In the complex tapestry of the human body, hormones play a pivotal role, not just in physical well-being but also in the intricate workings of the brain. Among these hormones, calcitonin, traditionally known for its role in bone health and calcium regulation, emerges as a subject of growing interest in the realm of neuroprotection and cognitive function. While often overshadowed by more prominent hormones, recent research suggests that calcitonin may hold key insights into preventing neurological damage and enhancing cognitive abilities.
Contents
Understanding Calcitonin
Before getting into the specifics of how calcitonin interacts with brain health, it’s essential to have a foundational understanding of what calcitonin is and its role in the human body.
Definition and Function of Calcitonin
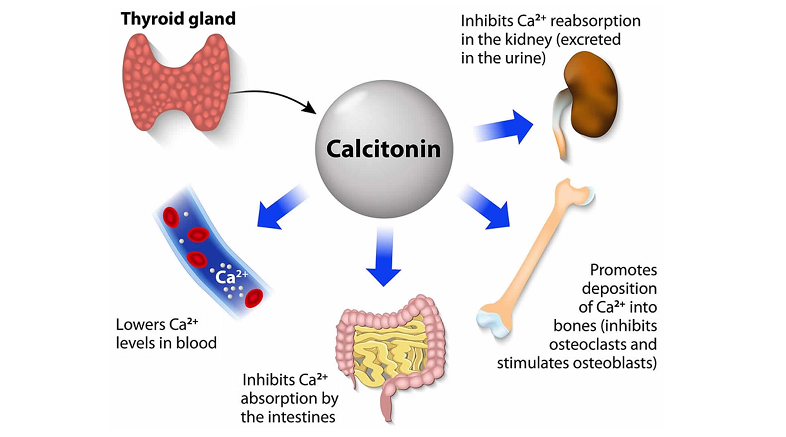
Calcitonin is a hormone primarily known for its role in regulating calcium levels in the human body. Produced in the thyroid gland, it works by counteracting the effects of another hormone, parathyroid hormone (PTH), which raises blood calcium levels. Calcitonin’s primary function is to lower these levels by inhibiting the activity of osteoclasts, cells that break down bone tissue, thereby reducing the release of calcium into the bloodstream.
Historical Perspective on Calcitonin Discovery
The discovery of calcitonin dates back to the early 1960s when researchers first identified its presence and role in birds. Subsequent studies in mammals, including humans, revealed its similar functions across species. This historical context is important because it underscores the evolution of our understanding of calcitonin, from a hormone initially perceived as exclusively related to bone health to one with potential implications in other physiological areas, including the brain.
Current Uses of Calcitonin in Medicine
Today, calcitonin’s medicinal applications are primarily focused on conditions related to bone health. It is used in the treatment of osteoporosis, a condition characterized by weakened bones, and Paget’s disease, which involves abnormal bone destruction and regrowth.
Additionally, it has been employed in managing conditions of hypercalcemia (high calcium levels in the blood). The hormone’s well-established role in these areas sets the stage for exploring its potential in new therapeutic domains, such as neuroprotection and cognitive enhancement.
Hormones and Brain Health
The intricate relationship between hormones and brain health is a subject of immense interest in the scientific community. Here we shed light on how hormones, as biochemical messengers, play a critical role in the functioning of the brain, particularly focusing on their influence on memory and cognition.
Role of Hormones in the Brain
Hormones act as key modulators in the brain, influencing various aspects of neurological function. They are involved in regulating mood, cognitive abilities, and even neuroplasticity—the brain’s capacity to change and adapt. For instance, hormones like serotonin and dopamine are well-known for their roles in mood regulation and reward pathways, whereas others, like estrogen and testosterone, have been linked to cognitive functions and memory processing [1].
Interplay Between Hormones and Neurological Function
The interaction between hormones and the brain is not just one-way; the brain, in turn, influences hormonal release through the endocrine system. This bidirectional communication is pivotal in maintaining a balanced physiological state. Hormonal imbalances can lead to various neurological conditions, from mood disorders to cognitive impairments, highlighting the importance of understanding this dynamic relationship.
Specifics of How Hormones Influence Memory and Cognition
Diving deeper into the realm of memory and cognition, certain hormones stand out for their significant roles. For example, cortisol, often termed the ‘stress hormone’, can impact memory formation and retrieval, particularly under stress. Another example is insulin, typically associated with glucose metabolism, which also plays a crucial role in memory by affecting synaptic plasticity and neurotransmitter regulation. These examples underscore the diverse ways in which hormones can influence brain function, paving the way for a closer examination of calcitonin’s potential role in this intricate network [2].
Calcitonin and Neuroprotection
The concept of neuroprotection involves strategies and mechanisms that protect the brain from injury and degeneration. In recent years, the potential role of calcitonin in neuroprotection has garnered significant interest.
Overview of Neuroprotection
Neuroprotection refers to the preservation of neuronal structure and function. It is a critical aspect in managing neurodegenerative diseases such as Alzheimer’s, Parkinson’s, and multiple sclerosis. Neuroprotective strategies aim to halt or slow the progression of these diseases by preventing neuron loss, reducing neuroinflammation, and promoting neuronal recovery and regeneration.
Mechanisms of Calcitonin in Neuroprotective Action
Emerging research suggests that calcitonin may play a role in neuroprotection through several mechanisms. One proposed pathway is its potential anti-inflammatory action in the brain, which could reduce the damage caused by neuroinflammatory processes commonly observed in neurodegenerative diseases. Additionally, calcitonin might influence neuronal survival and plasticity, crucial factors in maintaining cognitive functions and preventing neurodegeneration [3].
Research Studies and Findings Involving Calcitonin and Neuroprotection
Several studies have begun to shed light on the neuroprotective effects of calcitonin. For instance, research in animal models has shown that calcitonin can mitigate symptoms and pathology in models of Alzheimer’s disease. Other studies suggest that it might also have protective effects against oxidative stress, a key contributor to neuron damage in various neurodegenerative conditions.
Comparison of Calcitonin with Other Neuroprotective Hormones
When compared with other hormones known for their neuroprotective properties, such as estrogen and melatonin, calcitonin presents a unique profile. Unlike these hormones, which have been extensively studied, calcitonin’s role in the brain is relatively less understood. However, its potential for minimal side effects and different mechanism of action offers a promising avenue for further exploration and development of novel neuroprotective therapies.
Calcitonin and Memory Enhancement
Beyond its potential in neuroprotection, calcitonin also shows promise in the realm of memory enhancement. Understanding how this hormone might influence memory processes is crucial, especially in the context of age-related memory decline and neurodegenerative conditions.
Understanding the Link Between Calcitonin and Memory
Calcitonin’s role in memory is an area of burgeoning research interest. Memory formation and retrieval are complex processes involving various brain regions, neurotransmitters, and signaling pathways. Calcitonin may influence these processes through its interaction with neural pathways and neurotransmitter systems involved in memory and learning [4].
Experimental Evidence Supporting Calcitonin and Memory Enhancement
Several experimental studies provide insights into calcitonin’s potential for memory enhancement. For instance, animal studies have shown that calcitonin administration can improve performance in memory tasks. These findings are particularly intriguing as they suggest a direct link between calcitonin levels and memory function, opening new avenues for therapeutic interventions in memory-related disorders.
Theoretical Frameworks Explaining the Effects of Calcitonin
To understand how calcitonin could enhance memory, various theoretical frameworks have been proposed. One theory suggests that calcitonin might modulate synaptic plasticity, a key mechanism in learning and memory. Another hypothesis posits that calcitonin could influence the hippocampus, a brain region vital for memory formation. These frameworks, while still in the early stages of exploration, provide a basis for further investigation into the hormone’s memory-enhancing capabilities [5].
Implications for Future Research and Treatments Involving Calcitonin
The exploration of calcitonin in memory enhancement has significant implications for future research and potential treatments. If calcitonin is found to be effective in improving memory, it could lead to the development of new therapies for conditions like Alzheimer’s disease and other forms of dementia. Moreover, understanding the mechanisms behind its effects could provide insights into the broader field of cognitive health and memory disorders.
References
[1] Calcitonin gene-related peptide: a potential protective agent
[2] The role of calcitonin gene-related peptide in peripheral and central pain mechanisms
[3] Calcitonin gene-related peptide reduces brain injury
[4] Calcitonin gene-related peptide inhibits neuronal apoptosis
[5] Calcitonin Gene-Related Peptide: Physiology and Pathophysiology

