You may have heard about the thyroid gland’s essential role in regulating our metabolism, but did you know that it can also impact our cognitive health? There can be a strong relationship between thyroid function and brain fog, a term used to describe a cluster of cognitive symptoms that can leave you feeling mentally unclear, sluggish, and forgetful.
Contents
Introduction to Thyroid and Brain Fog
In recent years, the topic of brain fog has gained considerable attention as more people experience its effects on their daily lives. This elusive condition is often linked to various factors, with one significant connection being the thyroid gland.
Brief Overview of the Thyroid Gland
The thyroid gland is a small, butterfly-shaped organ located at the front of the neck, just below the Adam’s apple. It is part of the endocrine system and plays a crucial role in producing and regulating hormones that affect the body’s metabolism, growth, and development [1]. The primary hormones secreted by the thyroid gland are triiodothyronine (T3) and thyroxine (T4). These hormones influence numerous physiological processes, including energy production, heart rate, body temperature, and even cognitive function.
Definition of Brain Fog
Brain fog is a term used to describe a range of cognitive symptoms that can affect an individual’s ability to think clearly, focus, and remember information. It is not a medical diagnosis in itself but a subjective experience that can be caused by various factors. People with brain fog often report feelings of mental confusion, sluggishness, forgetfulness, and difficulty concentrating. These symptoms can be temporary or persistent, mild or severe, and may significantly impact daily functioning and quality of life [2].
Connection between Thyroid and Brain Fog
The thyroid gland’s role in regulating metabolism and energy production has a direct impact on cognitive function, making it a key player in the development of brain fog. Imbalances in thyroid hormone levels, such as those seen in hypothyroidism (underactive thyroid) or hyperthyroidism (overactive thyroid), can disrupt brain function and lead to symptoms associated with brain fog.
Understanding Thyroid Function
To better comprehend the link between thyroid function and brain fog, it is essential to first grasp the basics of thyroid function and its hormones.
Thyroid Hormones and Their Roles
The thyroid gland produces two primary hormones—triiodothyronine (T3) and thyroxine (T4)—that regulate various bodily processes [3].
Triiodothyronine (T3)
T3 is the active form of thyroid hormone and is responsible for regulating the body’s metabolism, which encompasses energy production, growth, and development. T3 plays a vital role in maintaining body temperature, heart rate, and muscle strength. It also affects brain development, mood, and cognitive function.
Thyroxine (T4)
T4 is the inactive form of thyroid hormone and is converted to T3 in the liver and other tissues. The primary function of T4 is to serve as a reservoir for T3 production. Like T3, T4 impacts metabolism, body temperature, heart rate, and cognitive function. The balance between T3 and T4 is critical for maintaining overall hormonal balance and bodily function.
Hypothyroidism and Hyperthyroidism
Thyroid imbalances, such as hypothyroidism and hyperthyroidism, can significantly affect cognitive function [4].
Symptoms and Causes
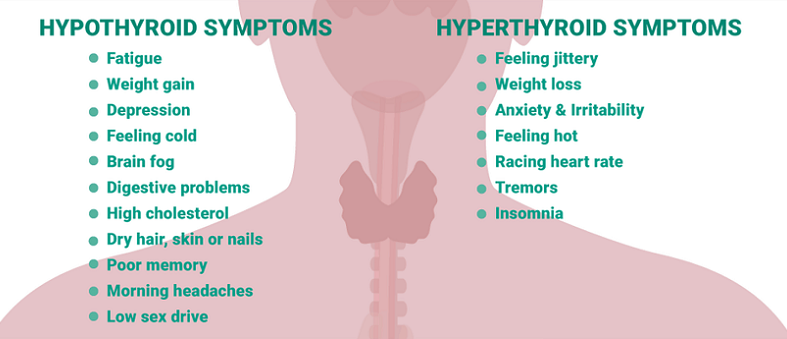
Hypothyroidism is a condition where the thyroid gland produces insufficient thyroid hormones, leading to a slowed metabolism. Common symptoms include fatigue, weight gain, sensitivity to cold, dry skin, hair loss, and depression. The most common cause of hypothyroidism is Hashimoto’s thyroiditis, an autoimmune disease in which the immune system attacks the thyroid gland.
Hyperthyroidism, on the other hand, occurs when the thyroid gland produces excessive amounts of thyroid hormones, causing an overactive metabolism. Symptoms of hyperthyroidism include weight loss, rapid heartbeat, nervousness, irritability, increased sweating, and sleep disturbances. Graves’ disease, an autoimmune condition, is the most common cause of hyperthyroidism.
Impact on Cognitive Function
Both hypothyroidism and hyperthyroidism can lead to cognitive dysfunction. In hypothyroidism, the reduced production of thyroid hormones can result in slowed cognitive function, memory problems, and difficulty concentrating. Conversely, hyperthyroidism may cause anxiety, restlessness, and overstimulation, which can impair cognitive function and contribute to brain fog.
Brain Fog: Symptoms and Causes
Brain fog is a complex and often misunderstood condition that can have numerous causes. To better understand the relationship between thyroid function and brain fog, it is important to first explore the symptoms of brain fog and the potential factors contributing to its development.
Common Symptoms of Brain Fog
While brain fog can manifest differently in individuals, there are several common symptoms that people often experience. These include:
- Difficulty concentrating or focusing on tasks
- Memory lapses or forgetfulness
- Feeling mentally sluggish or slow
- Confusion or disorientation
- Trouble processing information
- Mental fatigue, even after adequate rest
- Difficulty finding the right words during conversations
These symptoms can be temporary or chronic, and their severity can vary greatly, making it challenging for those affected to function optimally in their daily lives.
Potential Causes of Brain Fog
Brain fog can result from various factors, including hormonal imbalances, stress, poor diet, and other medical conditions [5]. It is essential to consider these potential causes when addressing brain fog, as understanding the root cause can help guide appropriate treatment and management strategies.
Hormonal Imbalances
As discussed in previous sections, imbalances in thyroid hormones can directly impact cognitive function and contribute to brain fog. However, other hormonal imbalances, such as those related to estrogen, progesterone, and cortisol, can also play a role in the development of brain fog.
Stress and Anxiety
Chronic stress and anxiety can take a significant toll on cognitive function. The constant release of stress hormones like cortisol can impair memory, focus, and overall cognitive performance, leading to brain fog.
Poor Diet and Lifestyle Choices
A poor diet lacking essential nutrients can affect brain function and contribute to brain fog. Inadequate hydration, excessive caffeine or alcohol consumption, and consuming processed foods high in sugar and unhealthy fats can all negatively impact cognitive health.
Other Medical Conditions
Various medical conditions can lead to brain fog, such as sleep disorders, chronic fatigue syndrome, fibromyalgia, nutritional deficiencies, and even certain medications. In some cases, addressing the underlying condition may help alleviate brain fog symptoms.
The Thyroid-Brain Fog Connection
Now that we have a better understanding of brain fog symptoms and potential causes, let’s examine the relationship between thyroid function and brain fog in greater detail.
Thyroid Hormones and Brain Function
Thyroid hormones play a critical role in maintaining optimal brain function. They influence various aspects of cognitive health, including neurotransmitter production, energy metabolism, and overall brain function [6].
Effects on Neurotransmitters
Thyroid hormones regulate the production and function of several neurotransmitters, including dopamine, serotonin, and norepinephrine. These neurotransmitters are essential for mood regulation, memory formation, and overall cognitive function. Imbalances in thyroid hormones can disrupt neurotransmitter levels, leading to impaired cognitive function and brain fog.
Impact on Energy Production
Thyroid hormones also play a vital role in energy production and metabolism within the brain. An imbalance in thyroid hormones can result in either too little or too much energy production, leading to cognitive dysfunction and brain fog.
Hypothyroidism and Brain Fog
Hypothyroidism, or an underactive thyroid, can contribute to brain fog in various ways [7]. The reduced production of thyroid hormones in this condition can result in slowed cognitive function, memory problems, and difficulty concentrating.
Slowed Cognitive Function
Individuals with hypothyroidism may experience slowed thinking and processing speed, which can make it difficult to concentrate and focus on tasks. This sluggish cognitive function is often a direct result of low thyroid hormone levels.
Memory and Concentration Issues
Memory and concentration can also be affected by hypothyroidism. Low thyroid hormone levels can impair the brain’s ability to form and retrieve memories, leading to forgetfulness and difficulty concentrating.
Hyperthyroidism and Brain Fog
Hyperthyroidism, or an overactive thyroid, can also contribute to brain fog. The excessive production of thyroid hormones in this condition can cause anxiety, restlessness, and overstimulation, all of which can impair cognitive function [8].
Anxiety and Overstimulation
Individuals with hyperthyroidism may experience increased anxiety and restlessness due to elevated thyroid hormone levels. This overstimulation can make it difficult to focus and may contribute to brain fog.
Sleep Disturbances
Hyperthyroidism can also lead to sleep disturbances, such as insomnia or poor sleep quality. Inadequate sleep can have a significant impact on cognitive function, contributing to brain fog and impaired mental clarity.

Diagnosing Thyroid-Related Brain Fog
Determining whether thyroid function is contributing to brain fog is crucial for developing an appropriate treatment plan.
Importance of Accurate Diagnosis
Accurately diagnosing thyroid-related brain fog is vital for several reasons. First, it allows for targeted treatment and management strategies that specifically address the underlying thyroid issue. Second, it can help rule out other potential causes of brain fog, ensuring that the root cause is appropriately addressed. Lastly, accurate diagnosis can provide patients with a better understanding of their condition and empower them to make informed decisions about their healthcare.
Blood Tests and Imaging
Several tests and imaging studies can help assess thyroid function and determine whether it may be contributing to brain fog.
Blood Tests
Blood tests that measure thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH), free T3, and free T4 levels are commonly used to diagnose thyroid disorders. Elevated TSH levels may indicate hypothyroidism, while low TSH levels may suggest hyperthyroidism. Abnormal T3 and T4 levels can further confirm the presence of a thyroid issue.
Imaging Studies
Ultrasound and nuclear medicine scans, such as a thyroid uptake scan or thyroid scintigraphy, can provide valuable information about the structure and function of the thyroid gland. These imaging studies can help identify issues such as thyroid nodules, inflammation, or autoimmune disease, which may be contributing to brain fog.
Considering Other Causes of Brain Fog
While it is essential to assess thyroid function in cases of brain fog, it is also crucial to consider other potential causes. As discussed in previous sections, brain fog can result from various factors, such as hormonal imbalances, stress, poor diet, and other medical conditions. A thorough evaluation, including a comprehensive medical history, physical examination, and additional laboratory tests, may be necessary to identify the root cause of brain fog and develop an appropriate treatment plan.
Treatment and Management of Thyroid-Related Brain Fog
Once a diagnosis of thyroid-related brain fog has been established, it is essential to implement appropriate treatment and management strategies to alleviate symptoms and improve cognitive function.
Medications
Depending on the underlying thyroid issue, different medications may be prescribed to help regulate thyroid hormone levels and alleviate brain fog symptoms.
Hypothyroidism
For individuals with hypothyroidism, thyroid hormone replacement therapy, typically in the form of levothyroxine (T4), is the standard treatment. This medication helps restore normal thyroid hormone levels, improving cognitive function and reducing brain fog symptoms. Regular blood tests are necessary to monitor thyroid hormone levels and adjust the dosage as needed.
Hyperthyroidism
Treatment options for hyperthyroidism include antithyroid medications, such as methimazole or propylthiouracil, which help reduce the production of thyroid hormones. In some cases, beta-blockers may also be prescribed to manage symptoms like anxiety and rapid heartbeat. Radioactive iodine therapy or surgical removal of the thyroid gland may be considered for more severe cases or if other treatments are not effective.
Lifestyle Changes
In addition to medications, making certain lifestyle changes can help improve thyroid function and reduce brain fog symptoms [9].
Diet
A balanced, nutrient-dense diet can support thyroid health and cognitive function. Consuming foods rich in essential nutrients like iodine, selenium, and zinc can help maintain proper thyroid function. Additionally, eating a diet high in antioxidants, healthy fats, and lean proteins can promote brain health and reduce inflammation.
Exercise
Regular physical activity can improve thyroid function, increase energy levels, and enhance cognitive function. Engaging in activities such as walking, swimming, or yoga can help reduce stress, improve mood, and alleviate brain fog symptoms.
Sleep
Prioritizing quality sleep is crucial for overall cognitive function and brain health. Establishing a regular sleep schedule, creating a relaxing bedtime routine, and maintaining a comfortable sleep environment can help improve sleep quality and reduce brain fog.
Alternative Therapies
Some individuals may find relief from brain fog symptoms through alternative therapies. While more research is needed to confirm their effectiveness, the following therapies may provide additional support for those experiencing thyroid-related brain fog:
Acupuncture
Acupuncture is a traditional Chinese medicine technique that involves inserting thin needles into specific points on the body. Some studies suggest that acupuncture may help improve cognitive function and reduce symptoms of brain fog.
Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT)
CBT is a form of psychotherapy that helps individuals identify and change negative thought patterns and behaviors. CBT may be useful in addressing stress and anxiety related to brain fog and improving coping strategies.
Meditation and Mindfulness
Practicing meditation and mindfulness techniques can help reduce stress, increase focus, and improve cognitive function. These practices may be particularly helpful in managing the anxiety and overstimulation associated with hyperthyroidism-related brain fog.
References
[1] Hypothyroidism: Symptoms, Causes, Treatment & Medication
[2] Hypothyroid patients described what brain fog feels like
[3] Brain Fog in Hypothyroidism: Understanding the Patient’s Perspective
[4] Coping with brain fog
[5] Brain fog
[6] Thyroid Disease Symptoms You Should Be Aware Of
[7] Thyroid disease: Can it affect a person’s mood?
[8] Causes – Underactive thyroid (hypothyroidism)
[9] Signs something could be wrong with your thyroid

