Neurons are the basic units of the nervous system and play a critical role in everything from basic bodily functions to complex cognitive tasks. As such, maintaining the health of these cells is not just a matter of neuroscientific curiosity but a crucial part of holistic well-being. Why should you care about the well-being of your neurons? Healthy neurons are central to optimal cognitive function, mood regulation, and even the prevention of debilitating neurological diseases like Alzheimer’s and Parkinson’s. Given the vital role they play, it’s clear that we should make neuron health a priority.
Contents
- Introduction to Neuron Health
- Factors That Affect Neuronal Health
- Neurological Disorders Linked to Unhealthy Neurons
- Concept of Neuroprotection
- Dietary Strategies for Neuroprotection
- Lifestyle Choices for Neuroprotection
- Medical Interventions and Supplements for Neuronal Health
- References
Introduction to Neuron Health
Neurons are more than just cells in your brain; they are the fundamental units of your nervous system. Responsible for transmitting information throughout your body, neurons play an indispensable role in everything from helping you move your fingers to making high-level decisions.
Definition of Neurons
Basic Unit of the Nervous System
Think of neurons as the “communication channels” within your body. They send and receive messages that govern not only your physical movements but also your thoughts, memories, and emotions.
Role in Brain Function and Cognition
Neurons are particularly crucial in the realm of brain function and cognition. A healthy network of neurons can lead to enhanced memory, faster problem-solving skills, and better emotional management. On the other hand, damaged or deteriorating neurons can result in the opposite: cognitive decline and emotional instability.
Importance of Neuron Health
Understanding neurons is not merely an academic exercise; it has direct implications for your well-being.
Cognitive Function
Healthy neurons are the cornerstone of effective cognitive function. Whether you’re solving complex problems at work or making day-to-day decisions, your neurons are hard at work processing the information needed to execute these tasks.
Mood Regulation
Did you know that your neurons also play a role in regulating your mood? Neurotransmitters, which are chemical messengers transmitted via neurons, can influence your feelings of happiness, anxiety, and overall emotional stability.
Disease Prevention
Perhaps one of the most compelling reasons to focus on neuron health is its role in preventing neurological disorders such as Alzheimer’s, Parkinson’s, and Multiple Sclerosis. These conditions often start with damaged or dysfunctional neurons, emphasizing the importance of keeping them healthy.
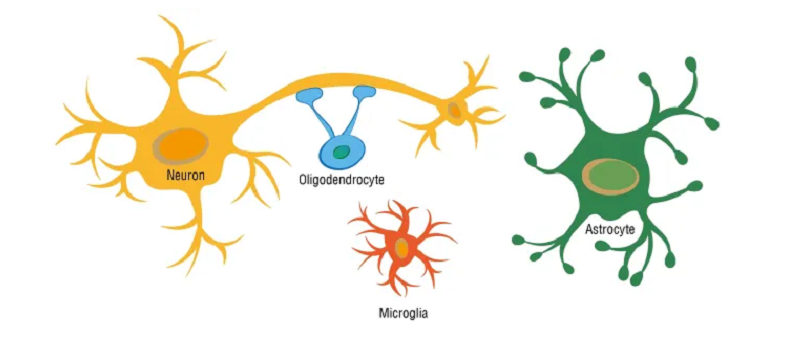
Factors That Affect Neuronal Health
Before getting into the strategies to protect your neurons, it’s essential to understand the various factors that can affect their health. Some of these factors are within our control, while others are part of natural processes like aging. By identifying these factors, we’re better equipped to tackle them head-on.
Aging
Aging is a natural process that affects all cells in the body, including neurons. However, the brain has a limited ability to regenerate, making it particularly susceptible to the aging process.
Cognitive Decline
As we age, cognitive abilities often decline, which is linked to changes in neuronal function. Reduced neuroplasticity, or the ability of neurons to form new connections, is one significant factor contributing to this decline.
Accumulation of Damage
Over time, neurons can accumulate damage from oxidative stress, inflammation, and other factors. This accumulation can lead to decreased function and increased susceptibility to diseases like Alzheimer’s and Parkinson’s [1].
Toxins
We often underestimate the impact of environmental toxins on neuronal health. These toxins can come from various sources, including food, air, and water.
Heavy Metals
Exposure to heavy metals like lead, mercury, and aluminum has been linked to neuronal damage. Such exposure often occurs through contaminated water or food.
Pesticides and Chemicals
Some pesticides and chemicals commonly used in agriculture have been shown to have neurotoxic effects, harming the neurons and increasing the risk for neurodegenerative diseases.
Stress
Stress isn’t just an emotional or psychological concern; it has real, tangible effects on neuronal health.
Cortisol and Brain Function
Chronic stress leads to elevated levels of the hormone cortisol, which, in high levels, can impair neuronal function. It can affect memory and learning while increasing the risk for depression and anxiety.
Stress-Induced Neuronal Damage
Stress activates certain pathways that can lead to neuronal damage and even death if sustained over long periods. Chronic stress can thus have long-term implications for brain health [2].
Lifestyle Choices
Lifestyle choices, many of which are within our control, can significantly influence neuronal health.
Poor Diet
A diet high in sugar, saturated fats, and processed foods can induce inflammation, which can harm neurons over time.
Lack of Physical Exercise
Physical exercise is not just good for the body but also for the brain. A sedentary lifestyle deprives the brain of increased blood flow and essential nutrients, impacting neuronal health negatively.
Substance Abuse
Alcohol, drugs, and even excessive caffeine can affect neuron function and structure, leading to long-term damage if abused.
Neurological Disorders Linked to Unhealthy Neurons
Now that we have an understanding of the various factors that can harm our neurons, it’s crucial to explore the long-term consequences of unhealthy neurons. Specifically, let’s look at some of the neurological disorders that can arise as a result of compromised neuronal health. By appreciating the severity of these conditions, we can better grasp the importance of proactive neuroprotective strategies.
Alzheimer’s Disease
Alzheimer’s disease is perhaps one of the most well-known neurological disorders associated with unhealthy neurons.
Amyloid Plaques and Neurofibrillary Tangles
Alzheimer’s is characterized by the accumulation of amyloid plaques and neurofibrillary tangles in the brain, which interfere with neuron function and lead to cell death. These changes impair memory and cognitive abilities, drastically affecting the quality of life.
Role of Neuron Health
Unhealthy neurons are more susceptible to the detrimental effects of these plaques and tangles. Early neuroprotective interventions can help in slowing down the disease’s progression or even mitigating its onset.
Parkinson’s Disease
Parkinson’s disease is another condition heavily influenced by the state of neurons in the brain, particularly those that produce dopamine.
Dopaminergic Neurons
The primary issue in Parkinson’s is the degeneration of dopaminergic neurons, which leads to the hallmark symptoms of tremors, stiffness, and impaired movement [3].
Preventative Strategies
While Parkinson’s cannot be fully prevented, maintaining overall neuronal health can reduce the risk and potentially slow down the progression of the disease.
Multiple Sclerosis
Multiple Sclerosis (MS) affects the brain and spinal cord, disrupting the flow of information within the brain and between the brain and body.
Myelin Sheath Degradation
The disease causes the immune system to attack the myelin sheath that protects neurons. This attack compromises neuron function and can result in a variety of symptoms ranging from fatigue and numbness to severe disability.
Importance of Early Intervention
The sooner neuronal health is optimized, the better the chances of managing the symptoms and progression of MS.
Stroke
Stroke occurs when the blood supply to parts of the brain is interrupted, causing a rapid loss of neuronal function.
Ischemic and Hemorrhagic Stroke
There are primarily two types of stroke: ischemic, caused by a clot or blockage, and hemorrhagic, caused by a burst blood vessel. Both types lead to a sudden loss of neurons due to lack of oxygen and nutrients.
Neuronal Resilience
Healthy neurons are more resilient and better equipped to recover from the damage caused by stroke. Therefore, a focus on neuroprotection can be especially beneficial in the context of stroke prevention or recovery.
Concept of Neuroprotection
Neuroprotection refers to the mechanisms and strategies aimed at protecting the brain’s neurons from injury or degeneration.
What Is Neuroprotection?
The term “neuroprotection” may sound complex, but its essence is straightforward: it’s all about safeguarding the neurons.
Definition and Scope
Neuroprotection involves both natural mechanisms within the body and external interventions designed to prevent neuronal injury, support neuron survival, and enhance function. This is a broad scope, covering everything from cellular processes to lifestyle choices.
Importance in Modern Healthcare
As we learn more about the intricacies of the brain, the concept of neuroprotection is gaining traction in healthcare. Increasingly, medical professionals are recognizing its potential in not just treating but also preventing neurological conditions.
Natural Mechanisms of Neuroprotection
The human body is equipped with its own set of natural neuroprotective mechanisms. It’s fascinating how our system is inherently designed to protect itself.
Antioxidant Defense
The body produces antioxidants that neutralize harmful free radicals, which can otherwise cause oxidative stress and damage neurons [4].
Anti-inflammatory Pathways
The immune system has pathways that act to control inflammation, a process that, when unregulated, can lead to neuronal damage.
Neurotrophic Factors
These are proteins that promote neuron survival, encourage the growth of new neurons, and even help in repairing damaged neurons.
The Need for External Intervention
Despite the body’s natural protective mechanisms, it often needs additional help, especially as we face aging, environmental toxins, and lifestyle-related challenges.
Limitations of Natural Mechanisms
While our bodies are remarkably resilient, the natural neuroprotective mechanisms have their limits. For instance, aging diminishes our antioxidant defense, making us more vulnerable to oxidative stress.
Necessity of a Multi-Pronged Approach
Given these limitations, a multi-pronged approach combining lifestyle choices, medical interventions, and perhaps even pharmacological solutions becomes essential for comprehensive neuroprotection.
Goal of Neuroprotective Strategies
The overarching goal is simple: to maintain or improve the health of your neurons, thereby enhancing cognitive function and reducing the risk of neurological disorders.
Immediate Benefits
Neuroprotective strategies can offer immediate benefits like improved focus, better mood regulation, and increased resilience against stress.
Long-term Benefits
In the long run, effective neuroprotection can potentially delay or mitigate the onset of neurological disorders, improve age-related cognitive decline, and even enhance the quality of your life.
Dietary Strategies for Neuroprotection
One of the most straightforward yet impactful methods is through dietary changes. The old adage, “You are what you eat,” holds significant weight when discussing neuronal health.
The Role of Nutrition
Nutrition plays a pivotal role in neuroprotection, serving as the primary source of compounds that can either benefit or harm our neurons.
Nutrient Absorption
The nutrients absorbed from our food directly affect cellular processes, including those that occur in neurons. Essential nutrients like antioxidants, vitamins, and fatty acids can all contribute to better neuronal health.
Gut-Brain Axis
Recent research has pointed to a strong connection between gut health and brain function, sometimes referred to as the gut-brain axis. A healthy diet can promote good gut health, which, in turn, can positively affect the brain [5].
Foods to Include
Certain foods have been shown to have neuroprotective effects, either through their nutrient content or other bioactive compounds.
Fruits and Vegetables
Rich in antioxidants, fruits and vegetables can help fight the oxidative stress that damages neurons. Berries, leafy greens, and citrus fruits are particularly beneficial.
Fatty Fish
Omega-3 fatty acids found in fatty fish like salmon and mackerel are essential for brain health. They form an integral part of cell membranes in neurons and also have anti-inflammatory properties.
Nuts and Seeds
High in Vitamin E, nuts and seeds can help fight off oxidative stress. Almonds, sunflower seeds, and hazelnuts are excellent options.
Foods to Avoid
Just as there are foods that can protect your neurons, there are also foods that can harm them.
Processed Foods
High in sugar and trans fats, processed foods can induce inflammation and contribute to neuronal damage over time.
Excessive Red Meat and Dairy
While not entirely bad, excessive consumption of red meat and dairy products can be detrimental due to their high saturated fat content, which can cause inflammation.
The Role of Supplements
In some cases, dietary intake might not be enough, and supplementation could be beneficial.
Curcumin
Derived from turmeric, curcumin has potent anti-inflammatory and antioxidant properties that can protect neurons.
Vitamin D
A deficiency in Vitamin D has been linked to various cognitive impairments and neurodegenerative diseases. Supplementing can be especially useful for people who do not get enough sun exposure.
Coenzyme Q10
This naturally occurring antioxidant has been shown to be beneficial in neurodegenerative diseases like Parkinson’s.

Lifestyle Choices for Neuroprotection
Diet is just one piece of the puzzle when it comes to neuroprotection. Your lifestyle choices, including physical activity, mental exercises, and even your social interactions, can have a profound impact on the health of your neurons.
Physical Exercise
The influence of physical exercise on cognitive health and neuronal well-being cannot be overstated.
Cardiovascular Benefits
Regular exercise, especially cardiovascular activities like running or swimming, enhances blood flow, which, in turn, ensures that your neurons receive a constant supply of essential nutrients and oxygen.
Neurogenesis
Exercise can also stimulate the growth of new neurons, a process known as neurogenesis, particularly in the hippocampus, a brain region crucial for memory and learning.
Cognitive Activities
Keeping your brain active is just as important as keeping your body active for overall neuronal health.
Learning New Skills
Whether it’s learning a musical instrument or a new language, challenging your brain helps in building new neural connections, making your neurons more resilient [6].
Puzzles and Games
Activities like crosswords, Sudoku, and strategic games can stimulate your brain and improve various aspects of cognitive function, including problem-solving and logical reasoning.
Stress Management
Chronic stress can be detrimental to your neurons, making effective stress management techniques a vital part of neuroprotection.
Mindfulness and Meditation
Practices like mindfulness and meditation can significantly reduce stress hormones that otherwise contribute to neuron damage.
Deep Breathing and Relaxation Techniques
Breathing exercises and other relaxation techniques can help you manage stress in the moment, safeguarding your neurons from immediate harm.
Social Interaction
Human beings are inherently social creatures, and our neurons thrive on social engagement.
Positive Relationships
Nurturing positive relationships and maintaining a strong social network can boost your mental health and, by extension, your cognitive functions.
Avoiding Social Isolation
Prolonged periods of social isolation can be harmful to neuronal health. Even simple interactions like a phone call or a meet-up can provide mental stimulation and emotional support.
Sleep Quality
Last but not least, the quality of your sleep has a significant bearing on your neurons’ well-being.
The Importance of REM Sleep
Rapid Eye Movement (REM) sleep is crucial for memory consolidation and emotional regulation, serving a neuroprotective function.
Sleep Hygiene
Adhering to good sleep hygiene practices, like maintaining a consistent sleep schedule and creating a calming bedtime routine, can improve the quality of your sleep and protect your neurons.
Medical Interventions and Supplements for Neuronal Health
While lifestyle adjustments and dietary choices are cornerstones of neuroprotection, there are instances where medical interventions and supplements can offer additional benefits. Whether it’s medication for chronic conditions that can affect neuronal health or supplements that can enhance cognitive function, medical science provides a range of options for neuroprotection.
Pharmaceutical Options
Sometimes, medication is necessary for controlling conditions that could otherwise harm your neurons.
Antioxidants and Anti-inflammatory Drugs
Certain medications have antioxidant and anti-inflammatory properties that can help mitigate the damage caused by oxidative stress and inflammation, both of which are detrimental to neurons.
Cognitive Enhancers
Drugs like nootropics and certain ADHD medications are designed to enhance cognitive function and may have some neuroprotective properties. However, they should only be used under medical supervision.
Over-the-Counter Supplements
Aside from prescription medications, there are over-the-counter supplements known for their neuroprotective benefits.
Fish Oil
Rich in Omega-3 fatty acids, fish oil supplements can offer the same neuroprotective benefits as consuming fatty fish.
Ginkgo Biloba
This herbal supplement is often touted for its ability to improve cognitive function, although more research is needed to confirm its efficacy.
L-Theanine
Found in tea leaves, L-Theanine supplements can promote relaxation without drowsiness, potentially reducing stress-related damage to neurons.
Hormonal Therapies
Hormones play a crucial role in brain function, and hormonal therapies are being investigated for their neuroprotective potential.
Estrogen Replacement
For postmenopausal women, estrogen replacement therapy has shown promise in preserving cognitive function, but it comes with its own set of risks and should be discussed thoroughly with a healthcare provider.
Growth Hormone Supplements
Growth hormones have been implicated in neuroprotection, but their use is controversial and requires further study.
Medical Procedures
In some cases, medical procedures can offer neuroprotection, particularly for individuals at high risk for certain diseases.
Deep Brain Stimulation
While generally reserved for severe cases of conditions like Parkinson’s disease, deep brain stimulation can help protect remaining neurons from further degeneration.
Stem Cell Therapy
Although still in the experimental stage, stem cell therapies hold the potential to repair or replace damaged neurons.
Risks and Precautions
While medical interventions can offer powerful benefits, it’s crucial to be aware of the associated risks.
Drug Interactions
Combining multiple medications and supplements can lead to harmful interactions. Always consult with a healthcare provider before starting a new treatment.
Individual Differences
People react differently to medications and supplements. What works for one person may not be effective for another, making personalized medical advice crucial.
References
[1] Neuroprotective Strategies
[2] Neuroprotective Strategies for Neurological Disorders
[3] 5 Neuroprotective Strategies to Reduce Brain Injury
[4] Development of Novel Neuroprotective Strategies
[5] Neuroprotective Strategies and Alternative Therapies
[6] Practice Parameter: Neuroprotective strategies and alternative therapies for Parkinson disease

