Leptin, often dubbed the “satiety hormone,” has garnered significant attention for its role in regulating hunger and maintaining energy balance within the body. However, this multifaceted hormone’s influence extends far beyond appetite control. Here we delve into the lesser-known aspects of leptin and its remarkable impact on various brain functions, including cognition, mood regulation, neuroprotection, and addiction.
Contents
What is Leptin?
Leptin is a hormone primarily produced by adipose (fat) cells in the body. It is sometimes referred to as the “satiety hormone” or “starvation hormone” because of its significant role in regulating appetite and energy balance. Leptin was first discovered in 1994 during research on obesity, and since then, it has become a critical player in our understanding of weight management and overall health.
Leptin Receptors and Their Distribution in the Brain
Leptin exerts its effects by binding to specific leptin receptors (LEPR) located on the surface of cells [1]. These receptors are found throughout the body, with a high concentration in the brain, particularly in the hypothalamus. The hypothalamus is an area responsible for many essential functions, including regulating hunger, thirst, body temperature, and energy expenditure. The presence of leptin receptors in other brain regions, such as the hippocampus, amygdala, and cortex, highlights its potential influence on various cognitive and emotional processes.
Role of Leptin in Energy Homeostasis and Body Weight Regulation
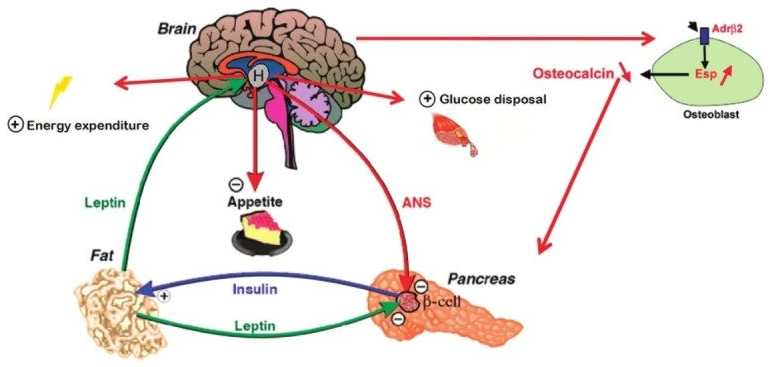
Leptin’s primary function is to communicate the body’s energy status to the brain [2]. When energy stores in the form of fat increase, leptin production rises, signaling to the brain that the body has enough stored energy and can reduce appetite. Conversely, when fat stores decrease, leptin production drops, and the brain receives a signal to increase appetite to replenish the body’s energy reserves.
Leptin’s role in energy homeostasis and body weight regulation is vital for maintaining a healthy weight and preventing obesity. The hormone helps to adjust appetite and energy expenditure in response to changes in nutritional status and body weight. However, it is essential to note that leptin is only one component of a complex regulatory system, and its effects can be modulated by other factors such as genetics, diet, and exercise.

Leptin and Cognition
While leptin is commonly associated with appetite regulation, its influence extends beyond hunger suppression, impacting various cognitive functions.
Relationship Between Leptin and Learning and Memory
The relationship between leptin and learning and memory is an exciting and relatively unexplored aspect of the hormone’s diverse effects on the brain.
Studies on leptin-deficient rodents
Research on leptin-deficient rodents has revealed that leptin plays a crucial role in learning and memory processes [3]. These animals display impaired spatial learning and memory abilities, which can be reversed by administering leptin. Moreover, studies have found that leptin treatment can enhance cognitive performance in both leptin-deficient and normal-weight animals.
Human studies
In humans, the relationship between leptin and cognitive function has also been observed [4]. Higher leptin levels are associated with better cognitive performance, particularly in older adults. However, it is essential to consider that extreme levels of leptin (either too high or too low) can be detrimental to cognitive health, emphasizing the importance of maintaining balanced leptin levels.
Leptin’s Influence on Synaptic Plasticity
Synaptic plasticity refers to the ability of the brain to strengthen or weaken synaptic connections in response to new information or experiences. This process is vital for learning and memory formation.
Long-term potentiation (LTP)
Leptin has been shown to enhance long-term potentiation (LTP), a process that strengthens synaptic connections between neurons [5]. This enhancement occurs in various brain regions, including the hippocampus, a critical area for learning and memory. The increase in LTP induced by leptin suggests that the hormone may contribute to the formation and consolidation of new memories.
Long-term depression (LTD)
Conversely, leptin has also been found to modulate long-term depression (LTD), a process that weakens synaptic connections between neurons [6]. This weakening is essential for eliminating irrelevant or outdated information, allowing the brain to maintain its plasticity and adapt to new experiences. By influencing both LTP and LTD, leptin plays a vital role in regulating synaptic plasticity and, consequently, cognitive function.
Leptin and Mood Regulation
Leptin’s influence on the brain extends to mood regulation, impacting both depression and anxiety.
Leptin’s Role in Depression
The link between leptin and depression is an emerging area of interest in the field of mood disorders.
Studies on leptin levels in depressed individuals
Research has shown a connection between leptin levels and depression in humans. Several studies have found that individuals with depression tend to have lower leptin levels compared to those without depression [7]. Interestingly, this relationship appears to be more pronounced in women. Furthermore, antidepressant treatment has been shown to increase leptin levels, suggesting a potential role for leptin in depression recovery.
Animal studies and the role of leptin in the reward system
Animal studies have also provided valuable insights into leptin’s role in mood regulation. Leptin has been shown to influence the brain’s reward system, which is implicated in the development of depression. Leptin-deficient rodents exhibit depression-like behaviors, while the administration of leptin has been found to alleviate these symptoms. This evidence further supports the idea that leptin plays a crucial role in depression and mood regulation.
Leptin and Anxiety
The connection between leptin and anxiety is another fascinating aspect of this hormone’s impact on mood regulation.
Leptin’s influence on stress response
Leptin has been found to modulate the body’s stress response, which plays a vital role in anxiety. Studies have shown that leptin can regulate the release of stress hormones, such as cortisol, and influence the function of the hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal (HPA) axis, a central component of the stress response system [8].
Studies on leptin’s anxiolytic effects
Research has demonstrated that leptin has anxiolytic (anxiety-reducing) effects in both animals and humans. In animal studies, the administration of leptin has been shown to reduce anxiety-like behaviors [9]. In humans, higher leptin levels have been associated with lower levels of anxiety. However, it is important to note that the relationship between leptin and anxiety is complex and may be influenced by various factors, such as genetics, sex, and body weight.
Leptin and Neuroprotection
Leptin’s influence on the brain goes beyond cognitive function and mood regulation, extending to neuroprotection.
Leptin’s Role in Protecting Against Neurodegenerative Diseases
The potential of leptin to protect against neurodegenerative diseases is an exciting and emerging area of research.
Alzheimer’s disease
Emerging evidence suggests that leptin may play a protective role against neurodegenerative diseases, such as Alzheimer’s disease. Studies have found that higher leptin levels are associated with a reduced risk of developing Alzheimer’s disease and slower cognitive decline in affected individuals [10]. Leptin’s neuroprotective effects are thought to be mediated by its ability to reduce the accumulation of beta-amyloid plaques and tau protein, both of which are hallmarks of Alzheimer’s disease.
Parkinson’s disease
Leptin has also been implicated in protecting against Parkinson’s disease, another common neurodegenerative disorder. Research has shown that leptin can promote the survival of dopaminergic neurons, which are primarily affected in Parkinson’s disease [11]. In animal models of the disease, leptin treatment has been found to alleviate motor symptoms and reduce the loss of dopaminergic neurons.
Mechanisms of Neuroprotection
Understanding the mechanisms underlying leptin’s neuroprotective effects is crucial for developing effective therapeutic strategies targeting neurodegenerative diseases.
Promotion of neuronal survival
Leptin exerts its neuroprotective effects through various mechanisms, one of which is promoting neuronal survival. Leptin activates several signaling pathways that enhance neuronal growth, differentiation, and survival. These pathways help protect neurons from damage caused by toxic substances, inflammation, or oxidative stress.
Reduction of inflammation and oxidative stress
Another critical aspect of leptin’s neuroprotective role is its ability to reduce inflammation and oxidative stress in the brain. Inflammation and oxidative stress are common features of neurodegenerative diseases and can contribute to neuronal damage and death. Leptin has been shown to suppress the production of pro-inflammatory molecules and reduce oxidative stress, ultimately protecting neurons from damage and promoting their survival.
Leptin and Addiction
Leptin’s diverse effects on the brain also extend to addiction, a complex and challenging area of research.
Leptin’s Role in the Reward System
The reward system plays a pivotal role in addiction, and leptin’s influence on this complex neural circuitry is an intriguing area of research.
Dopamine and the mesolimbic pathway
Leptin has been found to play a role in the brain’s reward system, which is crucial for understanding addiction [12]. The reward system, specifically the mesolimbic pathway, involves the release of dopamine, a neurotransmitter associated with pleasure, motivation, and reinforcement. Dysregulation of the reward system is a critical factor in the development of addiction to substances or behaviors.
Leptin’s influence on dopamine release
Leptin has been shown to modulate dopamine release in the mesolimbic pathway. Studies in animal models have demonstrated that leptin can directly affect the release of dopamine and the sensitivity of dopamine receptors [13]. These findings suggest that leptin may play a role in regulating the brain’s response to rewarding stimuli, including those associated with addiction.
Leptin and Drug Addiction
The connection between leptin and drug addiction is a fascinating and emerging area of investigation.
Alcohol addiction
Research has revealed a connection between leptin levels and alcohol addiction. Alcohol consumption can lead to alterations in leptin levels, and individuals with alcohol use disorder often exhibit dysregulated leptin signaling. Some studies have suggested that restoring leptin function might help reduce alcohol consumption and dependence.
Opioid addiction
Leptin has also been implicated in opioid addiction. Studies have found that leptin can modulate the rewarding effects of opioids in animal models, and altered leptin signaling has been observed in individuals with opioid use disorder. Further research is needed to determine if targeting leptin signaling could offer a potential therapeutic strategy for opioid addiction.
Leptin and Food Addiction
Food addiction, characterized by compulsive overeating and loss of control over food intake, has been linked to dysregulated leptin signaling. Individuals with food addiction often have elevated leptin levels, yet their brain’s response to the hormone is diminished, resulting in leptin resistance.
This resistance can contribute to the vicious cycle of overeating and further weight gain. Targeting leptin resistance and restoring the hormone’s function may provide a novel approach to treating food addiction and promoting healthy eating behaviors.
References
[1] Structural insights into the mechanism of leptin receptor activation
[2] Leptin signaling in brain: A link between nutrition and cognition?
[3] Effects of leptin on memory processing
[4] Harnessing the Power of Leptin: The Biochemical Link Connecting Obesity, Diabetes, and Cognitive Decline
[5] Leptin facilitates learning and memory performance and enhances hippocampal CA1 long-term potentiation
[6] Leptin regulation of hippocampal synaptic function in health and disease
[7] The Association between Depression and Leptin is Mediated by Adiposity
[8] Insulin’s Critical Role in Brain Health and Cognitive Function
[9] Leptin: A Potential Anxiolytic by Facilitation of Fear Extinction
[10] Leptin reduces pathology and increases adult neurogenesis in a transgenic mouse model of Alzheimer’s disease
[11] The role of leptin in central nervous system diseases
[12] The Impact of Appetite-Regulating Neuropeptide Leptin on Alcohol Use, Alcohol Craving and Addictive Behavior
[13] Articles, Cellular/Molecular
Leptin Regulates Dopamine Responses to Sustained Stress in Humans

