As our society becomes increasingly interested in optimizing brain function, the world of nootropics continues to expand and intrigue. Among the countless compounds that promise cognitive enhancement, two molecules—Coenzyme Q10 (CoQ10) and Idebenone — have attracted particular attention. While CoQ10, a naturally occurring antioxidant, has long been recognized for its health benefits, recent research suggests that its synthetic analogue, Idebenone, might offer superior cognitive advantages.
Contents
Introduction to the Nootropics Idebenone and CoQ10
In our fast-paced, information-saturated world, cognitive enhancement has become a significant area of interest. One pathway many are exploring to boost their mental prowess is through nootropics. These are substances that could potentially improve cognitive function, particularly executive functions like memory, creativity, or motivation, in healthy individuals.
Brief Overview of Idebenone and CoQ10
CoQ10, a substance produced naturally by the body, is known for its role in cellular energy production and as an antioxidant. It has been studied for its potential effects on cardiovascular health, mitochondrial function, and neurodegenerative diseases.
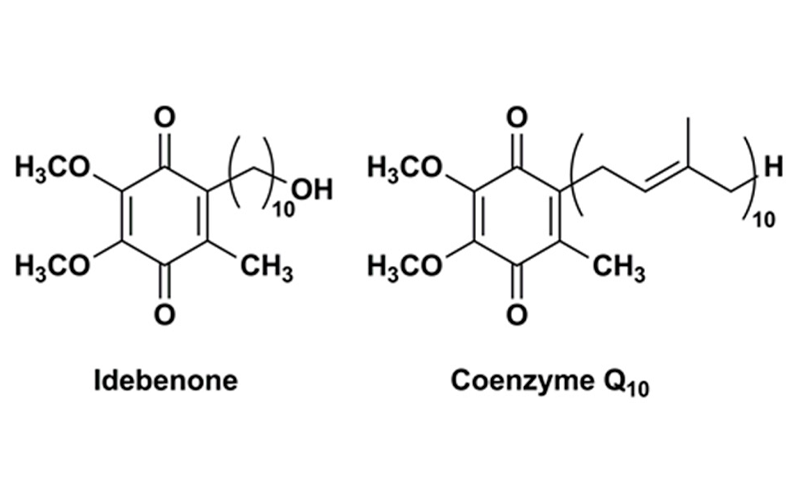
On the other hand, Idebenone is a synthetic analogue of CoQ10, designed to mimic its functions but potentially more potent. Idebenone has been studied in the context of neurodegenerative diseases, particularly for conditions causing vision loss, and is believed to have potential cognitive-enhancing effects.
Importance of Nootropics for Cognitive Enhancement
The search for cognitive enhancement is not a new concept. However, as our understanding of the brain and cognitive function grows, so too does the potential for improving these functions. Nootropics can play a key role in this quest, offering the potential to improve memory, attention, creativity, and even mood.
Understanding Coenzyme Q10 (CoQ10)
Before delving into the specifics of Idebenone, it is imperative to establish a fundamental understanding of its natural counterpart, Coenzyme Q10, commonly known as CoQ10. This substance has a crucial role in the human body, particularly in cellular energy production and antioxidant activities.
The Role of CoQ10 in the Body
CoQ10, also known as ubiquinone, is a naturally occurring compound in the body, primarily in the mitochondria of cells. The mitochondria, often referred to as the powerhouse of the cell, are where the majority of a cell’s energy is produced. CoQ10 is involved in the electron transport chain and plays a vital role in this energy-producing process. Moreover, as an antioxidant, CoQ10 helps neutralize harmful free radicals that could damage cells and contribute to aging and disease [1].
CoQ10 as a Nootropic: Research and Evidence
Research into CoQ10 as a nootropic is still emerging, but some promising studies suggest it may support cognitive health. In various models of neurodegenerative diseases, including Parkinson’s and Alzheimer’s, CoQ10 has shown potential neuroprotective effects. It’s thought that the combination of its energy-enhancing and antioxidant properties could contribute to these benefits.
Additionally, some studies have shown a potential benefit of CoQ10 in improving migraines and in age-related cognitive decline. However, it’s worth noting that more extensive, high-quality clinical trials are necessary to conclusively establish these potential benefits.
Potential Drawbacks or Side Effects of CoQ10
While CoQ10 is generally well-tolerated and considered safe at recommended dosages, it is not devoid of potential side effects. Some individuals may experience mild side effects, such as stomach upset, loss of appetite, nausea, and diarrhea. It’s also worth noting that CoQ10 may interact with certain medications, including blood thinners and medications for high blood pressure or cancer treatment.
Moreover, despite its potential benefits, it’s important to consider that the body’s ability to absorb CoQ10 decreases as we age, potentially limiting its effectiveness in older populations. This particular limitation sets the stage for a compelling comparison with its synthetic counterpart, Idebenone, which, as you’ll see, may offer similar benefits with improved potency and absorption.
Introduction to Idebenone
As we’ve unpacked the role and potential benefits of CoQ10, we can now turn our attention to a related compound that may offer some additional advantages, especially in the context of cognitive enhancement. This compound, Idebenone, is a synthetic derivative of CoQ10 but with some intriguing distinctions.
Idebenone: A Synthetic Analogue of CoQ10
Idebenone is a synthetic compound designed to mimic CoQ10. Structurally, it is very similar to CoQ10, but it also has unique features that differentiate it and may confer distinct benefits. One crucial difference is its ability to provide a protective effect under low oxygen conditions, an attribute not shared by CoQ10 [2].
Understanding the Differences between Idebenone and CoQ10
While Idebenone and CoQ10 have similar structures and functions, there are key differences between them. Idebenone has a shorter chain length compared to CoQ10, which influences its ability to distribute in the body. This difference makes Idebenone more water-soluble than CoQ10, potentially leading to better absorption and distribution in the body.
The Potential Nootropic Benefits of Idebenone
Preliminary research suggests that Idebenone may have cognitive-enhancing effects. This could be due to its potential to improve mitochondrial function and provide neuroprotection, much like CoQ10. However, some evidence suggests that Idebenone might offer superior neuroprotection compared to CoQ10 under certain conditions, particularly under oxidative stress and low oxygen conditions, which are common in various neurological diseases [3].

A Comparative Analysis: Idebenone vs CoQ10
Having established a foundational understanding of both CoQ10 and Idebenone, we’re now better equipped to evaluate them side by side. This comparative analysis will explore their mechanisms of action, potential benefits, and potential drawbacks, presenting a comprehensive view of these two intriguing compounds.
Comparison of Mechanisms: How Idebenone and CoQ10 Work in the Body
Both CoQ10 and Idebenone function as part of the electron transport chain in the mitochondria, facilitating the process that generates cellular energy. They also share potent antioxidant properties, helping to neutralize harmful free radicals in the body.
However, Idebenone’s unique structure allows it to maintain its effectiveness even under conditions of low oxygen, a feature not shared by CoQ10. This aspect makes Idebenone potentially more beneficial under certain circumstances, such as in neurodegenerative conditions characterized by reduced oxygen supply.
Comparing the Efficacy and Potential Benefits: What Research Says
Preliminary research suggests that both CoQ10 and Idebenone may have potential benefits for cognitive health. They may support mitochondrial function, provide neuroprotection, and potentially slow age-related cognitive decline.
Nonetheless, Idebenone may have an edge over CoQ10 due to its better bioavailability and superior efficacy under conditions of oxidative stress and low oxygen. These features could make Idebenone a more potent nootropic, although more research is needed to fully establish this [4].
Side Effects and Risks: What You Should Know
Both CoQ10 and Idebenone are generally well-tolerated, with reported side effects being relatively mild. However, like any substance, they carry potential risks that should be considered. CoQ10 may interact with certain medications, while Idebenone, being a synthetic compound, may have unknown long-term effects. Always consult a healthcare professional before starting a new supplement regimen.
Through this comparative analysis, we can appreciate the nuanced differences between Idebenone and CoQ10. These subtle variations in their mechanisms, efficacy, and potential risks set the stage for the compelling argument of Idebenone potentially being a superior nootropic.
Why Idebenone May Be the Better Nootropic
Given our comparative analysis, it’s evident that both CoQ10 and Idebenone offer intriguing potential benefits. However, Idebenone emerges as a compelling candidate for the superior nootropic based on a few key factors.
Presenting the Case for Idebenone
Firstly, Idebenone’s unique structural characteristics that make it more water-soluble can enhance its bioavailability compared to CoQ10. This feature means that Idebenone might be absorbed more effectively and distributed more broadly in the body, potentially leading to more pronounced benefits.
Review of Studies Indicating Superiority of Idebenone
Several studies suggest that Idebenone might outperform CoQ10 under certain conditions. Notably, under conditions of oxidative stress and low oxygen – scenarios common in several neurological disorders – Idebenone has been shown to maintain its effectiveness, while CoQ10 does not. This superior performance under stress conditions implies that Idebenone might offer more robust neuroprotection and cognitive enhancement [5].
Highlighting the Specific Advantages of Idebenone Over CoQ10
In summary, Idebenone’s advantages over CoQ10 stem from its enhanced bioavailability and superior performance under stress conditions. It’s also worth noting that while the body’s ability to absorb CoQ10 decreases with age, this does not appear to be the case with Idebenone, making it potentially a better choice for older individuals.
Guidance for Using Idebenone Safely and Effectively
While Idebenone shows significant promise as a nootropic, it’s crucial to approach its use with an informed and mindful strategy. Ensuring you use Idebenone safely and effectively will help you maximize its potential benefits while minimizing possible risks.
Recommended Dosage and Administration of Idebenone
Idebenone dosages used in research studies vary widely depending on the condition being studied. Dosages range from 90 mg to 1000 mg per day, usually divided into two or three doses. As a dietary supplement for healthy adults, a common dosage is around 90-150 mg per day [6].
It’s important to note that these are general guidelines and may not be appropriate for everyone. Always consult with a healthcare provider or a specialist in nootropics before starting to use Idebenone, and never exceed the recommended dosage.
Possible Side Effects and How to Minimize Them
Like any supplement, Idebenone has the potential for side effects. Most commonly, these include gastrointestinal symptoms such as nausea, upset stomach, or diarrhea. These symptoms can often be minimized by taking the supplement with food.
While less common, allergic reactions to Idebenone can occur. If you experience symptoms of an allergic reaction, such as hives, difficulty breathing, or swelling of your face, lips, tongue, or throat, you should seek medical attention immediately.
Precautions and Contraindications
Idebenone is generally considered safe for most healthy adults. However, certain individuals should exercise caution. If you are pregnant, planning to become pregnant, or breastfeeding, you should consult your healthcare provider before using Idebenone. Also, if you have any chronic health conditions or if you are taking any medications, you should discuss with your healthcare provider whether Idebenone is safe for you.
References
[1] Current Status and Future Prospects of Idebenone
[2] Idebenone and Neuroprotection: Antioxidant, Pro-oxidant, or Electron Carrier?
[3] Coenzyme Q10 Analogues: Benefits and Challenges for Therapeutics
[4] Evaluating the therapeutic potential of idebenone and related quinone analogues
[5] Clinical evidence review of idebenone for treating visual impairment in adults
[6] A Phase 3, Double-blind, Placebo-Controlled Trial of Idebenone

