
The Cingulum Bundle is a brain structure that serves as an intricate neural pathway that plays a crucial role in how we process emotions and form memories, acting as a bridge in our cognitive landscape. Understanding the Cingulum Bundle opens doors to comprehending how our brains handle the intricate dance between feeling and remembering. From its location and structure to its pivotal role in cognitive and emotional stability, here we navigate the complex interplay of this fascinating brain region.
Contents
Introduction to the Cingulum Bundle
The Cingulum Bundle is one of the brain’s most intriguing components. This neural pathway, while not as widely recognized as other brain structures, plays a fundamental role in the intricate workings of our cognitive and emotional processes.
Definition of the Cingulum Bundle
The Cingulum Bundle is a key part of the brain’s limbic system. It is a collection of white matter fibers situated deep within the brain, running longitudinally along the cingulate gyrus. This structure acts as a crucial communication pathway, linking various parts of the brain involved in emotional regulation and cognitive processes. It is not just a mere physical structure but a conduit through which our brain orchestrates complex emotional and memory-related functions.
Overview of the Cingulum Bundle Role in Brain Function
The role of the Cingulum Bundle in brain function is multifaceted. It is primarily involved in connecting the frontal lobes, which are responsible for higher cognitive functions, with the limbic system, the center of our emotional processing. This connection is essential for integrating cognitive and emotional information, thus playing a vital role in how we interpret and respond to the world around us. The Cingulum Bundle’s impact on brain function extends to various domains including attention, spatial orientation, memory, and emotional reactions.
Importance of the Cingulum Bundle in Emotions and Memory
Understanding the Cingulum Bundle is crucial in comprehending how emotions and memory intertwine in the human brain. It facilitates the interplay between our immediate emotional responses and the long-term formation of memories. This relationship is key in understanding various psychological conditions and neurodegenerative diseases. Disruptions or abnormalities in the Cingulum Bundle can lead to significant emotional and cognitive impairments, highlighting its importance in both brain health and disease [1].
Anatomy of the Cingulum Bundle
Diving into the anatomy of the Cingulum Bundle offers a fascinating glimpse into the brain’s internal architecture. Understanding its anatomy is key to appreciating its complex roles in our cognitive and emotional functions.
Location of the Cingulum Bundle in the Brain
The Cingulum Bundle is strategically positioned within the brain, running longitudinally around the corpus callosum, the main fiber tract connecting the brain’s two hemispheres. It’s nestled within the cingulate gyrus, part of the limbic system often associated with emotion formation and processing, and behavioral outcomes. This placement is significant as it allows the Cingulum Bundle to act as a bridge, linking the frontal lobes—responsible for higher cognitive functions—with the deeper parts of the brain involved in emotional and memory processing.
Structural Components of the Cingulum Bundle
Structurally, the Cingulum Bundle is comprised of a dense network of white matter fibers. These fibers are essentially axons, or long projections of nerve cells, that facilitate communication between different brain regions. The white matter attribute of the Cingulum Bundle indicates its role in rapid communication, necessary for efficient processing of complex cognitive and emotional information. The bundle varies in thickness and fiber composition along its length, reflecting the diversity of its functional connections [2].
Connectivity of the Cingulum Bundle to Other Brain Regions
The connectivity of the Cingulum Bundle is crucial for its function. It establishes connections with a variety of brain regions, including the frontal lobes, parahippocampal gyrus, and the entorhinal cortex. These connections are not just simple links but are involved in a myriad of functions such as decision-making, emotional responses, spatial orientation, and memory formation. By connecting these diverse areas, the Cingulum Bundle plays a pivotal role in ensuring that emotional and cognitive information is processed and integrated effectively.

The Cingulum Bundle and Emotions
The intricate relationship between the Cingulum Bundle and our emotional world is a fascinating area of study in neuroscience.
Role of the Cingulum Bundle in Emotional Processing
The Cingulum Bundle plays a pivotal role in emotional processing, acting as a conduit for emotional signals between different brain regions. It is particularly influential in how we process and respond to emotional stimuli. This includes the modulation of emotional intensity, the interpretation of emotional cues, and the regulation of emotional responses. The Cingulum Bundle’s interactions with areas like the amygdala, known for its role in fear and pleasure responses, and the prefrontal cortex, a key player in emotional regulation, are crucial in maintaining emotional balance.
Influence of the Cingulum Bundle on Mood and Emotional Stability
The health and functionality of the Cingulum Bundle are closely linked to mood and emotional stability. Disruptions or abnormalities in the Cingulum Bundle can lead to mood disorders such as depression and anxiety. It is believed that changes in the structural integrity or functional connectivity of the Cingulum Bundle can alter emotional processing, leading to an increased susceptibility to mood disturbances. Moreover, the Cingulum Bundle’s role in stress response regulation further underscores its importance in maintaining emotional well-being [3].
Case Studies and Research Findings Involving the Cingulum Bundle
Numerous studies and clinical observations have underscored the importance of the Cingulum Bundle in emotional processing. For instance, imaging studies have shown altered Cingulum Bundle activity in individuals with mood disorders compared to healthy controls.
Other research has focused on how changes in the Cingulum Bundle due to injury, disease, or developmental issues correlate with emotional processing difficulties. These findings collectively highlight the Cingulum Bundle’s critical role in our emotional lives and its potential as a target for therapeutic interventions in emotional disorders.
The Cingulum Bundle and Memory
The role of the Cingulum Bundle extends beyond emotional processing to encompass a critical aspect of our cognitive function: memory.
Impact of the Cingulum Bundle on Memory Formation
The Cingulum Bundle is integral to the process of memory formation. It interacts closely with the hippocampus, a key region involved in the formation of new memories. This interaction facilitates the consolidation of experiences into long-term memory, a process crucial for learning and cognition. The Cingulum Bundle’s role in attention and executive function also contributes to effective memory encoding, as these cognitive processes are essential for selecting and organizing the information to be remembered [4].
Contribution of the Cingulum Bundle to Memory Retrieval
Memory retrieval, the process of recalling stored information, is another area where the Cingulum Bundle plays a significant role. Its connections with various cortical regions enable the integration of memories into coherent narratives, essential for recall.
The Cingulum Bundle’s involvement in spatial memory is particularly notable, as it helps in navigating and remembering spatial environments. This aspect of memory is crucial for everyday tasks, such as finding one’s way in a familiar city or recalling the location of objects.
Connection of the Cingulum Bundle with Memory Disorders
The Cingulum Bundle’s significance in memory processes is further highlighted when considering memory disorders. Changes in the structural integrity or connectivity of the Cingulum Bundle have been associated with memory impairments in various conditions, including Alzheimer’s disease, traumatic brain injury, and other neurodegenerative disorders.
Research has shown that disruptions in the Cingulum Bundle can lead to difficulties in both forming new memories and retrieving existing ones. These insights underline the potential of targeting the Cingulum Bundle in therapeutic strategies for memory-related disorders.
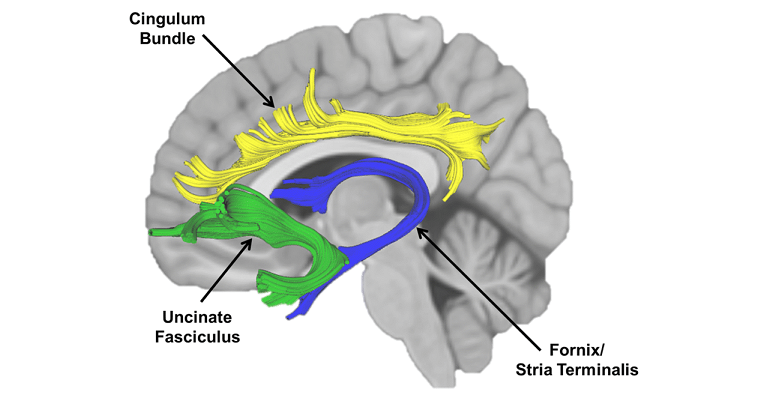
Disorders Associated with the Cingulum Bundle
The Cingulum Bundle’s role in the brain is so central that its dysfunction can lead to a variety of cognitive and emotional disorders. This section examines the range of disorders associated with abnormalities in the Cingulum Bundle, highlighting the spectrum of cognitive impairments, emotional and behavioral disorders, and the involvement in neurodegenerative diseases.
Cognitive Impairments Associated with the Cingulum Bundle
Disruptions in the Cingulum Bundle can lead to significant cognitive impairments. These include difficulties with attention, executive function, problem-solving, and memory. Such impairments are often observed in conditions like traumatic brain injury (TBI) and cerebral palsy, where the Cingulum Bundle may be damaged or develop abnormally. Additionally, cognitive deficits in schizophrenia and other psychiatric disorders have also been linked to alterations in the Cingulum Bundle, suggesting its crucial role in various aspects of cognitive functioning [5].
Emotional and Behavioral Disorders Involving the Cingulum Bundle
The Cingulum Bundle’s involvement in emotional regulation means that its dysfunction can manifest as various emotional and behavioral disorders. This includes conditions such as depression, anxiety disorders, and bipolar disorder. Alterations in the structure or function of the Cingulum Bundle in these disorders can lead to dysregulated emotional responses, mood instability, and impaired stress coping mechanisms. The study of the Cingulum Bundle in relation to these disorders offers insights into potential new therapeutic approaches targeting this brain pathway.
Neurodegenerative Diseases Associated with the Cingulum Bundle
Neurodegenerative diseases, such as Alzheimer’s disease and other forms of dementia, often involve changes in the Cingulum Bundle. These changes can include atrophy, loss of integrity, and disrupted connectivity. Such alterations are thought to contribute to the memory deficits, disorientation, and emotional changes characteristic of these diseases. The Cingulum Bundle’s involvement in neurodegenerative diseases underscores its importance in maintaining cognitive and emotional health throughout the lifespan.
The range of disorders associated with the Cingulum Bundle underscores its critical role in brain function. From cognitive impairments to emotional and behavioral disorders, and involvement in neurodegenerative diseases, the Cingulum Bundle’s health is paramount for overall brain wellness.
References
[1] The cingulum bundle: Anatomy, function, and dysfunction
[2] Organisation of cingulum bundle fibres
[3] Segmentation of the Cingulum Bundle in the Human Brain
[4] What is the Cingulum Bundle?
[5] The cingulate cortex and limbic systems for emotion, action, and memory

