The human brain, one of the most complex and vital organs, requires constant maintenance to function optimally. While the importance of a healthy diet, regular exercise, and adequate sleep is well-known, a lesser-known aspect of brain health is the glymphatic system. This system plays a crucial role in cleansing the brain of toxins and waste products, thus maintaining overall brain health and function.
Contents
Overview of the Glymphatic System
The glymphatic system is a recently discovered waste clearance network in the brain that plays a critical role in maintaining brain health. Named after the glial cells, which are essential to its function, the glymphatic system works in conjunction with the cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) to remove harmful waste products and deliver essential nutrients to the brain.
Comparison to the Lymphatic System
While the glymphatic system is unique to the central nervous system (CNS), it shares similarities with the lymphatic system that is present throughout the rest of the body. The lymphatic system is a network of vessels and nodes that helps to remove waste products, maintain fluid balance, and support the immune system. Both systems work to maintain homeostasis and protect the body from harmful substances, but the glymphatic system is specifically tailored to the unique environment of the CNS.
Role in Waste Removal and Nutrient Delivery
The glymphatic system plays a dual role in the brain. Firstly, it acts as a waste removal system, helping to clear away harmful substances and metabolic byproducts that accumulate during normal brain function. These waste products include proteins such as beta-amyloid, which, if not cleared, can form plaques that are associated with neurodegenerative diseases like Alzheimer’s. Secondly, the glymphatic system helps deliver essential nutrients and molecules to the brain, supporting the overall health and function of neurons and other brain cells.
How the Glymphatic System Cleans Your Brain
Understanding the glymphatic system’s role in waste removal and brain health highlights the importance of supporting and optimizing its function.
The Role of Glial Cells and Cerebrospinal Fluid (CSF)
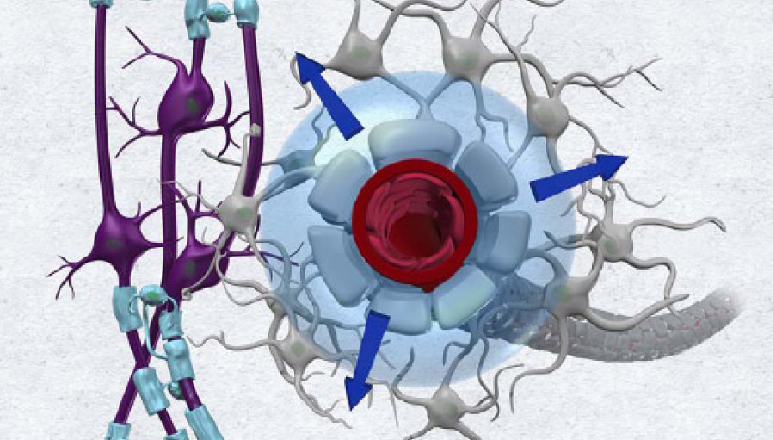
The glymphatic system relies on glial cells, specifically astrocytes, and the cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) to carry out its waste removal and nutrient delivery functions [1]. Astrocytes are star-shaped cells found throughout the CNS that have a range of functions, including providing structural support to neurons, maintaining the blood-brain barrier, and participating in waste removal.
Astrocytes have specialized extensions called endfeet that wrap around blood vessels in the brain. These endfeet, in conjunction with the blood vessels, create a network of channels through which CSF flows. The CSF is a clear, colorless fluid that bathes the brain and spinal cord, providing a means for the glymphatic system to remove waste products and deliver nutrients to the brain.
The Process of Waste Removal During Sleep
The glymphatic system’s waste removal process is most active during sleep. When we sleep, our brain cells shrink by about 60%, allowing the CSF to flow more freely through the glymphatic channels. This increased flow enables the efficient removal of waste products and the delivery of nutrients to the brain.
Sleep is a time when the brain’s metabolic activities are reduced, and the focus shifts to maintenance and repair. The glymphatic system takes advantage of this downtime to clear away potentially harmful waste products that have accumulated during the day, allowing the brain to start fresh and function optimally when we wake up.
The Link Between Glymphatic System Dysfunction and Neurodegenerative Diseases
Research has shown that dysfunction in the glymphatic system can lead to the accumulation of toxic waste products in the brain, such as beta-amyloid plaques [2]. These plaques are associated with the development of neurodegenerative diseases like Alzheimer’s. Insufficient waste removal can also lead to the buildup of other harmful substances, potentially contributing to cognitive decline and other neurological disorders.
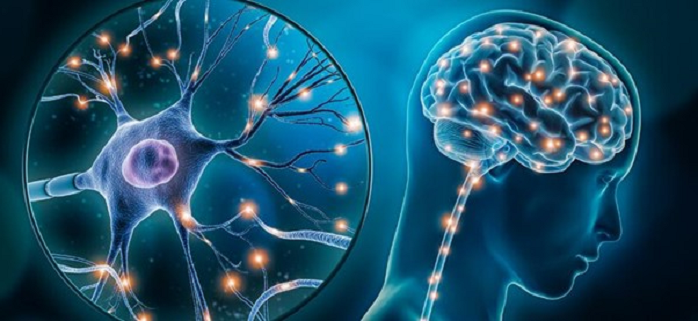
Tips to Optimize the Glymphatic System Function
Here we explore practical tips to optimize the glymphatic system’s function, ensuring your brain effectively removes waste products and receives essential nutrients. By incorporating these habits into your daily routine, you can support overall brain health and potentially reduce the risk of neurodegenerative diseases.
Prioritizing Sleep
Establishing a consistent sleep schedule, including going to bed and waking up at the same time each day, can help regulate your circadian rhythm and support the glymphatic system’s waste removal process. Aim for 7-9 hours of sleep per night, and try to maintain your schedule even on weekends or days off.
Ensuring that you get enough sleep each night is crucial for the optimal function of the glymphatic system. Lack of sleep can lead to reduced waste clearance and increased inflammation, potentially contributing to cognitive decline and other brain-related issues.
Research has shown that sleeping on your side, particularly on the left side, may improve the glymphatic system’s waste clearance efficiency. Experiment with different sleep positions and choose the one that is most comfortable for you while keeping in mind the potential benefits of side sleeping.
Diet and Hydration
Consuming a diet rich in anti-inflammatory foods, such as fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and healthy fats, can support brain health and reduce inflammation that may hinder the glymphatic system’s function. Avoid processed foods, excessive sugar, and unhealthy fats, which can contribute to inflammation.
Staying adequately hydrated is essential for the production of cerebrospinal fluid, which is crucial for the glymphatic system’s function. Aim to drink at least 8-10 glasses of water per day or more, depending on your individual needs and activity level.
Stress Management
Chronic stress can negatively impact brain health by increasing inflammation and contributing to the accumulation of harmful substances. Managing stress effectively is essential for maintaining optimal glymphatic system function.
Develop a stress reduction routine that incorporates activities such as mindfulness meditation, yoga, deep breathing exercises, or any other relaxation techniques that work for you. Regularly engaging in these activities can help reduce stress levels and support brain health.
Nutritional Supplements That Benefit the Glymphatic System
While more research is needed to fully understand the impact of nutritional supplements on the glymphatic system, some supplements have been suggested to potentially offer benefits.
Omega-3 Fatty Acids
Omega-3 fatty acids, particularly DHA (docosahexaenoic acid) and EPA (eicosapentaenoic acid), are essential fats known to support brain health. While the exact mechanisms of how omega-3 fatty acids may benefit the glymphatic system are not yet fully understood, there are several potential ways they could have a positive impact [3]:
- Anti-inflammatory properties: Omega-3 fatty acids have well-documented anti-inflammatory effects. By reducing inflammation in the brain, they may help create a more favorable environment for the glymphatic system to function efficiently and effectively.
- Supporting blood-brain barrier integrity: Omega-3 fatty acids, particularly DHA, are essential for maintaining the integrity of the blood-brain barrier (BBB). A healthy BBB is critical for the proper functioning of the glymphatic system, as it helps regulate the exchange of fluids and substances between the brain and the bloodstream.
- Enhanced brain cell function: DHA is an essential component of neuronal cell membranes, playing a crucial role in the structure, function, and signaling of brain cells. By supporting overall brain cell health, omega-3 fatty acids may indirectly support the glymphatic system’s function, since healthy neurons are more likely to efficiently remove waste products.
- Improved cerebral blood flow: Some studies suggest that omega-3 fatty acids may help improve cerebral blood flow, which could potentially enhance the function of the glymphatic system by promoting the circulation of cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) and the clearance of waste products.
Magnesium
Magnesium is an essential mineral involved in numerous physiological processes, including neurological function. There are several potential ways it might benefit the glymphatic system [4]:
- Supporting brain cell function: Magnesium plays a critical role in neuronal function, including the regulation of neurotransmitter release and synaptic plasticity. By contributing to overall brain cell health and function, magnesium may indirectly support the glymphatic system, as efficient waste removal relies on properly functioning neurons.
- Blood-brain barrier maintenance: Some research suggests that magnesium may help maintain the integrity of the blood-brain barrier (BBB), which is crucial for proper glymphatic system function. A healthy BBB facilitates the exchange of fluids and substances between the brain and the bloodstream, enabling the glymphatic system to clear waste effectively.
- Reducing inflammation and oxidative stress: Magnesium has anti-inflammatory and antioxidant properties that can help reduce inflammation and oxidative stress in the brain. By creating a more favorable environment for the glymphatic system to function, magnesium may indirectly enhance waste removal and nutrient delivery processes.
- Improved sleep quality: Magnesium is known to support sleep quality by regulating the neurotransmitter systems involved in the sleep-wake cycle. Since the glymphatic system is most active during sleep, ensuring adequate magnesium levels can contribute to optimal glymphatic system function by promoting better sleep.
Curcumin
Curcumin, the active compound found in turmeric, has been widely studied for its potential health benefits, including its effects on brain health. Ways in which curcumin might benefit the glymphatic system include [5]:
- Anti-inflammatory and antioxidant properties: Curcumin is known for its potent anti-inflammatory and antioxidant effects. By reducing inflammation and oxidative stress in the brain, it may create a more favorable environment for the glymphatic system to function efficiently, facilitating the clearance of waste products and the delivery of nutrients.
- Reducing amyloid-beta accumulation: Curcumin has been found to inhibit the aggregation of amyloid-beta, a protein that forms plaques in the brains of Alzheimer’s disease patients. Since the glymphatic system plays a crucial role in clearing amyloid-beta and other waste products, curcumin may support the glymphatic system’s function by reducing the burden of these harmful substances.
- Neuroprotective effects: Curcumin has been shown to exhibit neuroprotective properties, helping to protect brain cells from damage and supporting overall brain health. By promoting brain cell health, curcumin may indirectly support the glymphatic system, as efficient waste removal relies on properly functioning neurons.
- Potential impact on sleep: Some research suggests that curcumin may have a positive effect on sleep quality, which could indirectly benefit the glymphatic system. Since the glymphatic system is most active during sleep, improving sleep quality may contribute to more efficient waste removal and nutrient delivery processes.
Resveratrol
Resveratrol, a polyphenol found in grapes, red wine, and certain berries, has been studied for its potential health benefits, including its effects on brain health. Resveratrol’s impact on the glymphatic system derives from several properties [6]:
- Anti-inflammatory and antioxidant properties: Resveratrol is known for its potent anti-inflammatory and antioxidant effects. By reducing inflammation and oxidative stress in the brain, it may create a more favorable environment for the glymphatic system to function efficiently, aiding in the clearance of waste products and the delivery of nutrients.
- Neuroprotective effects: Resveratrol has been shown to exhibit neuroprotective properties, helping to protect brain cells from damage and supporting overall brain health. By promoting brain cell health, resveratrol may indirectly support the glymphatic system, as efficient waste removal relies on properly functioning neurons.
- Enhancing cerebral blood flow: Some studies suggest that resveratrol may improve cerebral blood flow, which could potentially enhance the function of the glymphatic system by promoting the circulation of cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) and the clearance of waste products.
- Potential impact on sleep: Although the research is limited, there is some evidence to suggest that resveratrol may have a positive effect on sleep quality, which could indirectly benefit the glymphatic system. Since the glymphatic system is most active during sleep, improving sleep quality may contribute to more efficient waste removal and nutrient delivery processes.
The Importance of Ongoing Research of the Glymphatic System and Brain Health
ongoing research on the glymphatic system is crucial for deepening our understanding of this critical aspect of brain health. As we continue to learn more about the glymphatic system and its role in maintaining optimal brain function, we can develop targeted strategies and interventions to support brain health and reduce the risk of neurodegenerative diseases.
Current Studies on the Glymphatic System
Since the discovery of the glymphatic system, researchers have been working to better understand its role in brain health and disease. Ongoing studies are investigating various aspects of the glymphatic system, such as its connection to sleep, the impact of aging, and potential links to neurodegenerative diseases like Alzheimer’s and Parkinson’s [7][8]. Researchers are also exploring the effects of various lifestyle factors, such as diet, exercise, and stress management, on the glymphatic system’s function.
Potential Future Developments and Therapies
As our understanding of the glymphatic system deepens, there is potential for the development of novel therapies and treatments targeting its function. These therapies may help prevent or slow down the progression of neurodegenerative diseases by enhancing the brain’s waste clearance capabilities. Additionally, insights from glymphatic system research could contribute to the development of personalized medicine approaches that take into account individual differences in glymphatic function.
References
[1] The Glymphatic System – A Beginner’s Guide
[2] The Gut-Brain Axis: How Your Microbiome Influences Cognitive Health
[3] Additional benefit of omega-3 fatty acids for the clearance of metabolites from the brain
[4] The Role of Magnesium in Neurological Disorders
[5] The Effect of Curcumin on Idiopathic Parkinson Disease: A Clinical and Skin Biopsy Study
[6] Resveratrol Modulates the Gut-Brain Axis: Focus on Glucagon-Like Peptide-1, 5-HT, and Gut Microbiota
[7] Research Evidence of the Role of the Glymphatic System and Its Potential Pharmacological Modulation in Neurodegenerative Diseases
[8] The Role of Glymphatic System in Alzheimer’s and Parkinson’s Disease Pathogenesis

