Adult neurogenesis refers to the process through which new neurons, or nerve cells, are generated in the adult brain. This process plays a critical role in aspects like learning, memory, and emotional regulation. Hormones, the chemical messengers of our body, have long been known to regulate various physiological processes, including those in our brain. Thyroid hormones, specifically, serve crucial roles in metabolism, growth, and development. But did you know that these hormones also have a nuanced role in the formation of new neurons in the adult brain? Understanding this interplay is vital not just for scientists and clinicians, but also for anyone interested in maintaining optimal cognitive health.
Contents
Introduction to Adult Neurogenesis
Adult neurogenesis may sound like a mouthful, but it’s a term that encapsulates a vital biological process. It refers to the generation of new neurons, or nerve cells, in the adult brain. For many years, it was widely believed that neurons could not be regenerated after reaching adulthood. However, groundbreaking research has revealed that specific regions of the adult brain continue to create new neurons throughout life.
Importance of Adult Neurogenesis for Cognitive Health
Why should you care about adult neurogenesis? Well, it turns out that the formation of new neurons is crucial for a variety of cognitive functions. These include learning new information, forming memories, and even regulating emotions. Research suggests that decreased rates of neurogenesis can lead to cognitive impairments and may contribute to mental health conditions like depression and anxiety.
Role of Hormones in Regulating Neurogenesis
Hormones are biochemical messengers that have a broad range of functions in the body, from regulating metabolism and growth to influencing behavior and immune responses. In the realm of the brain, hormones play a vital role in modulating various neural processes, including neurogenesis. Their influence extends from the embryonic stage and continues throughout life, affecting how our brains develop and function [1].
Introduction to Thyroid Hormones
Among the numerous hormones that our body produces, thyroid hormones occupy a special place. They are primarily known for regulating metabolism and energy use in the body. However, their role extends much further and impacts several other physiological processes, including brain function and development.

Basics of Thyroid Hormones
Understanding what thyroid hormones are, how they are regulated, and what functions they serve is crucial for grasping their role in adult neurogenesis.
Definition and Types of Thyroid Hormones
Thyroid hormones are biochemical substances produced by the thyroid gland, a butterfly-shaped organ located in the front of the neck. The two primary types of thyroid hormones are Triiodothyronine (T3) and Thyroxine (T4).
T3 (Triiodothyronine)
T3 is the more potent and bioactive form of thyroid hormone. It has three iodine atoms and plays a crucial role in regulating metabolism, heart rate, and even mood.
T4 (Thyroxine)
T4, on the other hand, is the more abundant but less potent form of thyroid hormone. It serves mainly as a reservoir that can be converted into T3 when the body needs it. T4 has four iodine atoms and also has a role in metabolism and energy regulation.
Understanding the nuanced differences between T3 and T4 is essential, as each has its unique properties and functions, but both are critical for normal physiological processes [2].
Production and Regulation of Thyroid Hormones
Thyroid hormones are not produced in isolation; rather, their production is tightly regulated by a feedback mechanism involving other hormones and organs. The hypothalamus in the brain releases Thyrotropin-Releasing Hormone (TRH), which then signals the pituitary gland to secrete Thyroid Stimulating Hormone (TSH).
TSH, in turn, stimulates the thyroid gland to produce T3 and T4. The levels of these hormones in the bloodstream provide feedback to the hypothalamus and pituitary, completing a regulatory loop that ensures hormonal balance.
Functions of Thyroid Hormones
Thyroid hormones serve a wide array of functions in the body, extending far beyond mere metabolic regulation. While the majority of people associate thyroid hormones mainly with weight control, their scope is indeed much broader.
Metabolism
The thyroid hormones play a significant role in regulating the metabolic rate, which is the rate at which the body uses energy. Imbalances in thyroid hormone levels can result in metabolic disturbances, manifesting as symptoms like weight gain, fatigue, or excessive sweating.
Growth and Development
Thyroid hormones are essential for normal growth and development, especially during infancy and childhood. They influence the development of bones and the brain, as well as the maturation of other vital organs.
Other Functions
In addition to metabolism and growth, thyroid hormones influence several other physiological processes. These include heart rate regulation, body temperature, and even cognitive function, which brings us back to the topic at hand—adult neurogenesis.
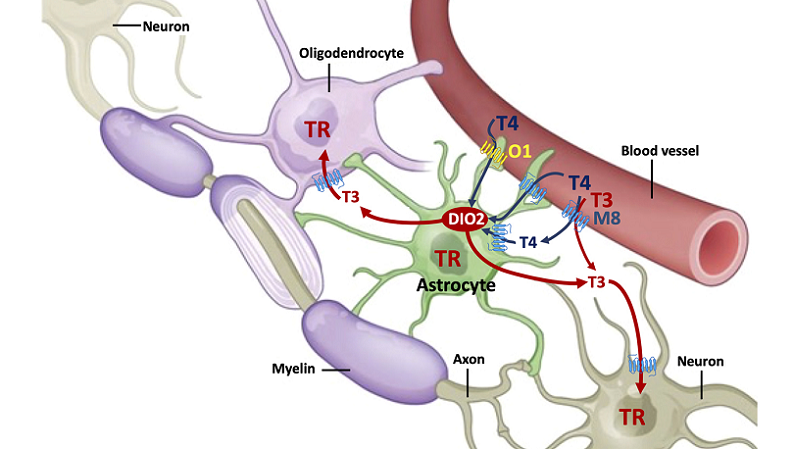
Overview of Adult Neurogenesis
Having explored the fundamentals of thyroid hormones, we’re now well-positioned to delve into the other half of our topic: adult neurogenesis. This process of generating new neurons in the adult brain has implications for everything from learning and memory to emotional well-being.
What Is Adult Neurogenesis?
Adult neurogenesis is a biological phenomenon that involves the formation of new neurons, or nerve cells, within the adult brain. For decades, the scientific consensus was that humans were born with a finite number of neurons that declined over time but could not regenerate. However, groundbreaking research in the late 20th century upended this notion, demonstrating that new neurons could, in fact, be generated in specific regions of the adult brain [3].
Locations of Adult Neurogenesis in the Brain
While neurogenesis happens extensively during embryonic development, its occurrence in the adult brain is limited to a few specific regions. Understanding these locations is key to grasping the impact of thyroid hormones on neurogenesis.
Hippocampus
The hippocampus is the most well-studied site of adult neurogenesis. Located deep within the brain’s medial temporal lobe, this structure is integral to processes such as learning and memory. The formation of new neurons in the hippocampus is thought to be particularly sensitive to various factors, including hormones, stress, and environmental stimuli.
Olfactory Bulbs
The olfactory bulbs, involved in the sense of smell, are another site where adult neurogenesis occurs. While less is known about the functional significance of new neuron formation in this area compared to the hippocampus, research suggests it may have implications for olfactory learning and memory.
Other Regions
While the hippocampus and olfactory bulbs are the most prominent sites, emerging research suggests that adult neurogenesis might occur in other, less-explored regions of the brain as well. However, the functional significance of neurogenesis in these areas is still under investigation.
Functions of Adult Neurogenesis
Now that we understand where adult neurogenesis occurs, it’s crucial to explore why this process is important. It turns out that newly formed neurons have several significant roles.
Learning and Memory
New neurons in the hippocampus are believed to contribute to the formation and storage of memories, as well as to the ability to learn new information. Studies have shown that an increase in neurogenesis can enhance learning capabilities.
Emotional Regulation
Neurogenesis also plays a role in emotional health. The hippocampus is not just a center for memory but is also involved in regulating emotions. New neurons may contribute to emotional resilience and the regulation of stress responses.
Stress Response
New neurons are also thought to play a role in how the brain responds to stress. Reduced levels of neurogenesis have been linked to increased susceptibility to stress and anxiety-like behaviors [4].
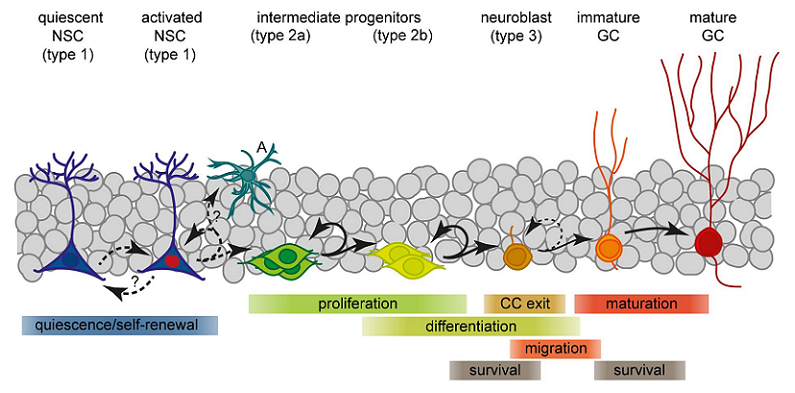
Link Between Thyroid Hormones and Neurogenesis
Having discussed the individual roles of thyroid hormones and adult neurogenesis, we are now primed to explore their intersection. The link between these two biological phenomena has been the subject of fascinating research, and the insights gleaned could have profound implications for cognitive and mental health.
Scientific Evidence
Recent studies have shed light on the profound ways in which thyroid hormones influence adult neurogenesis. This body of research has been instrumental in challenging traditional perspectives and opening up new avenues for understanding brain health.
Experimental Studies
Several experimental studies have shown that thyroid hormone levels can influence the rate of neurogenesis in animal models. For example, when levels of thyroid hormones are artificially elevated, there’s a marked increase in the generation of new neurons, particularly in the hippocampus.
Clinical Observations
In human subjects, clinical studies have also found correlations between thyroid hormone levels and cognitive functions associated with neurogenesis, such as learning and memory. Patients with hypothyroidism (low levels of thyroid hormone) often experience cognitive impairments, which may improve upon thyroid hormone replacement therapy.
Biological Mechanisms
While the scientific evidence is compelling, understanding the ‘how’ is equally important. Several biological mechanisms have been proposed to explain the influence of thyroid hormones on adult neurogenesis.
Gene Expression
One of the primary ways thyroid hormones could influence neurogenesis is through the regulation of gene expression. These hormones act as transcription factors, modifying the expression of genes that are crucial for neural development and function.
Neurotransmitter Regulation
Thyroid hormones also play a role in modulating the levels and activities of neurotransmitters like serotonin and dopamine, which are known to influence mood and could indirectly affect neurogenesis.
Metabolic Effects
Given their significant role in metabolism, thyroid hormones could influence the energy availability in neurons, thereby affecting their survival and integration into neural networks.
Clinical Implications
The link between thyroid hormones and neurogenesis isn’t just academic; it has meaningful clinical implications as well.
Diagnosis and Treatment of Cognitive Disorders
Understanding this relationship could inform the diagnosis and treatment of cognitive and mood disorders. For example, thyroid hormone levels could become a key parameter in the evaluation and treatment of conditions like depression or age-related cognitive decline [5].
Preventative Measures
The regulation of thyroid hormone levels might offer a preventive strategy against cognitive decline in aging or neurodegenerative diseases. Lifestyle changes and medications that stabilize thyroid hormone levels could be beneficial in maintaining cognitive health.
How Thyroid Disorders Can Impact Neurogenesis
The interplay between thyroid hormones and adult neurogenesis extends to clinical scenarios as well. Disorders of the thyroid can exert a significant impact on brain function, which can translate into altered neurogenesis and, consequently, cognitive and emotional changes.
Types of Thyroid Disorders
Thyroid disorders come in various forms, and each has unique consequences for neurogenesis and cognitive health. Here are some of the most common thyroid disorders:
Hypothyroidism
Hypothyroidism is a condition where the thyroid gland is underactive and does not produce enough thyroid hormones. This condition can lead to a sluggish metabolism, fatigue, and cognitive impairments such as memory loss and reduced mental clarity.
Hyperthyroidism
In contrast, hyperthyroidism is characterized by an overactive thyroid gland, resulting in excessive production of thyroid hormones. Symptoms might include anxiety, weight loss, and even cognitive impairments like attention deficit.
Hashimoto’s Thyroiditis
Hashimoto’s is an autoimmune condition where the immune system attacks the thyroid gland, often leading to hypothyroidism over time. The disease can manifest with a variety of symptoms, including cognitive issues.
Impact on Adult Neurogenesis
Thyroid disorders can profoundly affect neurogenesis, and understanding this relationship can offer critical insights into managing cognitive health.
Hypothyroidism and Reduced Neurogenesis
Research has indicated that reduced levels of thyroid hormones, as seen in hypothyroidism, are associated with decreased rates of adult neurogenesis. This could potentially contribute to the cognitive deficits observed in individuals with this condition.
Hyperthyroidism and Excessive Neurogenesis
Conversely, elevated levels of thyroid hormones could lead to increased rates of neurogenesis. While this might sound beneficial, it’s not necessarily the case. Excessive neurogenesis could lead to problems like increased anxiety and reduced emotional stability.
Autoimmune Effects
In autoimmune thyroid disorders like Hashimoto’s, the inflammation and immune response could have additional, direct effects on brain function and neurogenesis, beyond the effects of altered thyroid hormone levels.
Therapeutic Strategies and Recommendations
Given the profound impact of thyroid disorders on neurogenesis and, by extension, cognitive and emotional health, targeted therapeutic strategies are crucial.
Hormone Replacement Therapy
For hypothyroid conditions, hormone replacement therapy can help restore normal thyroid hormone levels, which may improve cognitive function and possibly boost neurogenesis.
Anti-Thyroid Medications
In cases of hyperthyroidism, medications that reduce thyroid hormone production can help bring the system back into balance, potentially normalizing rates of neurogenesis.
Lifestyle Interventions
Lifestyle changes, such as stress management techniques and dietary adjustments, can also have a positive impact on thyroid function and, consequently, neurogenesis.
References
[1] Thyroid hormone regulation of adult hippocampal neurogenesis
[2] Thyroid hormones affect neurogenesis
[3] Thyroid hormone signaling and adult neurogenesis
[4] Perspectives on thyroid hormone action in adult neurogenesis
[5] Dual effects of thyroid hormone on neurons and neurogenesis

