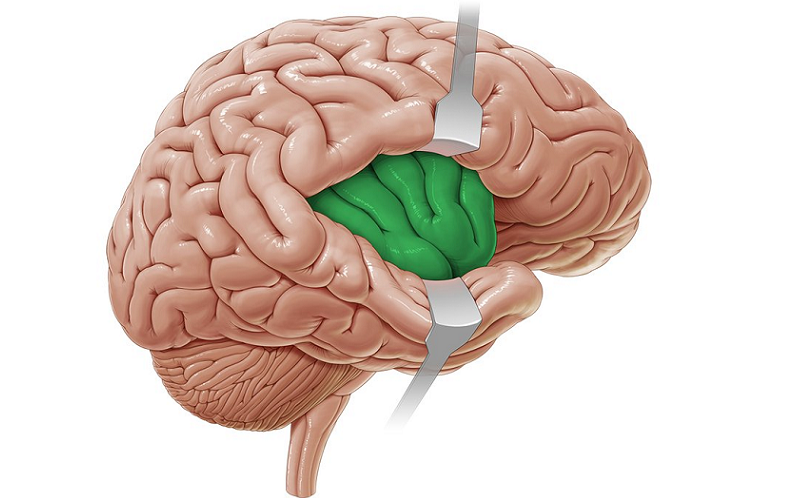
Nestled deep within the intricate tapestry of the human brain lies a fascinating and lesser-known region called the insula. Often referred to as the brain’s “hidden island,” this enigmatic structure has garnered significant interest from researchers in recent years, as it plays a crucial role in various cognitive, emotional, and physiological processes.
Contents
Anatomy of the Insula
To truly understand the insula’s significance in human cognition and behavior, it is essential to first familiarize ourselves with its unique anatomical features.
Location in the Brain
The insula is a small, hidden region of the brain, nestled deep within the lateral sulcus or Sylvian fissure, which separates the frontal and temporal lobes. Due to its concealed position, the insula can be challenging to study and remains less understood compared to other, more accessible brain regions.
The insula’s strategic location between the frontal and temporal lobes allows it to interact with and integrate information from various brain regions, contributing to its diverse range of functions.
Structure
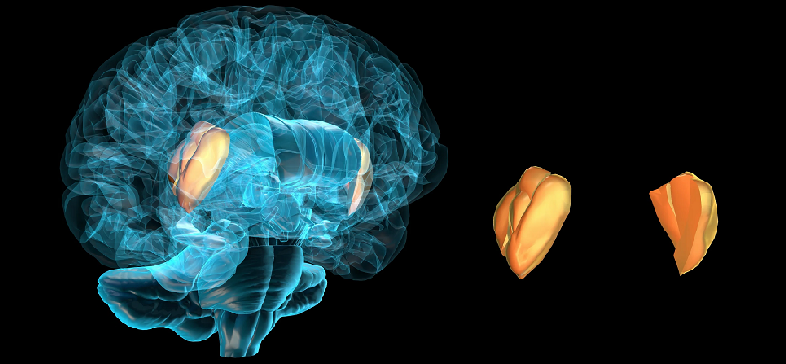
The insula is divided into two main sections, the anterior insula (AI) and the posterior insula (PI). These sections have distinct cytoarchitectonic features and are involved in different functions. The AI is more closely associated with cognitive and emotional processing, while the PI is primarily involved in sensory processing and interoception.
The insula’s unique position and structural organization enable it to form connections with numerous brain areas, including the prefrontal cortex, the limbic system, and the thalamus. These connections facilitate the integration of information from different sensory modalities and cognitive processes, allowing the insula to play a crucial role in various aspects of human experience and behavior.
The Insula’s Many Functions
Given its connections to various brain regions and its unique anatomical position, the insula plays a critical role in a diverse array of functions.
Interoception
Interoception refers to the process through which we perceive and interpret the internal state of our bodies, such as heart rate, breathing, and hunger. The insula is heavily involved in interoceptive processing, allowing us to maintain awareness of our physiological needs and respond accordingly [1].
The insula’s role in interoception is closely tied to emotional processing. By monitoring internal bodily states, the insula contributes to the generation and regulation of emotions, helping us understand and manage our emotional experiences.
Pain Perception
The insula plays a crucial role in the perception of pain. It receives and integrates information about pain signals from various sources, such as nociceptive (pain-related) neurons and the spinal cord, and processes this information to create our subjective experience of pain.
Given its central role in pain perception, the insula is a promising target for pain management interventions [2]. Developing strategies that modulate insular activity could lead to more effective pain relief and improved quality of life for individuals suffering from chronic pain.
Empathy and Social Cognition
The insula is also involved in empathy and social cognition, helping us to comprehend and respond to the emotions and intentions of others. By processing and integrating information about others’ internal states, the insula enables us to empathize with their experiences and make appropriate social decisions [3].
The insula’s role in empathy and social cognition has significant implications for social bonding and decision-making. By facilitating our understanding of others’ emotions and intentions, the insula supports the development of strong social bonds and enables us to navigate complex social environments effectively.
Taste and Appetite Regulation
The insula is a critical component of the gustatory system, which is responsible for the perception of taste [4]. When we consume food or drink, the insula processes information about taste qualities such as sweetness, bitterness, and saltiness, ultimately shaping our subjective experience of flavor.
The insula’s role in taste and appetite regulation has important implications for eating behavior and weight management. Understanding how the insula contributes to our experience of taste and food cravings could inform the development of novel strategies for promoting healthy eating habits and combating obesity.

The Insula and Mental Health
The insula’s diverse range of functions has significant implications for mental health, as disruptions in insular activity have been linked to various psychological disorders.
Anxiety and Depression
Research has demonstrated that the insula plays a critical role in the development and maintenance of mood disorders such as anxiety and depression [5]. Changes in insular activity have been observed in individuals with these conditions, indicating that the insula may be a key contributor to the emotional dysregulation characteristic of mood disorders.
The insula’s involvement in anxiety and depression suggests that it could be a promising target for novel treatments. Interventions aimed at modulating insular activity, such as neurofeedback or noninvasive brain stimulation, could potentially alleviate symptoms of mood disorders and improve emotional regulation in affected individuals.
Addiction
The insula has also been implicated in the neurobiology of addiction. It is thought to contribute to the development and maintenance of addictive behaviors by influencing the processing of reward-related information and modulating craving and withdrawal symptoms [6].
Given its role in addiction, the insula presents a potential target for interventions aimed at treating substance use disorders. Strategies that modulate insular activity could potentially disrupt the cycle of addiction, helping individuals to overcome cravings and maintain abstinence from addictive substances.
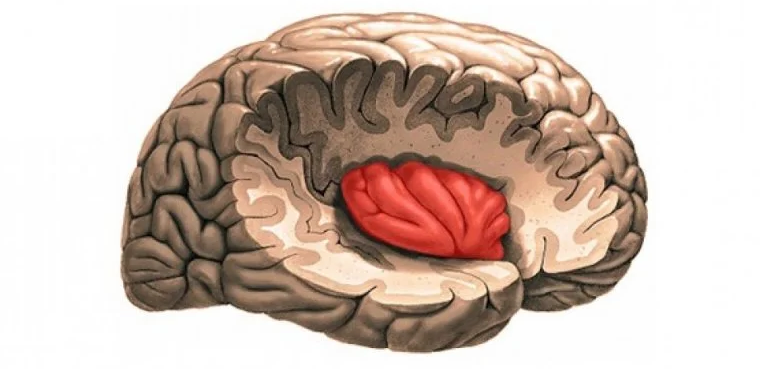
The Insula in Neurological Disorders
In addition to its implications for mental health, the insula has been linked to various neurological disorders.
Epilepsy
The insula has been implicated in the development and propagation of seizures in individuals with epilepsy [7]. Abnormal electrical activity within the insula can contribute to seizure generation, while the insula’s extensive connections to other brain regions facilitate the spread of seizure activity throughout the brain.
Given its role in epilepsy, the insula presents a potential target for the development of novel treatment strategies. Interventions that modulate insular activity, such as deep brain stimulation or targeted drug delivery, could potentially reduce seizure frequency and improve the quality of life for individuals with epilepsy.
Stroke
Strokes affecting the insula can have significant consequences for cognitive and emotional processing [8]. Individuals who have experienced an insular stroke may exhibit deficits in interoceptive awareness, emotional regulation, and social cognition, highlighting the critical role of the insula in these processes.
Given the potential consequences of insular strokes, early detection and treatment are crucial for minimizing long-term deficits and promoting optimal recovery. Rapid intervention, including the administration of clot-busting medications and rehabilitation strategies targeting insular function, can significantly improve outcomes for individuals who have experienced an insular stroke.
Current Research and Future Directions
As our understanding of the insula continues to grow, researchers are employing advanced techniques and exploring new avenues to unravel the full range of the insula’s functions and implications for human health.
The Use of Advanced Neuroimaging Techniques to Study the Insula
Recent advancements in neuroimaging technologies, such as functional magnetic resonance imaging (fMRI), diffusion tensor imaging (DTI), and magnetoencephalography (MEG), have allowed researchers to examine the insula’s structure and function with unprecedented detail [9]. These techniques enable scientists to observe insular activity during various cognitive and emotional tasks, as well as map the insula’s connectivity with other brain regions, providing valuable insights into its role in different processes.
The Potential for Insular-Targeted Therapies in a Range of Conditions
The growing body of knowledge about the insula’s functions has opened up new possibilities for developing targeted therapies to address mental health and neurological disorders. For example, deep brain stimulation, transcranial magnetic stimulation, or pharmacological interventions targeting the insula could potentially help alleviate symptoms of anxiety, depression, addiction, epilepsy, and other conditions. As our understanding of the insula continues to expand, we can expect the development of more innovative and effective treatment strategies in the future.
The Need for Further Research to Uncover the Full Range of the Insula’s Functions
Despite the progress made in understanding the insula’s role in various aspects of human experience and behavior, there is still much to learn about this enigmatic region. Further research is needed to uncover the full range of the insula’s functions, particularly in relation to lesser-known or poorly understood processes.
Additionally, longitudinal and large-scale studies are necessary to fully appreciate the insula’s involvement in the development and progression of various mental health and neurological disorders. By deepening our understanding of the insula, we can pave the way for more effective interventions and improved health outcomes for countless individuals.
References
[1] Mindfulness, Interoception, and the Body: A Contemporary Perspective
[2] The Role of the Insular Cortex in Pain
[3] Empathy and contextual social cognition
[4] Taste Quality Representation in the Human Brain
[5] Tapping into the Default Mode Network (DMN): Unlocking Creativity and Mind-Wandering
[6] The hidden island of addiction: the insula
[7] Identifying the neural network for neuromodulation in epilepsy through connectomics and graphs
[8] The Neuropsychological Impact of Insular Cortex Lesions
[9] Understanding Neuropsychiatric Disorders: Insights from Neuroimaging

