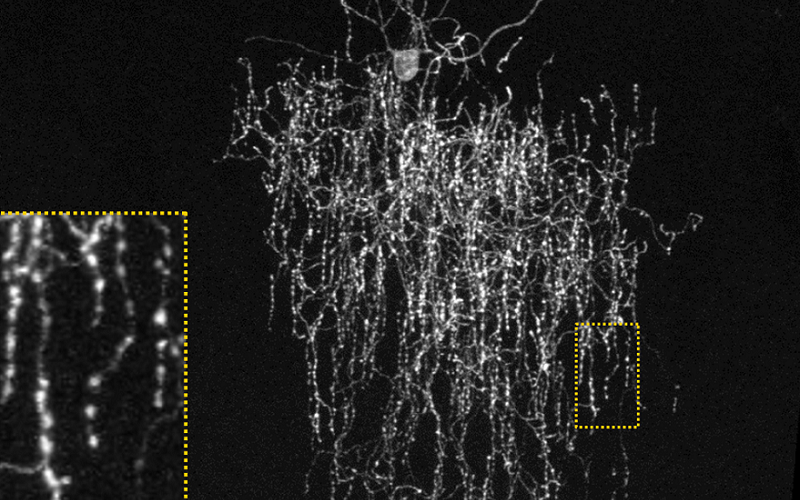
Chandelier Cells are unique inhibitory neurons that play a crucial role in regulating brain activity, impacting everything from our cognitive processes to our overall brain health. Chandelier cells, named for their chandelier-like structure, are a standout in the vast neural landscape of our brains. They act as the brain’s moderators, ensuring that neuronal activity remains balanced and efficient. This balance is key to maintaining cognitive functions and preventing neurological disorders.
Contents
Introduction to Chandelier Cells and Cognitive Health
Chandelier Cells are neurons that are not just fundamental to understanding the complex workings of the brain, but are also pivotal in maintaining our cognitive health and well-being.
Overview of Neurons in the Brain
The human brain, a marvel of biological engineering, is composed of an intricate network of neurons. These neurons are the core building blocks of the nervous system, responsible for transmitting information throughout the brain and body. They come in various types, each with unique functions, but all working in concert to process thoughts, emotions, and actions. Understanding these neurons is key to unraveling the mysteries of brain function and dysfunction.
Introduction to Chandelier Cells
Among the myriad of neuron types, Chandelier Cells stand out due to their unique structure and function. Named for their resemblance to ornate chandeliers, these cells are a type of inhibitory neuron. Unlike other neurons that typically stimulate brain activity, Chandelier Cells play the opposite role. They are essential in controlling and moderating the activity of other neurons, preventing overexcitement and ensuring the brain’s activities remain balanced.
Importance of Chandelier Cells in Cognitive Health
The significance of Chandelier Cells extends far beyond their inhibitory function. They are crucial in maintaining cognitive health, as imbalances in their activity can lead to various neurological disorders. By exploring the role of Chandelier Cells, researchers hope to gain insights into the treatment and prevention of conditions like epilepsy, schizophrenia, and bipolar disorder. Their study not only enriches our understanding of the brain’s inner workings but also opens up new avenues for therapeutic interventions in cognitive health.
Anatomy of Chandelier Cells
The anatomy of chandelier cells is as intricate as it is fascinating, setting them apart from other neurons in the brain. Understanding their structure provides crucial insights into their unique role in the neural network.
Physical Structure and Characteristics of Chandelier Cells
Chandelier cells are easily distinguishable by their distinctive morphology. They possess a set of axonal carriages that resemble the arms of a chandelier, hence their name. These carriages branch out and form connections called synapses with the axon initial segments of other neurons, primarily pyramidal cells. This positioning is strategic, allowing chandelier cells to exert powerful control over the output of these neurons [1].
Comparison of Chandelier Cells with Other Neurons
Unlike most neurons that connect with the dendrites or cell bodies of other neurons, chandelier cells target the axon initial segments. This unique connectivity is significant because it allows them to regulate the firing of other neurons more directly and efficiently. This feature sets them apart from other inhibitory interneurons, such as basket cells, which connect to different parts of the neuron.
Chandelier Cells Location in the Brain
Chandelier cells are found throughout the brain but are particularly abundant in the cerebral cortex, the brain’s outer layer responsible for higher-order functions like thought, perception, and decision-making. Their presence in the cortex underscores their essential role in complex cognitive processes. These cells are not uniformly distributed but instead are strategically positioned in areas where precise regulation of neural activity is most crucial.
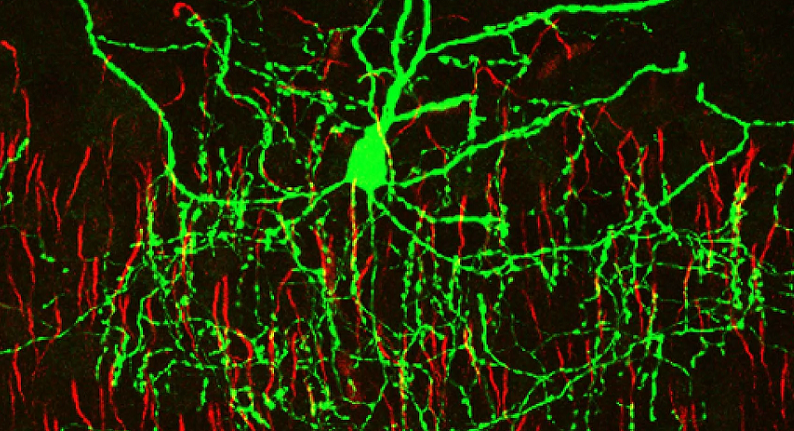
Function of Chandelier Cells
Chandelier cells play a pivotal role in the functioning of the brain. Their unique structure and location within the brain’s neural network enable them to perform critical tasks that regulate and shape our cognitive processes.
Role of Chandelier Cells in Inhibitory Signaling
At the heart of their function, chandelier cells are inhibitory neurons. They release neurotransmitters like GABA (gamma-aminobutyric acid), which binds to receptors on target neurons, typically the excitatory pyramidal cells. This binding action inhibits these cells’ activity, preventing them from firing excessively. By controlling the firing of pyramidal cells, chandelier cells maintain a balance between excitation and inhibition in the brain, crucial for normal cognitive function and preventing neurological disorders [2].
Chandelier Cells Impact on Neural Circuits
Chandelier cells’ influence extends to the broader neural circuits. By inhibiting the activity of pyramidal cells, they can modulate the flow of information within these circuits, impacting everything from sensory processing to decision-making. This modulation is vital in complex cognitive tasks, such as focusing attention, processing information, and regulating emotional responses.
Chandelier Cells Connection with Cognitive Processes
The inhibitory control exerted by chandelier cells is also fundamental in shaping various cognitive processes. For instance, their ability to regulate the timing and pattern of neural circuit activity plays a role in learning and memory. Additionally, the precise control they provide helps maintain the delicate balance necessary for normal brain function, preventing the neural hyperactivity that can lead to disorders like epilepsy. Understanding the function of chandelier cells thus offers valuable insights into the fundamental mechanisms of cognitive health and disease [3].
Chandelier Cells and Brain Disorders
The study of chandelier cells is not just academically intriguing; it has profound implications for understanding and potentially treating various brain disorders. Their unique role in the brain’s circuitry makes them a key focus in the exploration of neurological and psychiatric conditions.
Chandelier Cells Link to Neurological Conditions
Research has shown that abnormalities in chandelier cells are associated with several neurological conditions. For instance, in epilepsy, the disrupted function of these cells can lead to an imbalance between excitatory and inhibitory signals, resulting in seizures. Similarly, alterations in the structure and function of chandelier cells have been observed in schizophrenia and bipolar disorder. These findings suggest that the dysfunction of chandelier cells might contribute to the pathophysiology of these complex disorders.
Research on Chandelier Cells and Mental Health
Beyond neurological conditions, chandelier cells are also being studied for their potential role in mental health disorders. The fine-tuning they provide in neural circuits is crucial for cognitive and emotional processing. Disruptions in their functioning could contribute to the symptoms seen in conditions like anxiety, depression, and other mood disorders. Ongoing research is aiming to unravel these connections further, potentially opening new avenues for therapeutic interventions.
Potential Therapeutic Implications of Chandelier Cells
The growing understanding of chandelier cells’ role in brain health suggests they could be a target for novel therapeutic strategies. By modulating their activity, it might be possible to correct the imbalances in neural circuits associated with various disorders. This approach could lead to the development of new medications or neuromodulation techniques aimed specifically at chandelier cells, offering more effective and targeted treatments for a range of neurological and psychiatric conditions. As research progresses, the potential of chandelier cells in therapeutic applications continues to be a promising and exciting field of study [4].
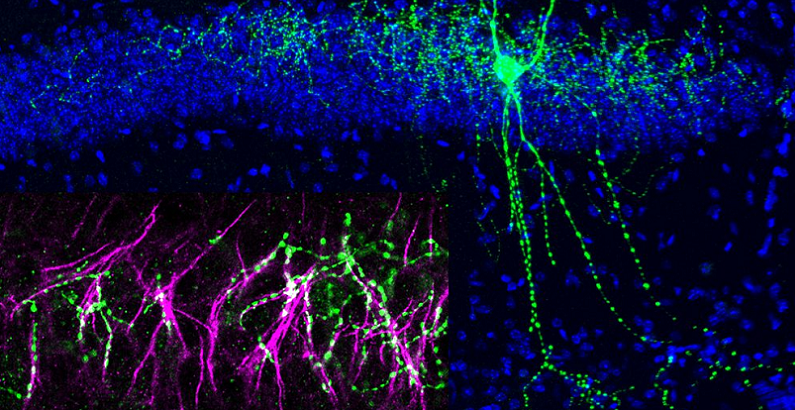
Chandelier Cells in Everyday Life
While chandelier cells may seem like a topic reserved for neuroscientists, their impact extends into our daily lives. Understanding how these cells influence brain function can offer insights into our everyday behavior, mental health, and overall well-being.
Everyday Effects of Chandelier Cells on Brain Function
The role of chandelier cells in regulating brain activity has a direct impact on our daily cognitive functions. These cells help maintain a balance between excitement and inhibition in the brain, essential for tasks like focusing attention, processing information, and making decisions. For instance, when you’re learning a new skill, chandelier cells help modulate the neural circuits involved, ensuring that the learning process is efficient and effective. Similarly, in social interactions, they contribute to the regulation of emotional responses, helping us navigate complex social dynamics.
Tips for Promoting Healthy Chandelier Cell Activity
Maintaining the health of chandelier cells, and by extension our brain health, can be influenced by our lifestyle choices. Activities that stimulate the brain, like learning new skills, engaging in challenging cognitive tasks, and even regular physical exercise, can promote healthy brain function and potentially support the health of chandelier cells. Additionally, adequate sleep and a balanced diet are crucial, as they contribute to the overall health of the brain’s neural networks [5].
Lifestyle and Its Impact on Cognitive Health
The connection between lifestyle and cognitive health is a vital aspect of understanding the importance of chandelier cells. Stress, for instance, can negatively impact the function of inhibitory neurons, including chandelier cells, potentially leading to imbalances in brain activity. On the other hand, practices like mindfulness and relaxation techniques can help in maintaining a healthy balance in brain activity. Recognizing the importance of these lifestyle factors in supporting the function of chandelier cells can guide us in making choices that promote cognitive health and resilience.
References
[1] Chandelier Cells in Functional and Dysfunctional Neural Circuits
[2] How chandelier cells light up the brain
[3] The chandelier cell, form and function
[4] Chandelier cells shine a light on the formation of GABAergic synapses
[5] Chandelier cell anatomy and function reveal a variably distributed but common signal

