Insulin, a hormone well-known for its crucial role in regulating blood sugar levels, plays a surprisingly vital part in maintaining brain health and cognitive function. Though its significance is often overshadowed by its involvement in diabetes and metabolism, insulin serves as a key player in various processes within the brain, including neuronal growth, synaptic plasticity, and memory formation.
Contents
What Is Insulin?
The hormone insulin, primarily known for its role in regulating glucose metabolism, has been the subject of extensive research due to its importance in maintaining overall health. While the connection between insulin and diabetes is well-established, recent studies have uncovered a lesser-known yet crucial aspect of insulin: its impact on brain health and cognitive function.
Importance of Insulin in the Human Body
Insulin, produced by the pancreas, is essential for allowing glucose to enter cells, providing them with the energy necessary to function. Beyond its role in glucose metabolism, insulin is involved in various other physiological processes, such as fat storage, protein synthesis, and cellular growth. Its importance in maintaining homeostasis underscores the need to understand insulin’s broader implications on human health.
Overview of Brain Health and Cognitive Function
Brain health refers to the ability of the brain to perform its essential functions, such as learning, memory, concentration, and decision-making, while maintaining its structural and functional integrity. Cognitive function, a crucial aspect of brain health, encompasses the mental processes that allow us to think, learn, and remember. It is increasingly important to explore the factors influencing brain health and cognitive function, as the prevalence of age-related cognitive decline and neurodegenerative diseases continues to rise.
Insulin’s Function in the Brain
While insulin’s role in glucose metabolism is well-established, its functions within the brain are not as widely recognized. Insulin receptors are abundant in areas of the brain responsible for learning and memory, suggesting that insulin plays a critical role in these processes.
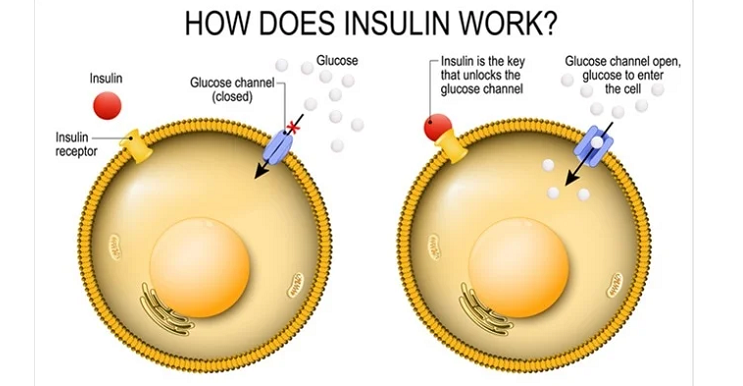
Insulin Receptors and Signaling Pathways
Insulin receptors are proteins found on the surface of cells that bind to insulin, initiating a series of reactions within the cell [1]. In the brain, insulin receptors are highly concentrated in regions such as the hippocampus, cerebral cortex, and hypothalamus, which are crucial for learning, memory, and appetite regulation. When insulin binds to its receptors in the brain, it activates a signaling cascade that influences various cellular processes, such as glucose uptake, protein synthesis, and gene expression.
Insulin’s Role in Neuronal Survival and Growth
Insulin plays a crucial role in promoting the survival and growth of neurons, the primary cells of the nervous system responsible for transmitting information [2]. Studies have shown that insulin promotes neuronal growth and differentiation by activating specific signaling pathways that regulate the expression of genes involved in these processes. Furthermore, insulin has been found to have neuroprotective effects, reducing neuronal cell death in response to various stressors.
Insulin’s Impact on Synaptic Plasticity
Synaptic plasticity refers to the ability of the brain’s synapses, or connections between neurons, to change in strength and structure. This plasticity is critical for learning and memory formation, as it allows the brain to adapt and respond to new information. Insulin has been found to modulate synaptic plasticity by regulating the release of neurotransmitters, the chemical messengers that facilitate communication between neurons [3]. Additionally, insulin influences the expression of proteins involved in the formation and maintenance of synapses, further supporting its role in learning and memory processes.
Insulin Resistance and Brain Health
As we have seen, insulin plays a critical role in maintaining brain health and cognitive function. However, when insulin signaling is disrupted, it can lead to insulin resistance, a condition that has been linked to various cognitive disorders.
Defining Insulin Resistance
Insulin resistance occurs when cells in the body, including those in the brain, become less responsive to insulin. As a result, the pancreas produces more insulin in an attempt to overcome this resistance, leading to elevated insulin levels in the bloodstream. Over time, this can strain the pancreas and contribute to the development of type 2 diabetes. Insulin resistance has also been implicated in several other health conditions, such as obesity, cardiovascular disease, and metabolic syndrome.
Insulin Resistance and Cognitive Decline
Numerous studies have found a link between insulin resistance and cognitive decline [4]. Impaired insulin signaling in the brain can disrupt the processes we previously discussed, such as neuronal survival, growth, and synaptic plasticity, ultimately affecting learning and memory. Furthermore, insulin resistance can lead to increased inflammation and oxidative stress in the brain, which may exacerbate cognitive decline.
Alzheimer’s Disease: The Connection with Insulin Resistance
Alzheimer’s disease, the most common form of dementia, has been increasingly linked to insulin resistance. Some researchers have even referred to Alzheimer’s as “type 3 diabetes” due to the similarities in the underlying mechanisms. Insulin resistance in the brain can contribute to the accumulation of amyloid-beta plaques and neurofibrillary tangles, hallmark features of Alzheimer’s disease. These toxic protein aggregates disrupt neuronal communication and lead to the death of brain cells, resulting in cognitive decline and memory loss.
Diabetes and its Impact on Brain Health
Individuals with diabetes, particularly type 2 diabetes, have an increased risk of developing cognitive decline and dementia [5]. High blood sugar levels can damage blood vessels in the brain, impairing the delivery of oxygen and nutrients to brain cells. Additionally, chronic inflammation associated with diabetes can contribute to neuronal damage and cognitive dysfunction. Understanding the link between diabetes, insulin resistance, and brain health is essential for developing effective prevention and treatment strategies.
Strategies for Maintaining Healthy Insulin Levels
Given the crucial role of insulin in brain health and cognitive function, it is essential to adopt strategies that promote healthy insulin levels and reduce the risk of insulin resistance.
Diet and Nutritional Approaches
The food we consume can have a significant impact on our insulin levels and sensitivity [6]. By making mindful choices about our diet, we can support healthy insulin function and, in turn, promote brain health.
Foods That Promote Insulin Sensitivity
Certain foods can help improve insulin sensitivity and reduce the risk of insulin resistance. These foods include:
- High-fiber foods: Whole grains, fruits, vegetables, and legumes provide dietary fiber that can help regulate blood sugar levels and improve insulin sensitivity.
- Healthy fats: Monounsaturated and polyunsaturated fats found in foods like avocados, nuts, seeds, and olive oil can help maintain healthy insulin levels.
- Lean protein sources: Fish, poultry, and plant-based proteins, such as beans and lentils, can help maintain stable blood sugar levels and promote insulin sensitivity.
- Antioxidant-rich foods: Colorful fruits and vegetables rich in antioxidants, such as berries, leafy greens, and bell peppers, can combat oxidative stress and inflammation associated with insulin resistance.
Foods to Avoid for Insulin Resistance
On the other hand, some foods can contribute to insulin resistance and should be limited or avoided:
- Refined carbohydrates: Foods high in refined carbohydrates, such as white bread, pasta, and sugary snacks, can cause rapid spikes in blood sugar levels, leading to increased insulin production and resistance.
- Trans fats: Found in some processed and fried foods, trans fats can increase inflammation and impair insulin sensitivity.
- Sugary beverages: Regular consumption of sugary drinks, such as soda and fruit juice, can lead to insulin resistance and increased risk of type 2 diabetes.
Exercise and Its Role in Insulin Sensitivity
Regular physical activity can play a significant role in improving insulin sensitivity and maintaining healthy insulin levels [7]. Exercise helps muscles use glucose more efficiently, reducing the amount of insulin needed to maintain stable blood sugar levels. Both aerobic activities, such as brisk walking, running, or swimming, and resistance training, like weight lifting, can help enhance insulin sensitivity and support brain health.
Sleep and Stress Management for Optimal Insulin Function
Adequate sleep and effective stress management are crucial for maintaining healthy insulin levels [8]. Lack of sleep and chronic stress can disrupt the body’s ability to regulate insulin, increasing the risk of insulin resistance. Prioritizing sleep by establishing a consistent sleep schedule and creating a relaxing bedtime environment can help support optimal insulin function. In addition, incorporating stress-reduction techniques, such as meditation, deep breathing, or yoga, can improve insulin sensitivity and promote overall well-being.
Therapeutic Interventions for Insulin-Related Cognitive Impairment
In addition to lifestyle modifications, various therapeutic interventions are being researched and developed to address insulin-related cognitive impairment. These interventions aim to target the underlying mechanisms of insulin resistance and cognitive decline, offering potential treatment options for individuals affected by these conditions.
Intranasal Insulin Administration
Intranasal insulin administration is a novel approach that delivers insulin directly to the brain, bypassing the bloodstream and potentially improving brain insulin signaling [9]. Studies have shown that intranasal insulin can enhance memory and cognitive function in individuals with mild cognitive impairment and Alzheimer’s disease. While more research is needed to determine the long-term effects and optimal dosing, intranasal insulin represents a promising therapeutic option for insulin-related cognitive impairment.
Medications for Insulin Resistance and Cognitive Health
Several medications used to treat insulin resistance and diabetes have shown potential benefits for cognitive health:
- Metformin: A commonly prescribed medication for type 2 diabetes, metformin has been shown to improve insulin sensitivity and reduce inflammation. Some studies have suggested that metformin may have neuroprotective effects, potentially reducing the risk of cognitive decline and Alzheimer’s disease.
- GLP-1 agonists: Glucagon-like peptide-1 (GLP-1) agonists, such as liraglutide and exenatide, are medications that help regulate blood sugar levels by stimulating insulin release. Recent research has indicated that these medications may also have neuroprotective properties and improve cognitive function in individuals with Alzheimer’s disease.
- DPP-4 inhibitors: Dipeptidyl peptidase-4 (DPP-4) inhibitors, such as sitagliptin and linagliptin, are another class of medications used to treat type 2 diabetes. They work by increasing the levels of hormones that stimulate insulin release.
Preliminary studies have suggested that these medications may have beneficial effects on cognitive function, although further research is needed.
Emerging Research and Potential Future Treatments
As our understanding of the relationship between insulin resistance and cognitive impairment continues to grow, researchers are exploring innovative therapeutic approaches to target the underlying mechanisms. Some potential future treatments include:
- Insulin-sensitizing agents: Novel compounds that specifically target and enhance brain insulin sensitivity may offer new treatment options for cognitive impairment related to insulin resistance.
- Anti-inflammatory and antioxidant therapies: Since inflammation and oxidative stress play a significant role in insulin resistance and cognitive decline, targeted therapies that reduce inflammation and combat oxidative stress may be beneficial in preserving cognitive function.
- Gene therapy: By targeting the specific genes involved in insulin signaling and neuronal growth, gene therapy may hold promise for treating cognitive impairment related to insulin resistance.
References
[1] Insulin Signaling Pathway
[2] Insulin in the nervous system and the mind: Functions in metabolism, memory, and mood
[3] Insulin effects on core neurotransmitter pathways
[4] Brain insulin resistance and cognitive function
[5] Diabetes and cognitive decline
[6] Ghrelin: The Hunger Hormone’s Role in Cognitive Function
[7] The Association Between Physical Activity and Insulin Level
[8] Sleep for a Good Cause
[9] Intranasal Insulin for Alzheimer’s Disease

