In the vast tapestry of the human body, the lymphatic system often remains an understudied and underappreciated player, particularly when it comes to brain health. Traditionally, we’ve acknowledged the lymphatic system for its crucial role in immunity and fluid balance. However, recent discoveries have unveiled its mysterious connection to our brain’s wellbeing. Here we unravel the intricate pathways of the lymphatic system, its surprising relationship with our cognitive functions, and why it might just be the missing link in our quest for optimal brain health.
Contents
Historical Context of the Lymphatic System and Cognition
Digging into the annals of medical history, one finds a roller coaster journey of the lymphatic system’s understanding. For much of our past, the importance of this vast network remained hidden, only gaining prominence in more recent years, especially regarding its ties to the brain.
Historical Understanding of the Lymphatic System
Centuries ago, the lymphatic system was mainly an enigma. Ancient medical practitioners and anatomists often confused lymphatic vessels with veins, primarily because of their similar appearance. The term “lymphatic” itself originates from the Latin word “lympha,” which means water, indicating early observations of the clear fluid within the system. However, the system’s exact role and importance were largely unexplored.
How Its Connection to the Brain Was Previously Overlooked
The brain, protected by the blood-brain barrier, was traditionally considered an “immune-privileged” organ. This status meant that, for the longest time, the brain was thought to be isolated from peripheral immune activities, including those of the lymphatic system. As a result, the idea that the lymphatic system could play a role in brain health was largely dismissed. It was believed that the brain had its own separate mechanism for waste removal and immunity.
Recent Discoveries Highlighting Brain-Lymphatic Connections
The turning point came with the discovery of the glymphatic system within the last decade. Researchers found that the brain did indeed have a lymphatic-like pathway responsible for clearing out waste and interfacing with the immune system. These findings caused a seismic shift in our understanding, suggesting that the lymphatic system or its mechanisms weren’t just peripheral but had central nervous system implications. This revelation opened the floodgates for further research, showing how the health of the lymphatic system could potentially influence various aspects of cognitive function and neurological health [1].
Anatomy and Physiology of the Lymphatic System
To truly grasp the significance of the lymphatic system’s connection to brain health, we must first understand its intricate architecture and fundamental functions. This complex network, often compared to the body’s drainage system, is designed not only to protect us from potential threats but also to maintain our body’s delicate internal balance.
Components: Lymph Nodes, Vessels, and Lymph Fluid
The lymphatic system is primarily composed of three main components, each playing a distinct role in our body’s well-being.
Lymph Nodes
These bean-shaped structures are scattered throughout the body. They act as filtration stations, trapping harmful substances like bacteria and viruses, which are then destroyed by white blood cells. Think of them as the body’s security checkpoints, ensuring only safe materials pass through.
Lymph Vessels
Much like blood vessels crisscross our anatomy, lymph vessels form an extensive network, transporting a clear fluid known as lymph. These vessels are equipped with one-way valves ensuring that lymph moves in only one direction, typically towards larger vessels and eventually back into the bloodstream [2].
Lymph Fluid
Lymph is the clear fluid that circulates through the lymphatic system. It is derived from the fluids surrounding our body’s cells. As it travels through the lymphatic pathways, it collects waste products, bacteria, and even dead or damaged cells, effectively cleansing our body as it circulates.
Primary Functions of the Lymphatic System
The lymphatic system is not just an anatomical marvel; its physiological roles are paramount to our overall health.
Immune System Support
One of the most recognized roles of the lymphatic system is its involvement in immunity. Lymph nodes house white blood cells, which are essential soldiers in our body’s fight against infections and diseases. As lymph fluid passes through these nodes, harmful substances are identified and neutralized, bolstering our defenses.
Waste Removal
As cells go about their daily tasks, they produce waste. The lymphatic system serves as a vital waste disposal mechanism, collecting and transporting cellular debris, ensuring that our body remains free of potentially harmful accumulations.
Fluid Balance
Our body’s cells are bathed in fluid, and maintaining a balance in this fluid environment is crucial. The lymphatic system plays a part in this by collecting excess fluid and returning it to the bloodstream, preventing swelling or edema in tissues [3].
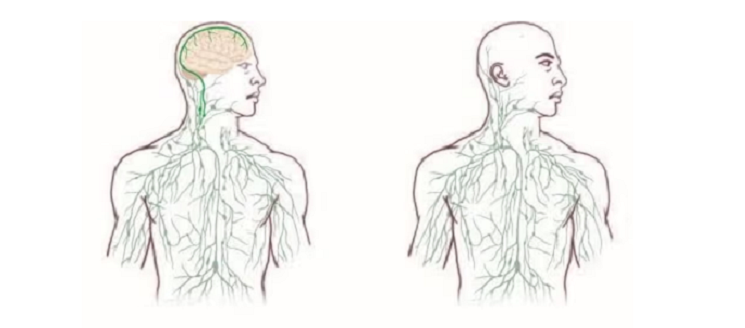
The Glymphatic System: Brain’s Special Lymphatic Pathway
While the lymphatic system has been long-established in medical literature, its connection to the brain remained enigmatic until the discovery of what’s now termed the “glymphatic system.”
Definition and Function
The glymphatic system is a recent discovery that has transformed our understanding of brain health. Although it operates similarly to the lymphatic system, its primary function is within the brain. This system efficiently clears waste products from the brain, particularly during sleep, acting as a kind of nightly maintenance crew for our most vital organ.
Role in Clearing Brain Waste
Just like the rest of our body, the brain produces waste. What makes it unique is the type of waste, including substances that, if not removed, can contribute to neurodegenerative diseases. The glymphatic system’s role in clearing out these potentially harmful byproducts, like beta-amyloid, a protein associated with Alzheimer’s disease, underscores its significance in maintaining cognitive health.
Importance of Lymphatic Health for Cognitive Wellness
At the crossroads of physical and cognitive health, the lymphatic system emerges as a silent guardian. Although traditionally not viewed through the lens of brain health, the health of our lymphatic system bears profound implications for our cognitive functions.
Fluid Circulation and Toxin Removal
The efficient movement of fluid throughout our body, and its subsequent purification, is a cornerstone of optimal health. When it comes to the brain, this becomes even more pivotal.
Impact on Brain Clarity
A well-functioning lymphatic system ensures the swift removal of waste from our body. In the brain, the glymphatic system operates similarly, clearing away toxins and metabolic waste. When these systems function optimally, we experience greater mental clarity, sharper focus, and improved cognitive agility [4].
Prevention of Neurodegenerative Diseases
Accumulation of waste, especially toxic proteins like beta-amyloid, is a known precursor to neurodegenerative conditions such as Alzheimer’s. A robust lymphatic and glymphatic system can help mitigate the risk by ensuring these harmful byproducts are efficiently eliminated from the brain.
Immune Response and Brain Health
The immune response, although primarily protective, can become a double-edged sword, especially when it concerns the brain.
Inflammation’s Role in Cognitive Impairments
Chronic inflammation has been linked to various cognitive challenges, from memory lapses to severe conditions like dementia. The lymphatic system plays a critical role in modulating our body’s inflammatory response, ensuring it doesn’t spiral out of control and negatively impact our brain.
Lymphatic System’s Role in Managing Inflammation
Lymph nodes, brimming with white blood cells, serve as hubs for immune activity. By regulating the production and release of these cells, the lymphatic system helps fine-tune our immune responses. An efficiently functioning lymphatic system ensures that inflammation, when it occurs, is targeted and temporary, thus safeguarding cognitive functions [5].
Nutrient Transportation to Support Brain Function
Beyond waste removal and immune modulation, the lymphatic system is also instrumental in nutrient transportation.
Supplying Vital Nutrients
As lymph circulates, it not only collects waste but also shuttles essential nutrients, such as fatty acids. These nutrients are paramount for brain health, supporting everything from neuronal function to neurotransmitter production.
Optimizing Brain Health with Balanced Nutrition
With the lymphatic system’s involvement in transporting nutrients, maintaining its health can ensure that the brain consistently receives the nourishment it needs. A well-fed brain is more resilient, adaptive, and capable of performing at its peak.
References
[1] Brain cleaning system uses lymphatic vessels
[2] Lymphatics and the Brain
[3] Brain Lymphatic System: Drainage system helps to clear the brain
[4] How a newly discovered body part changes our understanding of the brain (and the immune system)
[5] Meningeal Lymphatics And Neurological Disorders
