
In recent years, the significance of social cognition and emotional intelligence in our daily lives has become increasingly apparent. These key elements contribute to successful interpersonal relationships, workplace efficiency, and overall well-being. One intriguing hormone that plays a vital role in shaping these abilities is oxytocin. Known as the “love hormone,” oxytocin has captured the attention of researchers and the general public alike due to its multifaceted impact on human behavior.
Contents
What Is Oxytocin?
In recent years, the significance of social cognition and emotional intelligence in our daily lives has become increasingly apparent. These key elements contribute to successful interpersonal relationships, workplace efficiency, and overall well-being. One intriguing hormone that plays a vital role in shaping these abilities is oxytocin. Known as the “love hormone,” oxytocin has captured the attention of researchers and the general public alike due to its multifaceted impact on human behavior.
Brief Explanation of Oxytocin
Oxytocin is a neuropeptide hormone produced primarily in the hypothalamus and secreted by the posterior pituitary gland. It acts as both a hormone and a neurotransmitter, playing a crucial role in various physiological and behavioral functions, such as childbirth, lactation, pair bonding, and stress regulation.
Importance of Social Cognition and Emotional Intelligence
Social cognition refers to the mental processes involved in understanding, interpreting, and predicting the thoughts, feelings, and behavior of others. It is essential for navigating complex social environments and maintaining harmonious relationships. Emotional intelligence, on the other hand, encompasses our ability to recognize, understand, and manage our own emotions and those of others. High emotional intelligence is associated with better mental health, job performance, and relationship satisfaction.
Oxytocin’s Role in Social Cognition
Oxytocin has been extensively studied for its role in social cognition, as it appears to significantly influence various aspects of social perception and decision-making.
Definition of Social Cognition
Social cognition is the mental process through which we interpret, analyze, and understand social situations and the behavior of others. It encompasses a wide range of cognitive processes, including perceiving emotions, attributing intentions, and predicting future behavior based on past experiences. Social cognition enables us to navigate complex social environments, maintain relationships, and cooperate with others.
Oxytocin’s Influence on Social Perception
Social perception refers to the initial stage of social cognition, during which we gather and interpret information about others. Oxytocin has been found to affect various aspects of social perception, such as facial recognition and emotion detection [1].
Facial Recognition
Oxytocin has been shown to enhance facial recognition abilities in humans [2]. Research indicates that intranasal administration of oxytocin can improve the recognition of familiar faces and increase the ability to remember faces after brief exposure. This suggests that oxytocin may facilitate the formation of social memories and promote bonding by strengthening our ability to recognize and remember others.
Emotion Detection
Emotion detection is a crucial aspect of social perception, as it enables us to understand and respond to the emotional states of others. Studies have shown that oxytocin can enhance emotion detection by increasing the accuracy of identifying emotions from facial expressions [3]. This improvement in emotion detection may contribute to greater empathy and social understanding.
Oxytocin’s Effect on Social Decision-Making
Social decision-making refers to the cognitive processes through which we evaluate social situations, weigh the potential outcomes, and choose a course of action. Oxytocin has been implicated in several aspects of social decision-making, including trust and cooperation, as well as moral judgment.
Trust and Cooperation
Oxytocin has been found to promote trust and cooperation in social interactions. Research has demonstrated that intranasal oxytocin administration can increase trust in others, leading to more cooperative behavior in economic games and other social tasks [4]. This increased trust and cooperation may facilitate the formation and maintenance of social bonds and contribute to prosocial behavior.
Moral Judgment
Oxytocin may also influence moral judgment, which refers to our ability to evaluate the rightness or wrongness of actions in social contexts. Some studies have found that oxytocin can increase the likelihood of making moral decisions based on empathy and concern for others, rather than on cold, impersonal principles [5]. This suggests that oxytocin may promote a more compassionate approach to moral decision-making, which can have significant implications for social harmony and group cohesion.

Oxytocin’s Impact on Emotional Intelligence
Emotional intelligence is another crucial aspect of human behavior that oxytocin appears to influence.
Definition of Emotional Intelligence
Emotional intelligence refers to the ability to recognize, understand, and manage one’s own emotions and those of others effectively. It encompasses a set of skills, including emotional awareness, emotional regulation, empathy, and social skills. High emotional intelligence has been associated with various positive outcomes, such as improved mental health, increased job performance, and more satisfying relationships.
Oxytocin’s Role in Emotional Regulation
Emotional regulation is an essential component of emotional intelligence, as it allows us to manage our emotions in response to different situations. Oxytocin has been found to play a role in emotional regulation by reducing stress and promoting emotional resilience [6].
Stress Reduction
Oxytocin is known for its stress-reducing effects, which may contribute to better emotional regulation. Studies have shown that oxytocin can decrease cortisol levels, a stress hormone, and increase feelings of relaxation and well-being. By helping to mitigate the negative effects of stress, oxytocin may promote a more balanced emotional state, enabling individuals to better manage their emotions in challenging situations.
Emotional Resilience
Research has also suggested that oxytocin may enhance emotional resilience, which is the ability to recover from and adapt to emotionally challenging experiences [7]. For example, studies have found that oxytocin can reduce the emotional impact of negative social feedback and promote more positive reactions to social stressors. This increased emotional resilience may contribute to improved emotional regulation and overall emotional intelligence.
Oxytocin’s Influence on Empathy and Understanding Others
Empathy, the ability to share and understand the feelings of others, is a critical aspect of emotional intelligence. Oxytocin has been found to impact different dimensions of empathy, including cognitive and emotional empathy.
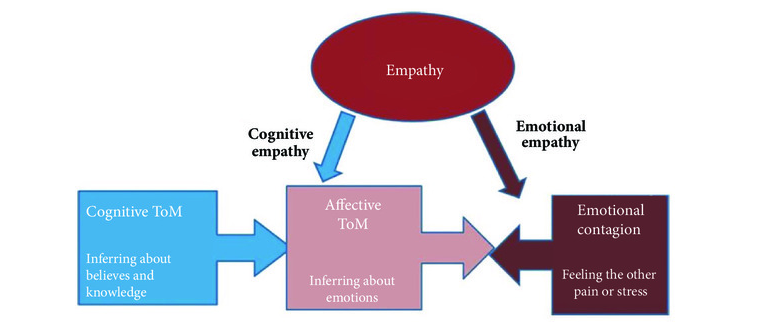
Cognitive Empathy
Cognitive empathy refers to the ability to understand and accurately infer the thoughts, feelings, and perspectives of others. Research has shown that oxytocin can enhance cognitive empathy by improving the accuracy of mentalizing or inferring the mental states of others. This heightened cognitive empathy may contribute to better social understanding and more effective communication.
Emotional Empathy
Emotional empathy involves experiencing and sharing the emotions of others. Studies have demonstrated that oxytocin administration can increase emotional empathy, leading to greater emotional contagion and increased feelings of compassion. By enhancing emotional empathy, oxytocin may promote prosocial behavior and strengthen social bonds, ultimately contributing to higher emotional intelligence [8].
Factors Affecting Oxytocin’s Influence on Social Cognition and Emotional Intelligence
While the effects of oxytocin on social cognition and emotional intelligence are well-documented, it is essential to recognize that individual differences and various factors can modulate these effects.
Genetic Factors
Genetic factors, such as variations in the oxytocin receptor gene (OXTR), can affect the way individuals respond to oxytocin. Specific OXTR polymorphisms have been associated with differences in social cognition, empathy, and emotional regulation [9]. These genetic variations may help explain why some individuals exhibit heightened sensitivity to oxytocin’s effects, while others may be less responsive.
Environmental Factors
Environmental factors, including early life experiences and social context, can also influence oxytocin’s effects on social cognition and emotional intelligence. For example, research has shown that early life stress or trauma can alter oxytocin functioning and affect social behavior later in life. Additionally, the social context in which oxytocin is administered can modulate its effects, with some studies suggesting that oxytocin’s prosocial effects may be more pronounced in supportive or cooperative settings compared to competitive or threatening environments.
Hormonal Interactions
Interactions between oxytocin and other hormones, such as testosterone and cortisol, can also play a role in modulating oxytocin’s influence on social cognition and emotional intelligence. For example, studies have found that the combination of high oxytocin and low testosterone levels is associated with increased empathy and prosocial behavior, whereas high testosterone levels may counteract some of oxytocin’s prosocial effects.
Similarly, cortisol, a stress hormone, may interact with oxytocin to influence social behavior and emotional regulation, with some evidence suggesting that oxytocin’s stress-reducing effects may be more pronounced in individuals with lower baseline cortisol levels [10].

Oxytocin Implications for Interventions and Treatments
The growing body of research on oxytocin’s influence on social cognition and emotional intelligence has sparked interest in its potential applications for interventions and treatments.
Potential Benefits of Oxytocin Supplementation
Given oxytocin’s role in social cognition and emotional intelligence, researchers have explored its potential use as a therapeutic agent for various clinical populations and conditions.
Enhancing Social Skills
Oxytocin supplementation may help improve social skills in individuals with social deficits, such as those with autism spectrum disorder (ASD) or social anxiety disorder [11]. Studies have shown that oxytocin administration can improve emotion recognition, eye contact, and trust in individuals with ASD, and can reduce social anxiety and enhance social functioning in those with social anxiety disorder. These findings suggest that oxytocin may hold promise as an adjunctive treatment for enhancing social skills in individuals with social difficulties.
Addressing Emotional Disorders
Oxytocin’s effects on emotional regulation and resilience may also make it a potential treatment for emotional disorders, such as depression and post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD). Preliminary research has shown that oxytocin can reduce depressive symptoms, increase feelings of social support, and promote emotional resilience in individuals with depression or PTSD. However, further research is needed to establish the efficacy and optimal dosing of oxytocin for these conditions.
Risks and Limitations
While oxytocin supplementation may offer potential benefits, it is essential to consider the risks and limitations associated with its use.
Overdose and Negative Effects
Oxytocin supplementation may carry risks, such as overdose or negative side effects [12]. Overdosing on oxytocin can lead to symptoms such as nausea, vomiting, and rapid heart rate. Additionally, some studies have reported negative side effects, such as increased aggression or jealousy, following oxytocin administration. These risks highlight the need for a careful and cautious approach to oxytocin supplementation.
Ethical Considerations
The use of oxytocin as a treatment for enhancing social cognition and emotional intelligence raises ethical questions about manipulating emotions and social behavior. Concerns have been raised about the potential for oxytocin to be misused, for example, to manipulate trust in others or to promote conformity in social settings. These ethical considerations must be carefully weighed against the potential benefits of oxytocin supplementation.
Oxytocin Future Research Directions
Although substantial progress has been made in understanding oxytocin’s influence on social cognition and emotional intelligence, many questions remain unanswered.
Long-Term Effects of Oxytocin Supplementation
Most studies on oxytocin’s effects on social cognition and emotional intelligence have focused on short-term administration and immediate outcomes. Future research should investigate the long-term effects of oxytocin supplementation, including potential changes in social and emotional functioning over time and the possible development of tolerance or dependence.
Individual Differences and Personalized Approaches
As discussed earlier, individual differences in genetics, early life experiences, and hormonal interactions can modulate oxytocin’s effects on social cognition and emotional intelligence [13]. Future research should further explore these factors and develop personalized approaches to oxytocin supplementation that take into account individual variability in response to treatment.
Combination Therapies
Given oxytocin’s multifaceted effects on social cognition and emotional intelligence, it may be useful to explore combination therapies that target multiple aspects of social and emotional functioning. For example, oxytocin supplementation could be combined with other treatments, such as cognitive-behavioral therapy, social skills training, or pharmacological interventions, to enhance its effectiveness in improving social cognition and emotional intelligence.
Cross-Cultural Research
Most research on oxytocin’s influence on social cognition and emotional intelligence has been conducted in Western populations. Cross-cultural research is needed to determine whether oxytocin’s effects on social cognition and emotional intelligence are universal or whether they vary across different cultural contexts. This information will be critical for developing culturally sensitive interventions and treatments.
Ethical Guidelines and Public Policy
As our understanding of oxytocin’s effects on social cognition and emotional intelligence continues to grow, it will be essential to develop ethical guidelines and public policies that govern its use. Future research should examine the potential risks and benefits of oxytocin supplementation from an ethical perspective, as well as explore strategies for regulating its use to minimize potential harms and promote responsible, evidence-based applications.
References
[1] In touch with your emotions: Oxytocin and touch change social impressions
[2] Intranasal inhalation of oxytocin improves face processing
[3] Effects of Oxytocin on Facial Expression and Identity Working Memory
[4] Effects of intranasal oxytocin administration on empathy and approach motivation
[5] From Oxytocin to Compassion: The Saliency of Distress
[6] Roles of Oxytocin in Stress Responses, Allostasis and Resilience
[7] The role of oxytocin in social bonding, stress regulation and mental health
[8] Promoting social behavior with oxytocin
[9] OXTR polymorphism predicts social relationships through its effects on social temperament
[10] Neurosteroids: A Hidden Key to Regulating Brain Health?
[11] Study shows which children with autism respond best to oxytocin treatment
[12] Oxytocin (Intravenous Route, Intramuscular Route) Side Effects – Mayo Clinic
[13] Links Between the Neurobiology of Oxytocin and Human Musicality

