
In the intricate symphony of hormones that orchestrate our body’s daily functions, Secretin emerges as a multifaceted player with a profound impact on both our digestive system and brain function. Discovered over a century ago, Secretin, traditionally known for its critical role in digestion, has recently stepped into the spotlight for its intriguing influence in the realm of neurotransmission. Here we examine this hormone’s dual roles in regulating stomach acidity and pancreatic secretions, and exploring its emerging significance as a neurotransmitter affecting cognitive functions.
Contents
Understanding Secretin
Before getting into the multifaceted roles of Secretin, it is crucial to understand what Secretin is and its place in the biological orchestra of the human body. Secretin is not just a hormone; it is a key communicator in our complex bodily systems.
Historical Discovery and Context of Secretin
The journey of Secretin began in the early 20th century, marking a significant milestone in endocrinology. Discovered in 1902 by William M. Bayliss and Ernest H. Starling, two British physiologists, Secretin was the first hormone to be identified. Their groundbreaking work unveiled the hormone’s role in the digestive process, a revelation that paved the way for modern endocrinological research. Bayliss and Starling’s discovery was not only crucial for understanding digestion but also established the concept of hormones and their systemic effects, revolutionizing our understanding of internal bodily communication.
Chemical Structure and Production of Secretin
Delving into the chemical essence of Secretin, we find a peptide hormone, composed of a sequence of 27 amino acids. This structure is pivotal for its function. Secretin is predominantly produced in the S cells of the duodenum, the first segment of the small intestine.
These cells release Secretin in response to the presence of acidic contents from the stomach, initiating a sequence of actions crucial for proper digestive functioning. The hormone’s structure allows it to interact effectively with specific receptors located in various organs, enabling it to carry out its regulatory roles efficiently [1].
Primary Functions of Secretin in the Body
The principal function of Secretin lies in its regulatory role in the digestive system. Its release triggers the pancreas to secrete bicarbonate-rich fluids, which are vital in neutralizing the acidic chyme entering the small intestine from the stomach. This not only protects the intestinal lining but also creates an optimal pH environment for the action of digestive enzymes.
Additionally, Secretin influences the production of bile in the liver, further aiding in digestion, particularly in the emulsification and absorption of fats. The influence of Secretin extends beyond these primary functions, playing a subtle yet significant role in regulating water homeostasis and influencing gastric motility, showcasing its versatile and critical role in maintaining digestive health.
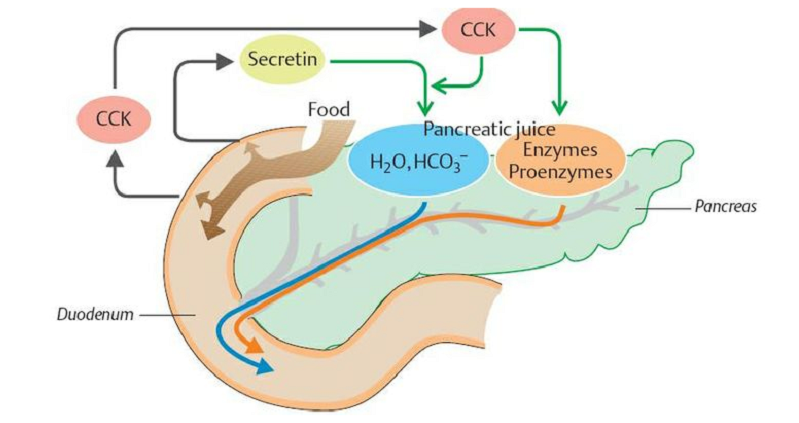
Secretin’s Role in Digestion
Having established a foundational understanding of Secretin, we now turn our attention to its critical role in the digestive system. Secretin’s influence extends from regulating stomach acidity to enhancing pancreatic and bile secretions, each function playing a vital role in the complex process of digestion.
Secretin’s Regulation of Stomach Acidity
One of the primary roles of Secretin is to regulate the acidity of the stomach’s contents as they enter the small intestine. When food leaves the stomach and enters the duodenum, it is highly acidic, which could potentially damage the delicate lining of the intestine. Secretin, released in response to this acidity, sends a signal to the stomach to reduce the secretion of gastric acid. This crucial feedback mechanism ensures a balance in the digestive process, protecting the intestine and facilitating the continued breakdown and absorption of nutrients [2].
Interaction of Secretin with Pancreatic Secretions
Another significant function of Secretin is its role in stimulating the pancreas. Upon its release, Secretin prompts the pancreas to secrete a bicarbonate-rich fluid. This fluid neutralizes the acidic chyme (partially digested food and stomach acids) that has entered the small intestine from the stomach.
This neutralization is essential for two reasons: firstly, it prevents damage to the intestinal lining, and secondly, it creates an optimal pH environment for the action of digestive enzymes. By ensuring that the small intestine has the right conditions, Secretin facilitates the effective breakdown and absorption of nutrients.
Impact on Secretin on Bile Production
In addition to its effects on the stomach and pancreas, Secretin also plays a role in bile production. While its influence here is less direct than in the pancreas, Secretin indirectly stimulates the liver to produce bile. Bile is crucial for the digestion and absorption of fats, as it emulsifies fat, making it easier for digestive enzymes to work. This aspect of Secretin’s function highlights its importance in the efficient processing and absorption of fats, an essential part of our diet.
Secretin as a Neurotransmitter
Moving beyond its well-established role in digestion, recent research has unveiled a surprising aspect of Secretin: its function as a neurotransmitter in the brain. This discovery has opened new avenues in understanding how digestive hormones can influence brain function, providing insights into the intricate connection between our gut and our brain.
Secretin’s Presence in the Brain
It was once believed that Secretin’s influence was confined to the gut, but studies have now identified its presence in various parts of the brain. This presence suggests a role beyond digestion, implicating Secretin in neurological processes. Secretin receptors have been found in key areas of the brain, including those involved in memory, learning, and emotional regulation. This distribution hints at a potential role for Secretin in modulating these crucial cognitive functions [3].
Effects of Secretin on Cognitive Functions
The role of Secretin as a neurotransmitter is still being unraveled, but emerging evidence suggests it may have significant effects on cognitive functions. Research indicates that Secretin can influence processes such as memory formation, learning capabilities, and even emotional responses.
Animal studies have shown that administration of Secretin can lead to improvements in memory and learning tasks, suggesting a direct link between Secretin levels and cognitive performance. Furthermore, there is growing interest in exploring Secretin’s potential therapeutic applications for neurodevelopmental disorders, given its apparent impact on brain function.
Recent Studies and Findings Regarding Secretin
Recent studies have been pivotal in expanding our understanding of Secretin’s role in the brain. For instance, research has explored how Secretin interacts with other neurotransmitters, influencing neural pathways and signaling mechanisms. These studies have shown that Secretin can modulate the activity of neurons, affecting neurotransmitter release and uptake.
There is also growing evidence linking Secretin to neuroprotective effects, suggesting it may play a role in guarding against neurodegenerative conditions. While this area of research is still developing, the findings so far highlight the potential of Secretin as a key player in brain health and cognitive function [4].
The Interconnection Between Digestion and Neurotransmission
As we have seen, Secretin plays a pivotal role in both digestion and neurotransmission. This dual functionality leads us to an intriguing aspect of human biology: the interconnection between the digestive system and brain function. The exploration of Secretin’s roles illuminates this gut-brain axis, demonstrating how digestive health can influence cognitive processes and vice versa.
How Digestive Health Influences Brain Function
The concept of the gut-brain axis is central to understanding the link between digestive health and brain function. This bi-directional communication pathway allows the gut and brain to send and receive signals to each other. Secretin, as part of this communication network, exemplifies how a hormone involved in digestion can also impact neurological functions.
For instance, the regulation of stomach acidity and bile production by Secretin not only ensures efficient digestion but also affects the production and release of neurotransmitters in the brain, influencing mood, cognition, and overall mental health [5].
Secretin as a Link Between the Gut and Brain
Secretin serves as a critical link in the gut-brain axis. Its role as a neurotransmitter suggests that it can directly influence brain activity and, conversely, its digestive functions imply that changes in gut health could impact brain function. This dual role makes Secretin a unique hormone that embodies the physiological connectivity between our digestive system and our cognitive processes. By understanding Secretin’s functions in both realms, researchers and medical professionals can gain a more holistic view of its impact on overall health.
Secretin’s Implications for Cognitive Health
The implications of Secretin’s roles for cognitive health are vast and multifaceted. The potential for using Secretin-based treatments to address cognitive and neurological disorders is an exciting area of ongoing research. Additionally, understanding the impact of digestive health on cognitive functions via hormones like Secretin could lead to more effective strategies for managing mental health conditions. This knowledge underscores the importance of maintaining a healthy digestive system as part of a holistic approach to overall brain health.
References
[1] Pancreas: What Is It, Function & Location
[2] Central and Peripheral Administration of Secretin
[3] Pleiotropic Effects of Secretin
[4] Teaching the role of secretin in the regulation of gastric acid secretion
[5] The physiological roles of secretin and its receptor

