Endorphins, often referred to as the brain’s natural painkillers, have captured the fascination of both scientists and the general public alike. These powerful chemical messengers play a vital role in pain relief, stress reduction, and the overall well-being of an individual. Endorphins also have intriguing cognitive effects, including improved memory, enhanced creativity, and increased focus.
Contents
Introduction to Endorphins
Endorphins, a term derived from the combination of the words “endogenous” and “morphine,” are naturally occurring peptides produced in the brain and nervous system. They function as neurotransmitters that transmit signals within the nervous system and play a significant role in the body’s response to pain and stress. In this section, we will explore the definition of endorphins, their purpose in the human body, and the connection between endorphins and well-being.
Definition of Endorphins
Endorphins are a class of neuropeptides that act on the body’s opiate receptors, producing a range of physiological effects. They are primarily produced in the pituitary gland, as well as in other parts of the brain and central nervous system. There are several different types of endorphins, with beta-endorphin being the most well-known and widely studied.
Purpose of Endorphins in the Human Body
Endorphins serve a variety of functions within the human body. Their primary role is to alleviate pain by binding to the same receptors that opiate painkillers target. This results in a reduction of pain perception, making endorphins a natural analgesic. In addition to their pain-relieving properties, endorphins also help regulate the body’s response to stress, enhance the immune system, and promote a sense of overall well-being.
Connection Between Endorphins and Well-Being
The release of endorphins is often associated with feelings of happiness, euphoria, and relaxation. This is due to their ability to counteract the effects of stress hormones, such as cortisol, and promote a sense of calm and positivity. When endorphin levels are high, individuals tend to experience a greater sense of well-being and are better equipped to manage stress and maintain emotional balance.
Endorphins as Natural Painkillers
Endorphins have gained widespread recognition for their natural pain-relieving properties. This section will explore the circumstances under which endorphins are released during painful situations, the mechanism behind their pain-relieving effects, and how they compare to synthetic painkillers.
Endorphin Release During Painful Situations
During times of physical or emotional pain, the body’s natural response is to release endorphins [1]. This can occur in various situations, such as during intense exercise, injury, or periods of extreme stress. The increased production of endorphins helps to mitigate pain and discomfort, enabling individuals to continue functioning despite the presence of pain. In some cases, endorphins can produce a sensation known as “runner’s high,” which is characterized by feelings of euphoria and reduced perception of pain during endurance activities.
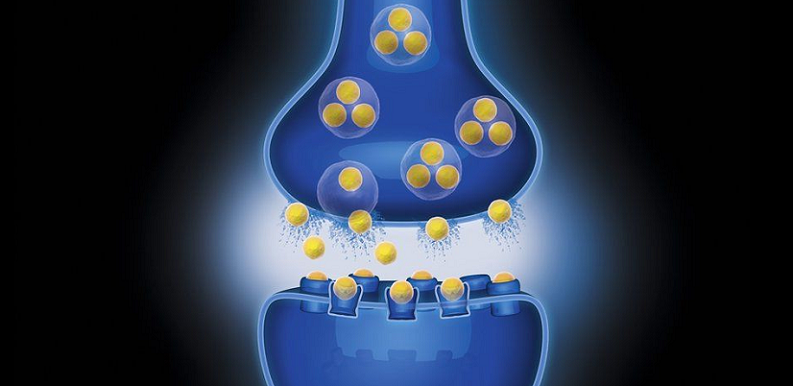
Mechanism of Endorphin-Induced Pain Relief
The pain-relieving effects of endorphins are primarily due to their ability to bind to opiate receptors in the brain and nervous system [2]. These receptors, which are also targeted by synthetic opioid painkillers, help to modulate pain perception. When endorphins bind to these receptors, they trigger the release of other neurotransmitters, such as dopamine, which further contribute to feelings of pleasure and reduced pain. This intricate system of pain modulation helps the body to adapt and respond to various pain stimuli.
Comparison to Synthetic Painkillers
While endorphins are the body’s natural painkillers, synthetic opioids are often prescribed for the management of severe or chronic pain. These medications, which include drugs such as morphine, oxycodone, and hydrocodone, also bind to opiate receptors to provide pain relief. However, there are several key differences between endorphins and synthetic painkillers.
Firstly, the release of endorphins is regulated by the body’s natural feedback mechanisms, ensuring that they are produced in appropriate amounts and at the right time. Synthetic painkillers, on the other hand, can be taken in excessive doses, which may lead to dependence, addiction, and other adverse effects.
Secondly, while both endorphins and synthetic painkillers provide pain relief, endorphins are also associated with other beneficial effects, such as enhanced immune function, reduced stress, and increased well-being. Synthetic painkillers, conversely, may produce unwanted side effects, such as drowsiness, constipation, and respiratory depression.
Sources of Endorphin Release
Endorphins are released in response to a variety of stimuli, many of which can be incorporated into daily life to help promote overall well-being. In this section, we will discuss several sources of endorphin release, including exercise, laughter, social interactions, meditation, spicy foods, and music.
Exercise and Physical Activity
One of the most well-known sources of endorphin release is physical activity [3]. Engaging in regular exercise has been shown to increase endorphin production and provide numerous health benefits. Activities that involve sustained, moderate-to-high intensity exercise, such as running, swimming, or cycling, are particularly effective at triggering endorphin release. This can lead to improved mood, reduced stress, and enhanced pain tolerance.
Laughter and Humor
Laughter has long been considered the best medicine, and research has shown that it can indeed stimulate the release of endorphins. Enjoying a good laugh with friends or watching a funny movie can help elevate mood, reduce stress, and even alleviate pain. By incorporating humor into daily life, individuals can harness the power of endorphins to promote mental and emotional well-being.
Social Interactions and Bonding
Positive social interactions and strong interpersonal connections are essential for overall health and happiness. Engaging in activities that promote bonding, such as spending time with loved ones, participating in group activities, or even cuddling with a pet, can trigger the release of endorphins [4]. These endorphins contribute to feelings of happiness, trust, and attachment, further reinforcing the importance of maintaining strong social ties.
Meditation and Mindfulness
Meditation and mindfulness practices have been found to stimulate endorphin release and provide a wide range of mental and physical health benefits. By focusing on the present moment and cultivating a non-judgmental awareness of thoughts and feelings, individuals can reduce stress, enhance emotional regulation, and tap into the body’s natural endorphin production.
Spicy Foods and Capsaicin
The consumption of spicy foods, particularly those containing capsaicin (the active component in chili peppers), has been linked to endorphin release. Capsaicin stimulates pain receptors in the mouth, prompting the brain to produce endorphins to counteract the discomfort. This can result in a sensation known as “pepper high,” characterized by feelings of euphoria and well-being.
Music and Emotional Response
Listening to music, especially music that elicits strong emotions or memories, can stimulate the release of endorphins. The emotional response to music can vary from person to person, but the connection between music and endorphin release is well-established. Incorporating music into daily life, whether through active listening or playing an instrument, can help boost endorphin levels and provide a range of cognitive and emotional benefits.

Cognitive Effects of Endorphins
In addition to their pain-relieving properties, endorphins have been found to influence various cognitive functions, such as memory, creativity, and focus. This section will explore these cognitive effects, as well as the role of endorphins in reducing stress and anxiety.
Improved Memory and Learning
Endorphins have been linked to enhanced memory and learning capabilities [5]. Research suggests that increased endorphin levels can promote long-term potentiation, a neural process that strengthens the connections between neurons and is crucial for learning and memory formation. By engaging in activities that stimulate endorphin release, individuals may be better equipped to retain new information and consolidate memories more effectively.
Enhanced Creativity and Problem Solving
Endorphins have also been associated with increased creativity and problem-solving abilities. The release of endorphins can promote a sense of relaxation and well-being, allowing individuals to think more freely and generate novel ideas. This may lead to enhanced problem-solving skills, as individuals are better able to approach challenges with an open and flexible mindset.
Increased Focus and Attention
Endorphin release has been shown to improve focus and attention by modulating the activity of certain neurotransmitters, such as dopamine and norepinephrine [6]. These neurotransmitters play a critical role in regulating attention and maintaining optimal cognitive function. By boosting endorphin levels, individuals may experience increased mental clarity and an enhanced ability to concentrate on tasks at hand.
Reduced Stress and Anxiety
Endorphins are known for their stress-relieving properties, as they can counteract the effects of stress hormones such as cortisol [7]. By promoting a sense of calm and well-being, endorphins can help alleviate feelings of anxiety and improve overall emotional regulation. This, in turn, can lead to better cognitive performance, as individuals are less likely to be hampered by stress and negative emotions.
Endorphin Deficiency and Related Disorders
While the benefits of endorphins are well-established, some individuals may experience a deficiency in endorphin production, which can lead to a variety of health issues [8]. In this section, we will discuss the symptoms of endorphin deficiency, conditions linked to low endorphin levels, and strategies for boosting endorphin production.
Symptoms of Endorphin Deficiency
Endorphin deficiency can manifest in various ways, with some common symptoms including:
- Chronic pain or increased sensitivity to pain
- Persistent feelings of sadness or depression
- Anxiety or increased susceptibility to stress
- Fatigue or low energy levels
- Difficulty concentrating or focusing
- Insomnia or other sleep disturbances
If you suspect that you may have an endorphin deficiency, it is essential to consult with a healthcare professional for a proper assessment and appropriate guidance.
Conditions Linked to Endorphin Deficiency
Several health conditions have been associated with low endorphin levels, including:
- Depression: Reduced endorphin production can contribute to feelings of sadness, hopelessness, and a lack of motivation, which are characteristic symptoms of depression.
- Chronic Pain: Low endorphin levels can impair the body’s natural pain-relief system, leading to increased sensitivity to pain and the development of chronic pain conditions.
- Fibromyalgia: This condition, characterized by widespread musculoskeletal pain, fatigue, and tenderness, has been linked to reduced endorphin production and a heightened sensitivity to pain.
- Migraines: Some research suggests that individuals who suffer from migraines may have lower endorphin levels, which could contribute to the development and persistence of these severe headaches.
Strategies for Boosting Endorphin Levels
If you are experiencing endorphin deficiency or are seeking to increase your endorphin levels for overall well-being, there are several strategies to consider:
- Engage in regular physical activity, such as aerobic exercise or strength training, to stimulate endorphin release.
- Incorporate laughter and humor into your daily routine by watching funny videos, attending comedy shows, or spending time with friends who make you laugh.
- Cultivate strong social connections by participating in group activities, volunteering, or joining clubs and organizations.
- Practice meditation and mindfulness to reduce stress and promote endorphin production.
- Consume spicy foods containing capsaicin to stimulate endorphin release.
- Listen to music that elicits strong emotions or memories to trigger endorphin production.
By adopting these strategies, individuals can help to increase their endorphin levels and mitigate the negative effects of endorphin deficiency on their physical and mental health.
Limitations and Potential Risks of Endorphins
While endorphins have numerous benefits for physical and mental well-being, it is important to consider their limitations and potential risks. In this section, we will discuss the potential drawbacks of excessive endorphin release, the risks associated with endorphin-based therapies, and the importance of balance in endorphin levels.
Drawbacks of Excessive Endorphin Release
While the release of endorphins can be beneficial for mood, pain relief, and overall well-being, excessive endorphin production can also have negative consequences [9]. For example, individuals who engage in extreme exercise may experience a temporary high due to increased endorphin release, but this can also lead to overtraining, injuries, or even addiction to exercise. Excessive endorphin release can mask pain, which may prevent individuals from recognizing the severity of an injury or medical condition and seeking appropriate treatment.
Risks Associated with Endorphin-Based Therapies
Some therapies and treatments aim to stimulate endorphin release or target the endorphin system to alleviate pain or improve mood. While these approaches can be effective for some individuals, they may also carry risks, such as:
- Dependence or addiction: Some medications that target the endorphin system, such as opioid painkillers, can lead to dependence or addiction if not used as prescribed or monitored carefully by a healthcare professional.
- Tolerance: Over time, individuals may develop a tolerance to the effects of endorphin-based therapies, requiring higher doses or more frequent treatments to achieve the desired results.
- Side effects: As with any medication or therapy, endorphin-based treatments may cause side effects or interact with other medications, making it crucial for individuals to consult with their healthcare provider before starting any new treatment.
Importance of Balance in Endorphin Levels
Maintaining balance in endorphin levels is crucial for overall health and well-being. While low endorphin levels can contribute to pain, depression, and other health issues, excessive endorphin production can also have negative consequences, as discussed earlier. Therefore, it is essential to engage in activities and practices that promote balanced endorphin production and to consult with a healthcare professional if concerns about endorphin levels arise.
References
[1] Endorphins: The brain’s natural pain reliever
[2] Endogenous opioid systems alterations in pain and opioid use disorder
[3] Exercise and stress: Get moving to manage stress – Mayo Clinic
[4] Endorphins: What They Are and How to Boost Them
[5] Dopamine’s Dual Role in Brain Health and Cognitive Function
[6] The role of the opioid system in decision making and cognitive control
[7] Exercise for Stress and Anxiety
[8] Endorphin – an overview | ScienceDirect Topics
[9] Endorphins, Exercise, and Addictions: A Review of Exercise Dependence

