability of the brain to perform essential mental processes. It encompasses various aspects of mental functioning, including memory, attention, language, and problem-solving [1]. Maintaining cognitive health is crucial for overall well-being and quality of life, as it allows individuals to effectively engage in daily activities, socialize, and make informed decisions.
Key Cognitive Functions
There are several cognitive functions that play a significant role in our daily lives. The following are some of the most important functions that can be affected by excessive screen time:
Memory
Memory is the ability to store, retain, and retrieve information. It is a fundamental cognitive function that enables us to learn from past experiences and apply that knowledge to new situations. Memory can be divided into short-term (or working) memory, which allows us to hold and manipulate information temporarily, and long-term memory, which stores information for more extended periods.
Attention
Attention refers to the ability to selectively focus on specific information, tasks, or stimuli while ignoring irrelevant distractions. It is essential for effectively processing and retaining information and is a prerequisite for other cognitive functions, such as memory and problem-solving.
Language
Language is the ability to understand and produce spoken and written communication. It is a complex cognitive function that involves multiple processes, including comprehension, expression, and reasoning. Language skills are vital for effective communication, social interaction, and cognitive development.
Problem-Solving
Problem-solving is the capacity to identify, analyze, and resolve complex issues or situations. This cognitive function relies on various mental processes, such as attention, memory, and reasoning, and is crucial for making informed decisions and adapting to new challenges.
Factors Affecting Cognitive Health
Various factors can influence cognitive health in adults. Some of these factors include age, genetics, level of education, lifestyle habits, and environmental factors. Additionally, certain behaviors and activities, such as excessive screen time, can have a significant impact on cognitive functioning. In the following sections, we will discuss how excessive screen time can affect key cognitive functions and overall cognitive health in adults.

The Impact of Excessive Screen Time on Cognitive Health
Now that we have a clear understanding of both screen time and cognitive health, we can explore the potential impacts of excessive screen time on various cognitive functions. Research suggests that spending extended periods in front of screens can have negative consequences on memory, attention, language, and problem-solving abilities.
Memory Impairment
Excessive screen time can adversely affect memory function in adults, leading to both short-term and long-term memory issues.
Short-Term Memory Loss
Spending long hours in front of screens may contribute to short-term memory loss by overloading the working memory. As we constantly switch between tasks and consume vast amounts of information, our working memory struggles to process and retain this information, leading to reduced short-term memory capacity [2].
Long-Term Memory Degradation
Prolonged screen exposure can also interfere with the consolidation of long-term memories. The constant bombardment of new information hinders the brain’s ability to process and store information effectively, ultimately leading to weakened long-term memory [3].
Attention and Focus Issues
Excessive screen time can also have detrimental effects on attention and focus in adults.
Decreased Attention Span
Frequent use of digital devices and constant exposure to new stimuli can condition the brain to expect constant novelty. This can lead to a decreased attention span, as individuals may find it challenging to focus on a single task or piece of information for extended periods [4].
Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder (ADHD)
Research has suggested a potential link between excessive screen time and the development or exacerbation of ADHD symptoms in adults. The constant stimulation provided by screens may contribute to attention difficulties, impulsivity, and hyperactivity [5].
Language and Communication Difficulties
Prolonged screen exposure can also impact language and communication skills in adults.
Reduced Vocabulary
Spending extended periods in front of screens, particularly engaging in activities that involve minimal verbal communication, can lead to a reduction in vocabulary. This can manifest as a decreased ability to express oneself effectively or comprehend complex language [6].
Weakened Verbal Skills
Excessive screen time can also weaken verbal skills by reducing opportunities for face-to-face communication and social interaction. Overreliance on digital communication may hinder the development of essential verbal and nonverbal communication skills, leading to difficulties in social settings [7].
Problem-Solving and Decision-Making Challenges
Excessive screen time can negatively impact problem-solving and decision-making abilities in adults.
Reduced Analytical Skills
Spending long hours on digital devices, particularly engaging in passive activities, can diminish analytical skills. This can result in a decreased ability to critically evaluate information, synthesize complex concepts, and solve problems effectively [8].
Poor Judgment and Decision-Making
The constant influx of information and stimuli associated with excessive screen time can interfere with the brain’s ability to make informed decisions. This can lead to impulsive decision-making and poor judgment, as individuals may struggle to weigh the pros and cons of different options or assess potential risks and benefits [9].
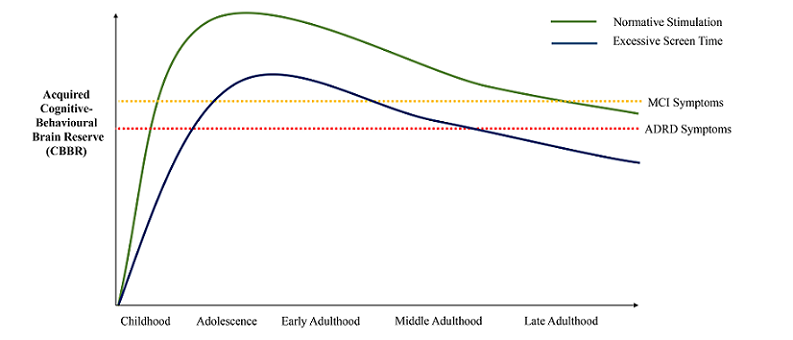
Role of Sleep in Screen Time and Cognitive Health
Sleep is a critical factor in maintaining cognitive health, and it is closely linked to screen time. In this section, we will explore the importance of sleep for cognitive functioning, the impact of blue light exposure on sleep quality, and the relationship between sleep deprivation and cognitive health.
The Importance of Sleep for Cognitive Functioning
Sleep plays a vital role in maintaining and enhancing cognitive functions. During sleep, the brain consolidates memories, processes information, and repairs itself. Adequate sleep is essential for optimal memory, attention, problem-solving, and decision-making abilities. A lack of sleep can lead to impaired cognitive functioning and a decline in overall cognitive health.
Blue Light Exposure and Sleep Quality
One of the significant concerns related to screen time and sleep is the exposure to blue light emitted by screens [10]. Blue light can interfere with the production of melatonin, a hormone that regulates the sleep-wake cycle. Prolonged exposure to blue light, especially in the evening, can disrupt the body’s natural circadian rhythm, making it difficult to fall asleep and stay asleep. This disruption can lead to poor sleep quality and reduced sleep duration.
Sleep Deprivation and Cognitive Health
Sleep deprivation, often resulting from excessive screen time and blue light exposure, can have a significant impact on cognitive health. A lack of sleep can lead to:
- Memory impairment: Sleep deprivation can hinder the consolidation of memories and reduce the ability to recall information.
- Reduced attention and focus: A lack of sleep can result in difficulty concentrating and maintaining focus on tasks, leading to decreased productivity and an increased likelihood of errors.
- Impaired problem-solving and decision-making: Sleep-deprived individuals may struggle with problem-solving, critical thinking, and decision-making, as the brain’s ability to process information and evaluate options is compromised.
- Mood disturbances: Sleep deprivation can also lead to mood disturbances, such as irritability, anxiety, and depression, which can further impact cognitive functioning.
Strategies to Minimize Screen Time
To mitigate the negative effects of excessive screen time on cognitive health, it is essential to adopt strategies that help reduce screen exposure and promote a healthier balance between digital and offline activities. The following are some practical approaches to minimize screen time and support cognitive well-being.
Setting Time Limits
One effective way to reduce screen time is to set daily or weekly limits for different devices or activities. Establishing boundaries can help individuals become more aware of their screen usage and prioritize essential tasks or activities over mindless screen consumption.
Establishing Screen-Free Zones
Creating screen-free zones in the home, such as the bedroom or dining room, can encourage more meaningful interactions and reduce overall screen time. By designating specific areas for screen use and others for screen-free activities, individuals can create a more balanced environment that supports cognitive health.
Engaging in Alternative Activities
Replacing screen time with alternative activities can help adults maintain cognitive health while reducing their reliance on screens. Some examples of alternative activities include:
Physical Exercise
Engaging in regular physical activity has numerous benefits for cognitive health, including improved memory, attention, and problem-solving abilities. Exercise can also help reduce stress and improve sleep quality, further supporting cognitive well-being.
Social Interactions
Spending time with friends and family, participating in social events, or joining clubs and organizations can foster social connections and provide opportunities for meaningful face-to-face communication, which is essential for maintaining language and communication skills.
Hobbies and Interests
Pursuing hobbies and interests can help individuals develop new skills, foster creativity, and maintain cognitive health. Examples of hobbies include painting, reading, gardening, playing musical instruments, or learning a new language.
Monitoring and Adjusting Screen Time Habits
Regularly assessing and adjusting screen time habits can help individuals become more mindful of their screen usage and make necessary changes to maintain cognitive health. Tools such as screen time monitoring apps and built-in device features can provide valuable insights into screen usage patterns and encourage healthier habits.
By implementing these strategies and creating a more balanced lifestyle, adults can reduce the negative impact of excessive screen time on cognitive health and promote overall well-being.
References
[1] What Is Cognitive Health & Why Is It Crucial for Wellbeing?
[2] Screen Time and the Brain
[3] What Does Too Much Screen Time Do to Children’s Brains?
[4] Investigating Screen Time’s Impact on the Attention Span
[5] ADHD Brains on Screens: Decoding a Complicated Relationship
[6] Screen Time and Speech/Language Delays
[7] Effects of screen exposure on young children’s cognitive development
[8] The Role of Epigenetics in Age-Related Cognitive Decline
[9] What Does Screen Time Do To My Brain?
[10] Blue light has a dark side

