In the quest for enhanced cognitive function and mental clarity, many people have turned to nootropics — substances known for their brain-boosting capabilities. While the efficacy of these “smart drugs” is often the focus of scientific studies and anecdotal experiences, there’s a significant, yet often overlooked, factor that plays a pivotal role in how effective nootropics can be: gut health. The intricate relationship between our gut and our brain — commonly known as the gut-brain axis — is increasingly recognized for its impact on our emotional and cognitive well-being.
Contents
Introduction to Nootropics and the Gut-Brain Axis
When it comes to achieving peak cognitive performance, much attention has been given to nootropics, or “smart drugs,” for their ability to enhance various aspects of mental function. While nootropics have grown in popularity, there’s another crucial player in the cognitive well-being game that doesn’t get nearly as much attention: your gut health. The complex ecosystem of microorganisms in your gut has a surprisingly significant impact on your brain. This gut-brain axis creates a symbiotic relationship that can greatly affect your cognitive performance.
Definition of Nootropics
Before we dive deep into the heart of our subject, let’s get acquainted with what nootropics really are. The term might sound complex, but understanding it is key to grasping the connections we’re about to explore.
Importance of Brain Health and Cognitive Function
You might wonder why the quest for better brain health and improved cognitive function is crucial. To truly comprehend the significance of this issue, we need to discuss the roles cognitive function plays in our daily lives, careers, and overall well-being.
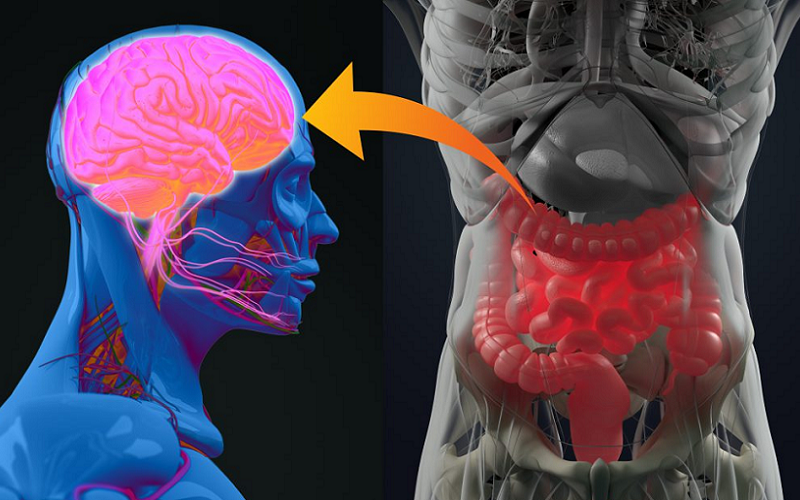
Brief Overview of the Gut-Brain Axis
At first glance, the gut and the brain might seem like two very different entities. However, they are closely connected through a network of neurons, hormones, and other biological mechanisms, forming what is known as the gut-brain axis. Understanding this intricate relationship sets the stage for our exploration of how gut health influences the effectiveness of nootropics.
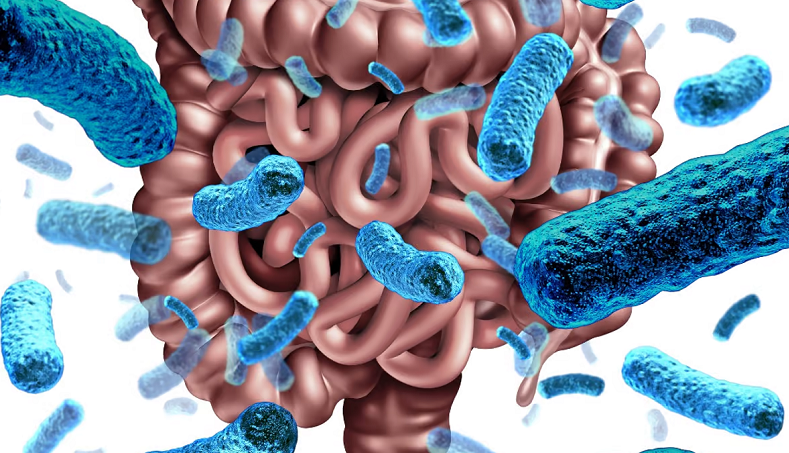
Understanding Gut Health
Understanding the gut isn’t just about knowing what makes your stomach turn or what affects digestion — it’s a gateway into comprehending a complex ecosystem that significantly influences your overall well-being, including your cognitive health.
Importance of the Microbiome
The gut is far more than a digestive tract; it’s home to trillions of microorganisms, including bacteria, viruses, and fungi. This community, often referred to as the gut microbiome, plays a key role in various aspects of our health, from regulating immune responses to synthesizing essential nutrients. Its role is so crucial that some experts refer to the gut microbiome as a “second brain.”
Functions of the Gut
Now that you know how significant the microbiome is, let’s explore the various functions that the gut serves, apart from its role as a microbial habitat.
Digestion and Absorption
The most basic function of the gut is the digestion of food and the absorption of essential nutrients. This process is aided by various enzymes and the gut microbiota, which help break down complex molecules into simpler forms that the body can utilize [1].
Immune System Regulation
Perhaps less commonly known is the role the gut plays in immune regulation. The gut is an active organ in the immune system, and its microbiome interacts with immune cells to help fight off pathogens and maintain overall health.
Implications for Brain Health
Understanding the gut’s role doesn’t stop at digestion and immunity; it extends to how it affects our brain. The gut microbiome produces various neurotransmitters and metabolites that can travel through the bloodstream and directly affect brain function. These substances are part of the complex communication system that links the gut and brain, influencing everything from mood to cognitive performance.
How Poor Gut Health Affects You
Finally, it’s essential to consider the repercussions of poor gut health. An imbalanced microbiome, often termed “dysbiosis,” can lead to a range of issues including digestive disorders, poor immune response, and even cognitive and mood disturbances. Given our focus on nootropics and cognitive function, it’s crucial to understand that poor gut health can be a significant roadblock to achieving the mental clarity and performance you’re seeking [2].
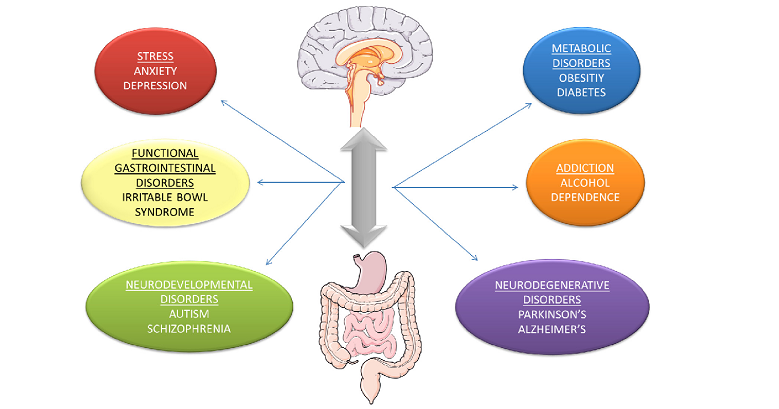
The Gut-Brain Axis: A Two-Way Street
Having examined the importance of gut health, it’s time to examine the fascinating relationship between the gut and the brain — a biological conversation often referred to as the gut-brain axis. The existence of this axis suggests that gut health and brain health are inextricably linked, offering new avenues for optimizing cognition.
Communication Mechanisms
The gut and the brain are not neighbors in the anatomical sense, but they communicate in an astonishingly efficient manner. This communication occurs through various pathways, ensuring a level of coordination that has far-reaching implications for your health and cognitive well-being.
Neural Communication
The most direct pathway between the gut and the brain is neural, primarily through the vagus nerve. This nerve transmits signals in both directions, allowing for real-time communication. For example, think about the feeling of “butterflies in your stomach” when you’re anxious—that’s the gut-brain axis at work.
Hormonal Communication
Apart from neural connections, hormonal pathways also play a vital role in the gut-brain dialogue. The gut produces several hormones that can cross the blood-brain barrier and affect mental states. For instance, serotonin, commonly known as the “happy hormone,” is largely produced in the gut [3].
Immune Communication
Lastly, immune responses also serve as a channel of communication between the gut and brain. Gut health can influence systemic inflammation, which in turn can have neuroinflammatory consequences that affect cognitive function and mood.
Influence of the Gut on the Brain
Understanding these pathways leads us to an intriguing question: How does the gut influence the brain? Well, an unhealthy gut can lead to systemic inflammation, potentially triggering or exacerbating mental health conditions like depression and anxiety. Furthermore, the gut’s microbial composition can also impact your ability to focus, solve problems, and manage stress, underlining its role in cognitive health.
Influence of the Brain on the Gut
The relationship is not one-sided; the brain also has a significant influence on the gut. Stress or anxiety can lead to digestive issues, such as irritable bowel syndrome (IBS), due to the brain signaling the gut to slow down or speed up certain processes. It’s clear that a stressed mind can lead to a stressed gut, creating a cycle that’s detrimental to both mental and physical health.
Interplay Between Nootropics and Gut Health
After gaining a robust understanding of both nootropics and gut health — as well as the crucial pathways connecting the gut and the brain — it’s time to focus on how these elements intersect.
Nootropics’ Impact on Gut Health
It’s important to begin by examining how nootropics themselves can affect the state of your gut. After all, what you put into your body can significantly influence the microbial communities that reside there.
Positive Effects
Some nootropics have been shown to promote gut health by encouraging the growth of beneficial bacteria. For instance, certain natural nootropics like omega-3 fatty acids can have an anti-inflammatory effect, which can be beneficial for gut health [4].
Negative Effects
On the flip side, some synthetic nootropics may disturb your gut microbiota balance, potentially leading to dysbiosis—an imbalance of good and bad bacteria. Dysbiosis can result in poor nutrient absorption and inflammation, which can in turn affect cognitive function negatively.
How Gut Health Affects Nootropic Efficacy
Now let’s explore the flip side of the equation: how your gut health can impact the efficacy of the nootropics you consume.
Absorption and Bioavailability
A healthy gut optimizes the absorption of nutrients, including nootropics. When your gut is functioning well, it’s better equipped to absorb the active ingredients in nootropics, making them more effective. On the contrary, a gut that’s not in optimal condition could reduce the bioavailability of nootropics, essentially making them less effective [5].
Mood and Mental State
Remember the gut-brain axis we discussed? A healthy gut microbiome contributes to better mental health, creating an optimal state of mind for nootropics to do their job effectively. When you’re in a good mental state, the cognitive enhancements from nootropics can be more pronounced, further underlining the importance of a well-functioning gut.
References
[1] The Microbiota-Gut-Brain Axis
[2] The Gut-Brain Axis: How Microbiota and Host Inflammasome Influence Brain Physiology and Pathology
[3] The gut-brain axis: interactions between enteric microbiota, central and enteric nervous systems
[4] The Simplified Guide to the Gut-Brain Axis – How the Gut Talks to the Brain
[5] Probiotics may help boost mood and cognitive function

