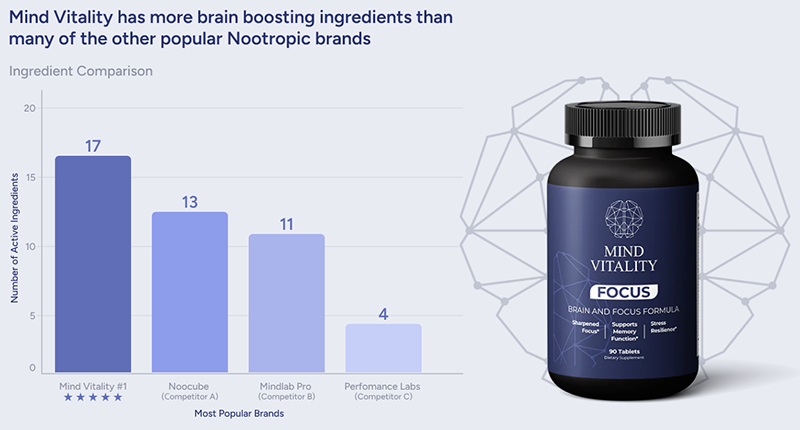
The Adam’s Apple, a prominent feature of the human neck, has long fascinated observers and sparked a myriad of myths and tales. Many people are familiar with its anatomical significance in voice modulation, especially during puberty. But can this seemingly simple cartilage structure impact our thought processes? In an age where nootropics and brain-boosting solutions are all the rage, some have begun to question whether the Adam’s Apple has a hidden role in our cognitive health.
Contents
- Anatomy and Physiology of the Adam’s Apple
- Nootropics: A Brief Overview
- The Mythical Connection Between the Adam’s Apple and Cognition
- Scientific Evidence of an Adam’s Apple and Cognition Connection: Separating Fact from Fiction
- References
Anatomy and Physiology of the Adam’s Apple
The Adam’s Apple, beyond being a physical feature, serves an essential role in our anatomy and physiology. Whether you notice a pronounced bump or a more subdued curve, understanding its structure and purpose can help dispel some of the myths related to its cognitive implications.
Composition and Location of the Adam’s Apple
Situated in the front of the neck, the Adam’s Apple is part of the larynx, or voice box. Its prominence is due to the thyroid cartilage, a shield-like structure that protects the vocal cords. The size and visibility of the Adam’s Apple vary among individuals, influenced by factors such as age, genetics, and hormonal levels.
Primary Functions of the Adam’s Apple
The Adam’s Apple isn’t just for show. It has specific tasks that aid in daily physiological processes.
Vocal Modulation
The larynx, where the Adam’s Apple is located, houses the vocal cords. As we mature, especially during puberty, the thyroid cartilage grows, leading to a change in voice depth and pitch. This is most noticeable in males, as their voices tend to drop, but it’s a process that occurs in all genders to varying degrees.
Protection of the Windpipe
The Adam’s Apple, given its cartilaginous structure, serves as a protective barrier for the windpipe. It ensures that the trachea, responsible for channelling air to the lungs, remains unobstructed and safe from potential harm [1].
Adam’s Apple Differences Between Genders
You might have observed that the Adam’s Apple appears more pronounced in men than in women. This difference isn’t just a matter of casual observation but rooted in our biology.
During puberty, the surge of testosterone in males results in the enlargement of the larynx, making the Adam’s Apple more prominent. On the other hand, females, influenced by estrogen, have a smaller larynx, which usually results in a less noticeable Adam’s Apple and a higher-pitched voice. However, it’s essential to remember that there’s a wide range of natural variation. Some women may have a more prominent Adam’s Apple, and some men might have one that’s less noticeable. Genetics, individual hormonal levels, and other factors play a part in these variations.
Nootropics: A Brief Overview
In our quest to optimize brain function and improve cognitive abilities, the mention of nootropics is inevitable. These “smart drugs” have gained significant attention in recent years. But what exactly are they, and how do they influence our cognitive function? Let’s break it down to understand the world of nootropics better and how it relates to our broader discussion about the Adam’s Apple.
Definition and Categories of Nootropics
Nootropics, often referred to as “cognitive enhancers” or “smart drugs,” are compounds that claim to improve cognitive functions, particularly memory, creativity, and motivation, in individuals with otherwise normal brain function. They come in various forms.
Synthetic Compounds
These include drugs like Modafinil and Racetams, which are often prescribed for medical conditions but are sometimes used off-label for cognitive enhancement [2].
Natural Supplements
This category includes compounds derived from natural sources, such as Ginkgo Biloba, Bacopa Monnieri, and Lion’s Mane mushroom. They often boast a long history of traditional use and are widely available as over-the-counter supplements.
Nutraceuticals
A blend of “nutrition” and “pharmaceuticals”, these are food-derived compounds that might offer cognitive benefits, such as Omega-3 fatty acids and certain vitamins.
How Nootropics Influence Cognitive Function
Nootropics act on the brain in various ways, depending on their mechanism of action. Some might improve blood flow to the brain, while others may modulate neurotransmitters, the chemicals responsible for transmitting signals between nerve cells.
Neurotransmitter Modulation
Nootropics work by influencing the levels or actions of neurotransmitters like dopamine, serotonin, and acetylcholine. By modulating these neurotransmitters, nootropics can potentially affect mood, memory, and focus.
Neuroprotection
Some nootropics claim to protect brain cells from damage, which could, in theory, preserve cognitive functions as we age.
Brain Plasticity
Certain nootropics may promote neuroplasticity—the brain’s ability to reorganize itself by forming new neural connections. This could be beneficial for learning and memory [3].
The Ongoing Quest for Understanding Brain Optimization
While the allure of nootropics is undeniable, it’s essential to approach them with a dose of skepticism. The field of brain optimization is still in its infancy. Although some nootropics have shown promising results in preliminary studies, comprehensive research is often lacking. Potential side effects, drug interactions, and long-term implications are areas that require further exploration.
The Mythical Connection Between the Adam’s Apple and Cognition
Throughout history, the human body has been a subject of curiosity, mystery, and awe. The Adam’s Apple, given its visible and distinct nature, has not been spared from this fascination. Over time, numerous tales, myths, and theories have sprouted around it — some harmless, others misleading.
Historical Beliefs and Myths About the Adam’s Apple
The lore surrounding the Adam’s Apple is as old as human civilization itself. These tales often intertwine with cultural and medical beliefs, offering insights into how ancient societies perceived this anatomical feature.
Cultural and Religious Interpretations
One of the most enduring tales comes from the biblical story of Adam and Eve. According to this interpretation, the bump on Adam’s throat formed when he swallowed a forbidden fruit in the Garden of Eden. While this narrative is symbolic, it has influenced the name “Adam’s Apple” and the way many perceive this feature [4].
Early Medical Beliefs
Ancient physicians and healers, working with a limited understanding of human anatomy, often ascribed various roles to the Adam’s Apple. In some cultures, it was believed to influence a person’s truthfulness, while in others, it was seen as a determinant of one’s vocal abilities or even their life force.
Modern-Day Misconceptions and Theories Regarding the Adam’s Apple
While we might assume that modern science has dispelled all myths, some misconceptions and unfounded theories persist, especially in the age of internet and pop culture.
Pseudoscience and Its Influence
With the rise of alternative medicine and the spread of misinformation online, some have started to link the Adam’s Apple to cognitive abilities. Theories, devoid of scientific backing, claim that its size or prominence might indicate intelligence or particular thought patterns.
Internet and Pop Culture References
Memes, social media challenges, and even TV shows occasionally make light-hearted or misinformed references to the Adam’s Apple. For instance, a character with a prominent Adam’s Apple might be portrayed as more intelligent or cunning, reinforcing baseless associations in the public’s mind.

Scientific Evidence of an Adam’s Apple and Cognition Connection: Separating Fact from Fiction
As with many myths and misconceptions that surround human anatomy, it’s crucial to turn to science to discern reality from fiction. When it comes to the Adam’s Apple and its purported connection to cognitive processes, rigorous scientific research provides invaluable insights.
Current Research on the Adam’s Apple’s Impact on Cognition
To date, no reputable scientific studies have directly linked the size, prominence, or any other characteristic of the Adam’s Apple to cognitive abilities. Most research concerning the larynx and the Adam’s Apple revolves around its primary functions: voice production and the protection of the trachea.
Cognitive Implications of Voice Modulation
While the Adam’s Apple plays a role in voice modulation, it doesn’t have a direct impact on cognition. Some studies suggest that the tone and pitch of one’s voice might influence perception in social contexts (e.g., perceived trustworthiness or leadership capabilities), but this is a matter of social psychology rather than cognitive enhancement [5].
No Direct Neural Connections
The Adam’s Apple and the larynx don’t have direct neural pathways connecting them to parts of the brain responsible for higher-order thinking, memory, or other cognitive functions. Thus, the anatomical framework doesn’t support claims of a direct influence.
Role of the Thyroid and Cognitive Function
While the Adam’s Apple itself doesn’t influence cognition, it’s worth noting its proximity to the thyroid gland, an organ that does play a role in brain function.
Thyroid’s Proximity to the Adam’s Apple
Located just below the Adam’s Apple, the thyroid gland produces hormones that regulate various bodily functions, including metabolism, energy production, and temperature regulation.
Impact of Thyroid Health on Brain Function
Thyroid hormones are essential for brain development in infancy and childhood. In adults, an imbalance in thyroid hormones—be it hyperthyroidism or hypothyroidism—can impact mood, memory, and concentration. However, these cognitive effects are related to hormonal imbalances and not the structure or function of the Adam’s Apple.
Review of Studies on Voice Modulation and Cognitive Processes
Several studies have explored the impact of voice modulation on cognition, but not in the way one might think.
Perception and Cognition
Research shows that the pitch, tone, and modulation of a voice can influence a listener’s perception and judgments. For instance, deeper voices in males might be associated with authority in certain cultures. However, these are cognitive biases in the listener and not a reflection of the speaker’s cognitive abilities.
Voice and Emotion
The voice can convey emotional states, and our cognitive processing of these emotional cues is an area of active research. However, this is more about emotional intelligence and empathy than direct cognitive enhancement related to the Adam’s Apple.
References
[1] Anatomy, Head and Neck: Adam’s Apple
[2] Adam’s apple
[3] All About The Adam’s Apple
[4] Adam’s Apple
[5] What’s the Purpose of an Adam’s Apple?