Neuropeptides are the unsung heroes of our brain’s complex symphony. Neuropeptides are small protein-like molecules that play a pivotal role in the intricate dance of brain functions. They are not just mere participants in the neural communication network; they are key conductors orchestrating a wide range of physiological processes. From influencing our mood and emotions to shaping our learning and memory, neuropeptides are central to understanding how our brain operates and maintains cognitive health. Here we explore the nature of neuropeptides — their structure, how they differ from other neurotransmitters, and their unique roles in the brain.
Contents
Introduction to Neuropeptides and Brain Function
Welcome to a deep dive into the intriguing world of neuropeptides and their role in brain function. As the frontier of neuroscience expands, understanding complex molecules like neuropeptides becomes crucial for unraveling the mysteries of the brain. Neuropeptides, though tiny, have a monumental impact on how our brain operates, influencing everything from our emotions to our cognitive abilities.
Definition of Neuropeptides
Neuropeptides are small chains of amino acids produced and released by neurons. They differ from classical neurotransmitters in both their structure and function. Acting as key messengers within the nervous system, neuropeptides influence a myriad of physiological processes. Unlike neurotransmitters that typically transmit signals over short distances, neuropeptides often have a more prolonged and widespread effect, making them vital in regulating various aspects of brain activity.
Overview of Neuropeptides Role in Brain Function
Neuropeptides are multifaceted in their roles within the brain. They participate in a range of functions, from modulating neural communication to influencing behavior and emotions. Their ability to impact different aspects of brain function makes them a subject of great interest, particularly in understanding conditions like depression, anxiety, and neurodegenerative diseases. By diving into the role of neuropeptides, we can gain insights into how our brain works in health and disease.
Importance of Understanding Neuropeptides
The study of neuropeptides is not just an academic pursuit but a journey towards potential breakthroughs in treating various brain disorders. Understanding these molecules opens up new avenues for therapeutic interventions and provides a deeper comprehension of how our brain maintains its intricate balance. As we explore the world of neuropeptides, we step closer to unlocking new strategies for enhancing brain health and combating neurological disorders.
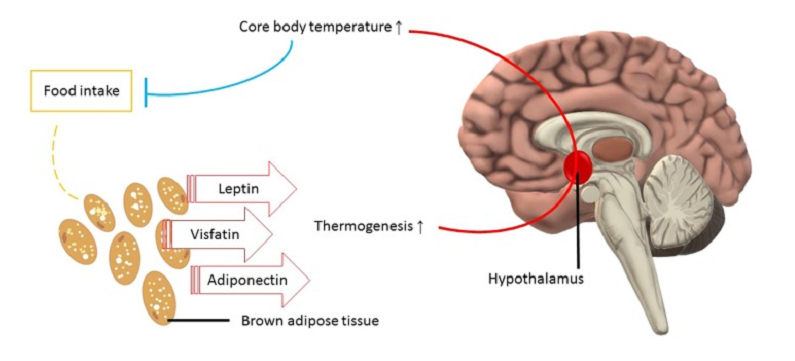
The Nature of Neuropeptides
Understanding the nature of neuropeptides is key to appreciating their role in brain function. These molecules, though often overshadowed by their neurotransmitter counterparts, are fundamental to the way our brain communicates and processes information.
Chemical Structure and Classification of Neuropeptides
Neuropeptides are essentially small proteins, composed of short chains of amino acids. This structure is more complex than that of classic neurotransmitters, which are usually small molecules. Neuropeptides vary greatly in size and sequence, leading to a diverse range of functions. They are often classified based on their amino acid sequence or their functional roles in the nervous system. This diversity not only underscores their complexity but also their versatility in influencing brain function [1].
Comparison of Neuropeptides with Other Neurotransmitters
While both neuropeptides and classical neurotransmitters serve as chemical messengers in the brain, their modes of action and effects differ significantly. Neurotransmitters typically act quickly and over short distances at synaptic junctions. In contrast, neuropeptides often act more slowly and can have both local and widespread effects, modulating not just neural communication but also the overall physiological state of the brain. This difference highlights the unique role of neuropeptides in maintaining long-term physiological balance and response within the brain.
Neuropeptides Production and Release Mechanisms in the Brain
The production and release of neuropeptides in the brain are complex processes. Neuropeptides are synthesized in the cell body of neurons and are packaged into vesicles. They are then transported to various parts of the neuron, including distant axon terminals, where they are stored until released. Unlike neurotransmitters, which are released in response to fast, electrical signals, neuropeptides are often released in response to more sustained stimuli, contributing to their role in longer-term regulation of brain functions and states.
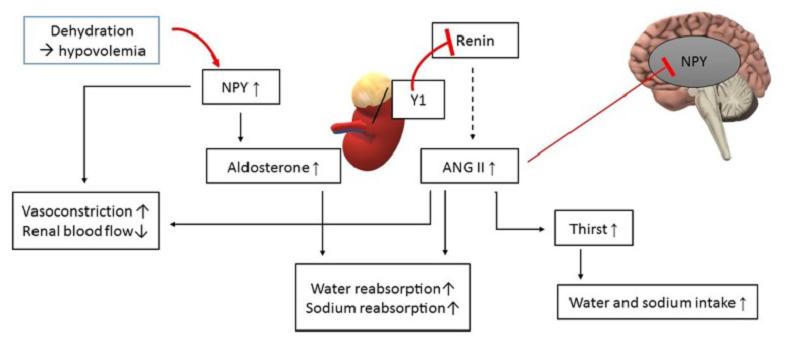
Functions of Neuropeptides in the Brain
Neuropeptides serve a multitude of functions within the brain, playing a pivotal role in various aspects of neural communication and regulation. Their diverse roles range from influencing neurotransmission to affecting various physiological states like mood, learning, and sleep. This section will explore these various functions, highlighting the versatility and importance of neuropeptides in brain function.
Neuropeptides Role in Neurotransmission
Neuropeptides significantly influence neurotransmission in the brain. Unlike classical neurotransmitters that facilitate rapid, short-lived communication between neurons, neuropeptides often modulate this communication over a longer duration. They can enhance or inhibit the effects of neurotransmitters, thereby playing a crucial role in determining the overall output of neural circuits. This modulation is essential in fine-tuning the brain’s response to various stimuli and maintaining neural network stability [2].
Influence of Neuropeptides on Mood and Emotion
One of the most notable roles of neuropeptides is their impact on mood and emotion. Certain neuropeptides are directly involved in regulating emotional responses and mood states. For instance, substances like endorphins are well-known for their role in producing feelings of well-being and pain relief. Dysregulation of neuropeptide systems can be linked to various mood disorders, underscoring their importance in mental health.
Impact of Neuropeptides on Learning and Memory
Neuropeptides also play a crucial role in learning and memory. They are involved in the processes of synaptic plasticity – the ability of synapses to strengthen or weaken over time, which is a fundamental mechanism underlying learning and memory. Neuropeptides can modulate synaptic strength and are involved in the formation and retrieval of memories, making them crucial for cognitive functioning [3].
Neuropeptides Regulation of Sleep and Wakefulness
Lastly, neuropeptides are key regulators of sleep and wakefulness. They are involved in the complex neural networks that govern sleep patterns, including the regulation of rapid eye movement (REM) and non-REM sleep. Certain neuropeptides have been identified to either promote wakefulness or facilitate sleep, playing a critical role in maintaining the balance between these two states and thus ensuring overall health and well-being [4].
Neuropeptides and Brain Health
The impact of neuropeptides extends beyond basic brain functions to play a significant role in overall brain health. Their involvement in cognitive processes and mental health, along with their potential as therapeutic agents, highlights their importance in both the maintenance of brain health and the treatment of brain disorders. This section delves into these aspects, illustrating the critical role neuropeptides play in our brain’s well-being.
Neuropeptides in Cognitive Health and Disorders
Neuropeptides are integral to maintaining cognitive health. They are involved in various cognitive functions, including learning, memory, and decision-making. Imbalances or dysfunctions in neuropeptide systems can lead to cognitive impairments. For example, research has shown links between certain neuropeptide irregularities and neurodegenerative diseases like Alzheimer’s and Parkinson’s. Understanding these connections is crucial for developing strategies to prevent or slow down cognitive decline associated with such disorders.
Neuropeptides Role in Mental Health Conditions
Similarly, neuropeptides play a vital role in mental health. They are involved in regulating emotions, stress responses, and coping mechanisms. Dysregulation of neuropeptide systems can contribute to the development of psychiatric conditions such as depression, anxiety, and schizophrenia. For instance, alterations in the levels of neuropeptides like oxytocin and vasopressin have been associated with mood and anxiety disorders. This knowledge opens up new avenues for the development of neuropeptide-based therapies for these conditions [5].
Potential Therapeutic Applications of Neuropeptides
The therapeutic potential of neuropeptides is an area of growing interest. Given their role in various brain functions and disorders, they present promising targets for drug development. For example, neuropeptide-based treatments are being explored for conditions like depression, chronic pain, and even obesity. The ability to modulate neuropeptide activity offers a novel approach to treating a range of neurological and psychiatric disorders, potentially leading to more effective and targeted therapies.
References
[1] Overview of neuropeptides: awakening the senses?
[2] Neuropeptides and Behaviors: How Small Peptides Regulate Nervous System Function and Behavioral Outputs
[3] Understanding Neuropeptide Transmission in the Brain
[4] The role of neuropeptide somatostatin in the brain and its application in treating neurological disorders
[5] Neuropeptides