
Estrogen, the primary female hormone, plays a vital role in women’s health, affecting everything from reproductive functions to mood regulation. But did you know that it also has a significant impact on brain health? Here we explore the fascinating relationship between estrogen and cognitive function, shedding light on how this powerful hormone influences memory, learning, and neuronal growth.
Contents
Estrogen: The Key Female Hormone
Estrogen is a vital hormone in the female body, responsible for regulating a variety of functions, including reproductive and sexual development. To gain a better understanding of estrogen’s influence on brain health, let us delve deeper into its definition, production, and role in different stages of a woman’s life.
Definition and Functions of Estrogen
Estrogen is a group of steroid hormones primarily responsible for the development and regulation of the female reproductive system. There are three main types of estrogen: estrone (E1), estradiol (E2), and estriol (E3). Estradiol is the most potent and prevalent form of estrogen in premenopausal women.
Apart from its role in reproductive health, estrogen affects various other aspects of a woman’s well-being, such as bone density, skin elasticity, and cardiovascular health. Additionally, it modulates the immune system and plays a vital role in maintaining mood balance.
Estrogen Production and Fluctuations
Estrogen is primarily produced in the ovaries, but it can also be generated in smaller amounts in the adrenal glands, fat tissue, and the brain [1]. The production of estrogen is regulated by the hypothalamus and the pituitary gland through a complex feedback mechanism involving various hormones.
Throughout a woman’s life, estrogen levels fluctuate in response to different factors, such as the menstrual cycle, pregnancy, and menopause. During the menstrual cycle, estrogen levels rise and fall, reaching their peak during ovulation. This fluctuation has a significant impact on a woman’s mood, energy levels, and overall well-being.
The Role of Estrogen in Menstrual Cycle and Menopause
Estrogen plays a critical role in regulating the menstrual cycle, stimulating the growth of the uterine lining (endometrium) in preparation for a potential pregnancy. It also influences the maturation and release of eggs from the ovaries during ovulation.
As women approach menopause, estrogen levels begin to decline, leading to changes in menstrual patterns and eventually the cessation of menstruation. The hormonal fluctuations associated with menopause can cause various symptoms, such as hot flashes, night sweats, and mood swings [2]. Moreover, the decline in estrogen levels during menopause has been linked to increased risk of cognitive decline and other brain-related issues.
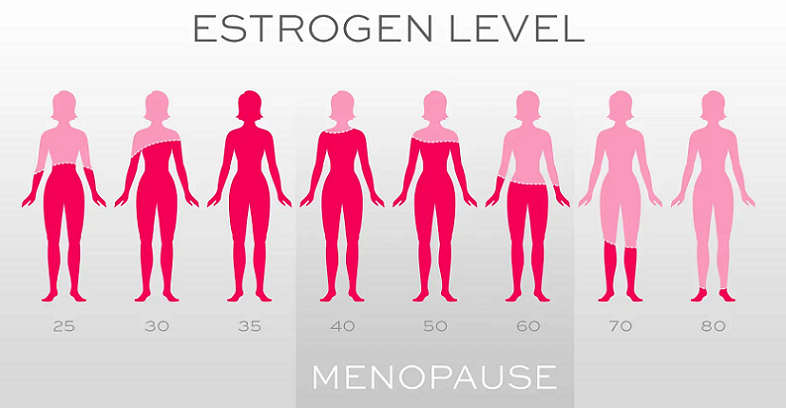
Estrogen’s Positive Impact on Brain Health
Research has demonstrated that estrogen has a significant influence on various aspects of brain health, including neural connectivity, neurogenesis, and cognitive abilities such as memory and learning.
Enhancing Neural Connectivity and Plasticity
Estrogen has been shown to enhance neural connectivity and plasticity, which are crucial for learning, memory formation, and overall cognitive function [3]. Neural plasticity refers to the brain’s ability to change and adapt in response to new experiences and information. This includes the formation of new neural connections (synapses) and the strengthening or weakening of existing connections.
Estrogen acts on specific receptors in the brain, promoting the release of growth factors that encourage the growth and development of neurons and synapses. This increased connectivity enhances the brain’s ability to process and store information, contributing to improved cognitive performance.
Promoting Neuronal Growth and Survival
Estrogen also plays a vital role in promoting the growth and survival of neurons, which are the primary cells responsible for transmitting information throughout the brain [4]. It does so by stimulating the production of neurotrophic factors, which are proteins that help neurons grow, differentiate, and survive.
By supporting the health and vitality of neurons, estrogen contributes to the maintenance of cognitive function and helps prevent age-related neuronal loss, which can lead to cognitive decline and neurodegenerative disorders.
Supporting Memory and Learning Abilities
Memory and learning are essential cognitive functions that rely on the proper functioning of the hippocampus, a region of the brain closely associated with these processes. Estrogen has been found to have a direct effect on the hippocampus, promoting the growth of new neurons and enhancing synaptic plasticity [5].
Studies have shown that women with higher estrogen levels tend to perform better on memory and learning tasks, indicating a strong connection between this hormone and cognitive performance. Additionally, research suggests that estrogen may help protect against age-related memory decline, further emphasizing the importance of maintaining optimal estrogen levels for brain health.

Estrogen and Cognitive Decline Prevention
Given the significant role estrogen plays in supporting brain health, it is essential to examine its implications for preventing cognitive decline, particularly in the context of age-related neurodegenerative disorders such as Alzheimer’s disease.
The Relationship Between Estrogen and Alzheimer’s Disease
Alzheimer’s disease, the most common cause of dementia, is characterized by the progressive loss of cognitive function, leading to memory loss, disorientation, and eventual inability to perform daily tasks. Research has shown that women are at a higher risk of developing Alzheimer’s disease compared to men, and this increased risk has been linked to the decline in estrogen levels during menopause [6].
Estrogen is believed to have a neuroprotective effect, reducing the risk of cognitive decline and Alzheimer’s disease by promoting neuronal growth, enhancing synaptic plasticity, and modulating inflammatory responses in the brain. As estrogen levels decline during menopause, these protective effects are diminished, which may contribute to the increased risk of Alzheimer’s disease in postmenopausal women.
Menopause and Cognitive Changes
During menopause, women may experience various cognitive changes, such as difficulties with memory, concentration, and mental processing speed. While these changes are often mild and temporary, they can be distressing and have a significant impact on daily functioning and quality of life.
The decline in estrogen levels during menopause has been implicated in these cognitive changes, as estrogen plays a crucial role in maintaining cognitive function and brain health [7]. However, further research is needed to fully understand the relationship between menopause, estrogen, and cognitive function, as well as to identify potential interventions to mitigate these effects.
Hormone Replacement Therapy (HRT) Benefits and Risks
Hormone replacement therapy (HRT) is a treatment that involves the administration of estrogen, with or without progesterone, to alleviate menopausal symptoms and restore hormonal balance in postmenopausal women. Some studies have suggested that HRT may help prevent cognitive decline and reduce the risk of Alzheimer’s disease by maintaining optimal estrogen levels and preserving brain health.
However, the use of HRT for cognitive decline prevention remains a subject of debate, as the benefits must be weighed against the potential risks [8]. Some studies have shown that HRT can increase the risk of blood clots, stroke, and certain types of cancer, such as breast cancer. Therefore, it is essential for women considering HRT to discuss the potential benefits and risks with their healthcare provider and make an informed decision based on their individual needs and circumstances.
Lifestyle Factors to Support Estrogen Levels and Brain Health
Maintaining optimal estrogen levels and promoting brain health are essential for preventing cognitive decline and ensuring overall well-being. Adopting a healthy lifestyle can significantly contribute to hormone balance and support cognitive function.
Diet and Nutrition for Estrogen Balance
A balanced diet rich in nutrients is crucial for supporting hormonal balance and brain health. Some key dietary considerations for maintaining optimal estrogen levels and promoting cognitive function include:
- Incorporating phytoestrogens: Phytoestrogens are plant-based compounds that have a weak estrogenic effect, helping to balance estrogen levels in the body. Foods high in phytoestrogens include soy products, flaxseeds, sesame seeds, and legumes.
- Consuming omega-3 fatty acids: Omega-3 fatty acids, found in fatty fish, walnuts, and chia seeds, have been shown to support brain health and cognitive function. They also have anti-inflammatory properties, which can be beneficial for hormone balance.
- Including antioxidant-rich foods: Antioxidants help protect the brain from oxidative stress, which can contribute to cognitive decline. Foods rich in antioxidants include berries, leafy green vegetables, nuts, and dark chocolate.
- Avoiding excess sugar and processed foods: A diet high in sugar and processed foods can negatively impact hormonal balance and brain health. Opt for whole, unprocessed foods whenever possible.
Exercise and Its Impact on Hormone Levels
Regular physical activity is essential for maintaining hormone balance, including estrogen levels. Exercise can help regulate estrogen by:
- Supporting weight management: Excess body fat can lead to increased estrogen production. Regular exercise helps maintain a healthy weight, promoting hormone balance.
- Reducing stress: Exercise has been shown to reduce stress levels, which can have a positive impact on hormone regulation.
- Boosting cognitive function: Physical activity stimulates the release of growth factors that promote brain health and improve cognitive function.
Incorporating a mix of aerobic exercises, such as brisk walking or swimming, and strength training can provide the most benefits for both hormone balance and brain health.
Stress Management and Its Role in Hormonal Health
Chronic stress can negatively impact hormone balance, including estrogen levels, and contribute to cognitive decline [9]. Implementing effective stress management techniques can help maintain hormonal balance and support brain health. Some useful strategies include:
- Practicing mindfulness meditation: Mindfulness meditation has been shown to reduce stress, improve focus, and enhance cognitive function.
- Engaging in relaxation techniques: Deep breathing exercises, progressive muscle relaxation, and visualization can help manage stress and promote mental well-being.
- Prioritizing sleep: Adequate sleep is crucial for hormone regulation and brain health. Aim for 7-9 hours of quality sleep each night.
- Seeking social support: Connecting with friends and family can help reduce stress levels and promote emotional well-being.
The Role of Estrogen in Mental Health
In addition to its impact on cognitive function and brain health, estrogen plays a critical role in regulating mood and overall mental well-being.
Estrogen and Mood Regulation
Estrogen has been shown to modulate the production and function of various neurotransmitters, such as serotonin, dopamine, and norepinephrine, which are crucial for mood regulation [10]. By influencing the levels and activity of these neurotransmitters, estrogen can have a significant impact on mood, emotional well-being, and overall mental health.
Estrogen’s Influence on Anxiety and Depression
Research suggests that fluctuations in estrogen levels can contribute to the development of anxiety and depressive symptoms in some women. For example, premenstrual syndrome (PMS) and premenstrual dysphoric disorder (PMDD) are characterized by mood swings, irritability, and emotional symptoms, which are often linked to hormonal changes during the menstrual cycle.
Similarly, the decline in estrogen levels during menopause can result in mood disturbances, such as increased anxiety, depressive symptoms, and mood swings. Estrogen’s neuroprotective and mood-regulating properties may help explain its influence on mental health during these periods of hormonal fluctuation.
Hormonal Imbalances and Mental Health Disorders
Hormonal imbalances, including estrogen imbalances, can contribute to the development and exacerbation of mental health disorders. For example, women with polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS), a hormonal disorder characterized by elevated levels of androgens and often accompanied by estrogen imbalances, are at a higher risk of experiencing anxiety and depression.
Furthermore, women with thyroid disorders, which can also impact hormonal balance, are more likely to develop mental health issues such as depression and anxiety. These examples highlight the importance of addressing hormonal imbalances and maintaining optimal estrogen levels for overall mental well-being.
References
[1] Endocrine Glands | Junqueira’s Basic Histology
[2] Dealing with the symptoms of menopause
[3] Neuron-Derived Estrogen Regulates Synaptic Plasticity and Memory
[4] Neuroprotection by estrogen in the brain: the mitochondrial compartment as presumed therapeutic target
[5] Uncovering the Mechanisms of Estrogen Effects on Hippocampal Function
[6] Endorphins: The Brain’s Natural Painkillers and Their Cognitive Effects
[7] Role of Estrogen and Other Sex Hormones in Brain Aging. Neuroprotection and DNA Repair
[8] Hormone replacement therapy is associated with improved cognition and larger brain volumes in at-risk APOE4 women
[9] Chronic Stress and Hormone Disruption
[10] Steroid Hormones and Their Action in Women’s Brains: The Importance of Hormonal Balance

