
Deep within the intricate labyrinth of the human brain lies a cluster of neurons, often overshadowed by its more renowned counterparts, yet holding profound significance in our understanding of pleasure, reward, and learning. Welcome to the world of the septal nuclei, a realm where ancient neurological inquiries meet modern-day revelations. Here we go on a journey through time and neuroscience, unraveling the mysteries of these enigmatic structures. From their profound influence on emotions to their potential implications for nootropics and cognitive enhancement, the septal nuclei are a testament to the boundless wonders of the human mind.
Contents
- Historical Context of the Septal Nuclei
- Anatomy of the Septal Nuclei
- Septal Nuclei Role in Pleasure and Reward
- Septal Nuclei and Learning and Memory Enhancement
- The Septal Nuclei and Mental Health
- Nootropics and the Septal Nuclei
- References
Historical Context of the Septal Nuclei
Peeling back the pages of neuroscience history, the septal nuclei emerge as a focal point of curiosity and exploration. Their story is a tapestry woven with pioneering experiments, paradigm shifts, and a constant quest for understanding the brain’s intricate symphony of emotions and behavior.
Early Discoveries and Research on Septal Nuclei
The story of the septal nuclei began in the early 20th century when anatomists first identified these distinct clusters of neurons situated near the brain’s midline. Initial research was primarily focused on mapping their anatomical connections, and the septal nuclei were found to have intricate links to regions like the hypothalamus and the hippocampus.
In the 1950s, a wave of interest was ignited when researchers began using electrical stimulation techniques to explore the functional implications of various brain regions. Notably, James Olds and Peter Milner conducted experiments where they placed electrodes in the septal area of rats. When these rats were given the ability to self-stimulate this region by pressing a lever, they did so compulsively, sometimes neglecting basic needs like food and water. This groundbreaking discovery suggested that the septal nuclei had a direct role in mediating pleasure and reward.
Evolution of Understanding of Septal Nuclei in Neuroscience
The latter half of the 20th century saw the blossoming of technologies like functional magnetic resonance imaging (fMRI) and positron emission tomography (PET) scans. These allowed neuroscientists to delve deeper into the mysteries of the septal nuclei without resorting to invasive procedures.
As the tools became more refined, the understanding of the septal nuclei expanded. No longer were they just the “pleasure centers” of the brain. They were understood as hubs of connectivity, playing crucial roles in emotional regulation, learning, and memory.
One influential study in the 1980s highlighted the septal nuclei’s role in modulating aggressive behavior. When lesions were made in this region in animal models, there was a marked increase in aggression, suggesting that the septal nuclei might serve as a sort of “brake” on aggressive impulses.
By the turn of the millennium, a more nuanced understanding of the septal nuclei had emerged, considering not just their function in isolation, but how they interacted within the broader network of the brain. The “pleasure centers” of yesteryears were now seen as critical nodes in a vast, interconnected web of emotion, cognition, and behavior [1].
Anatomy of the Septal Nuclei
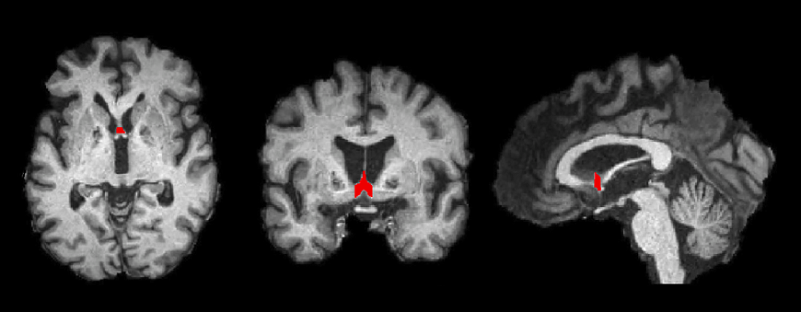
Diving deep into the structural intricacies of the brain, we find that the septal nuclei aren’t merely significant for their function but also for their complex anatomical configuration. Their location and connections within the brain paint a vivid picture of their roles and potential influence on various cognitive and emotional processes.
Physical Location of Septal Nuclei within the Brain
Nestled near the brain’s midline, the septal nuclei can be found at the base of the cerebral hemispheres. They lie anterior to the thalamus and just beneath the rostrum of the corpus callosum. To visualize their placement, imagine a central hub from which numerous neuronal pathways radiate, connecting various brain regions. This strategic position gives the septal nuclei a unique advantage in influencing a wide range of neural activities.
Septal Nuclei Neuronal Connections and Networks
The septal nuclei are a veritable crossroads of neural connections. These intricate networks are pivotal to understanding their multifaceted roles in the brain.
Hippocampal Connections
One of the most prominent connections is with the hippocampus, a region crucial for memory formation. The two-way communication between the septal nuclei and the hippocampus plays a key role in modulating and fine-tuning memory processes.
Limbic System Linkage
The septal nuclei also form a part of the limbic system, a collection of brain structures responsible for emotions, motivation, and certain aspects of memory. Through this system, the septal nuclei interact with other significant regions like the amygdala and the hypothalamus.
Connections with Basal Ganglia and Brainstem
Further expanding their influence, the septal nuclei also have connections to the basal ganglia, which plays a role in movement and reward, and to the brainstem, a region fundamental for many of our vital functions.
Septal Nuclei Interactions with Other Brain Regions
Beyond their structural connections, the septal nuclei maintain a dynamic relationship with numerous other brain areas. For instance, the septal nuclei can influence the release of neurotransmitters in distant regions, effectively modulating their activity. This long-range influence underscores the septal nuclei’s role as not just anatomical structures but as pivotal regulators of brain function.
In the intricate ballet of neural activity, the septal nuclei emerge as a masterful conductor, orchestrating harmonies between disparate brain regions. Whether fostering the gentle melodies of memory or the powerful crescendos of emotion, their anatomical structure and connections are central to their influential role in the cerebral symphony [2].
Septal Nuclei Role in Pleasure and Reward
The realm of pleasure and reward is a fundamental aspect of human existence. These sensations drive many of our actions, from the basic pursuit of food to the complex intricacies of human relationships and achievements. At the heart of these experiences, orchestrating the symphony of satisfaction and motivation, lie the septal nuclei. Their involvement in these processes is both profound and captivating, revealing the depth of their significance in our lives.
The Septal Nuclei as a Pleasure Center
The term “pleasure center” evokes images of immediate gratification, euphoria, and an innate drive to seek out enjoyable experiences. The septal nuclei, with their deep-rooted connections in this arena, play an instrumental role in shaping these sensations.
Historical Experiments
As touched upon earlier, the landmark experiments by James Olds and Peter Milner in the 1950s used electrical stimulation to illuminate the septal nuclei’s role in pleasure. Rats, when given the opportunity, repeatedly stimulated their septal area, often to the exclusion of other essential activities. This compelling behavior demonstrated the septal nuclei’s powerful pull in the domain of pleasure.
Contemporary Findings
With advancements in neuroimaging techniques, our understanding of the septal nuclei’s role in pleasure has grown more nuanced. Modern studies have shown that they not only induce immediate sensations of pleasure but also modulate how we perceive and value rewards, influencing decision-making processes and priority setting.
Septal Nuclei Connection to Dopamine and Reward Pathways
Dopamine, often dubbed the “feel-good neurotransmitter,” plays a pivotal role in the brain’s reward system. The septal nuclei, through their extensive network of connections, have a profound influence on dopamine release and regulation.
Dopaminergic Projections
The septal nuclei interact with key dopaminergic regions, such as the ventral tegmental area (VTA) and the nucleus accumbens. These interactions help modulate the brain’s reward pathways, influencing behaviors from motivation to addiction.
Influence on Behavior
The intricate dance between the septal nuclei and dopamine-rich areas shapes various behaviors. For example, the anticipation of a reward, the drive to achieve it, and the satisfaction upon attainment are all modulated by this interplay [3].
Septal Nuclei Implications for Understanding Addiction and Dependency
Given their central role in pleasure and reward, it’s no surprise that the septal nuclei have implications in the realm of addiction. Substance abuse often hijacks the brain’s natural reward pathways, leading to destructive patterns of behavior.
Alterations in Septal Activity
Chronic substance abuse can lead to alterations in septal nuclei activity, potentially leading to heightened cravings and decreased sensitivity to natural rewards.
Potential Therapeutic Targets
Understanding the septal nuclei’s role in addiction provides opportunities for targeted interventions. Future therapies might focus on modulating septal activity to reduce cravings or enhance natural reward sensitivity.
Septal Nuclei and Learning and Memory Enhancement
Our ability to learn and remember is a cornerstone of human experience, enabling us to evolve, adapt, and flourish in an ever-changing world. Beyond the simple mechanics of retaining information, the processes of learning and memory enhancement lie at the nexus of biology, experience, and cognition.
Relationship Between Septal Nuclei and Hippocampus
The intricate dance between the septal nuclei and the hippocampus is akin to a time-tested partnership, where each entity amplifies the capabilities of the other.
Bidirectional Communication
The septal nuclei and the hippocampus maintain a continuous dialogue. Signals from the hippocampus can influence the septal nuclei’s activity, and in return, the septal nuclei modulate various processes within the hippocampus. This feedback loop is crucial for the consolidation and retrieval of memories.
Rhythmic Coordination
The septal nuclei play a role in orchestrating theta rhythms, a type of brainwave prominently observed in the hippocampus during tasks requiring attention and memory. These rhythms are believed to enhance neural plasticity, thereby facilitating learning and memory.
Septal Nuclei Influence on Long-Term Potentiation (LTP)
Long-Term Potentiation, or LTP, is a process where synaptic connections between neurons become stronger with repeated activation. It’s widely considered one of the primary molecular mechanisms underlying learning and memory.
Regulation of LTP
The septal nuclei, through their intricate network of connections, can influence the onset and strength of LTP in various brain regions, including the hippocampus. By modulating neurotransmitter release and neural excitability, the septal nuclei can enhance or inhibit this synaptic strengthening [4].
Implications for Memory Formation
With their hand in the LTP process, the septal nuclei indirectly shape our ability to form and retain memories. Optimal LTP regulation can lead to more robust memory formation, while disruptions might contribute to memory deficits.
Septal Nuclei Potential for Nootropic Interventions
The burgeoning field of nootropics, substances that enhance cognitive function, has shown interest in the septal nuclei’s role in learning and memory.
Targeting the Septal-Hippocampal Pathway
Some nootropics may enhance memory by bolstering the communication between the septal nuclei and the hippocampus. By strengthening this pathway, it’s possible to optimize the processes of memory consolidation and retrieval.
Enhancing Neural Plasticity
Nootropics that target the septal nuclei’s modulation of LTP could offer potential benefits in memory enhancement. By optimizing the strength and duration of synaptic connections, these interventions might provide a boost in learning capabilities.

The Septal Nuclei and Mental Health
In the multifaceted realm of mental health, understanding the intricate roles of various brain structures is paramount. The septal nuclei, with their extensive connections and diverse functions, have been implicated in a range of psychological conditions and emotional states. Their influence, both direct and indirect, shines a light on the delicate balance of neural networks and offers potential pathways for therapeutic interventions.
Septal Nuclei Role in Emotional Regulation
Emotions, in their myriad shades and intensities, form the vibrant palette of our psychological experiences. The septal nuclei, with their profound connections to the limbic system, play a pivotal role in shaping these emotional landscapes.
Modulation of Fear and Anxiety
The septal nuclei have been found to interact closely with regions like the amygdala, a center for fear processing. By modulating the activity in these regions, the septal nuclei can influence our responses to threatening or anxiety-provoking stimuli, potentially serving as a calming influence during moments of heightened fear.
Influence on Positive Emotions
On the flip side, the septal nuclei’s association with pleasure and reward also suggests a role in the generation and regulation of positive emotions. Their interactions with dopamine-rich areas can shape feelings of joy, contentment, and motivation.
Implications for Septal Nuclei Role in Mood Disorders
Mood disorders, such as depression and bipolar disorder, are complex conditions influenced by a constellation of genetic, environmental, and neural factors. The septal nuclei, with their intricate web of connections, emerge as potential contributors to the onset, progression, and treatment of these disorders.
Depression
Reduced activity or altered functioning of the septal nuclei may be associated with symptoms of anhedonia (a reduced ability to experience pleasure) commonly seen in depression. Additionally, the septal nuclei’s role in dopamine regulation hints at its involvement in the motivational deficits often observed in depressive states.
Bipolar Disorder
The cyclical nature of mood swings in bipolar disorder, oscillating between manic highs and depressive lows, may be influenced by the septal nuclei’s modulation of emotional and reward circuits. While the exact mechanisms remain an area of active research, understanding the septal nuclei’s influence provides a fresh lens to view this condition [5].
Septal Nuclei Potential Therapeutic Avenues
Armed with insights into the septal nuclei’s role in mental health, there emerges a horizon of therapeutic possibilities.
Neuromodulation Techniques
Techniques such as deep brain stimulation (DBS) or transcranial magnetic stimulation (TMS), which influence neural activity, might target the septal nuclei or its associated pathways to alleviate symptoms of mood disorders or enhance emotional regulation.
Pharmacological Interventions
Drugs designed to modulate the activity or connectivity of the septal nuclei could offer relief for conditions ranging from anxiety disorders to depression. By targeting the neurotransmitter systems influenced by the septal nuclei, tailored treatments might be developed.
Cognitive Behavioral Approaches
Understanding the septal nuclei’s role in emotional processing can also inform cognitive-behavioral therapies. Techniques that aim to reframe or redirect emotional responses might leverage insights into the septal nuclei’s modulation of these emotions.
Nootropics and the Septal Nuclei
In the rapidly expanding world of cognitive enhancement, nootropics stand at the forefront as agents of potential and promise. These substances, designed to boost various facets of cognition, have seen a surge in popularity and research interest. But how do these cognitive enhancers intersect with the multifunctional septal nuclei? Let’s delve into the interplay between nootropics and this enigmatic brain region.
Septal Nuclei Mechanism of Action: A Broad Overview
Nootropics, often termed “smart drugs” or “cognitive enhancers,” function by modulating various neurotransmitter systems, improving blood flow to the brain, or influencing neural plasticity. Their interaction with the septal nuclei is a topic of burgeoning interest.
Neurotransmitter Modulation
Many nootropics target neurotransmitter systems, such as cholinergic, dopaminergic, or glutamatergic pathways. Given the septal nuclei’s role in regulating these systems, it’s plausible that some nootropic effects are mediated through their influence on this region.
Neuroprotection and Plasticity
Some nootropics possess neuroprotective qualities, safeguarding neurons against damage. They may also promote neural plasticity, enhancing the brain’s ability to adapt and reorganize. The septal nuclei, being pivotal for processes like long-term potentiation, could be central in mediating these benefits.
Potential Nootropics Targeting the Septal Nuclei
While the realm of nootropics is vast, several compounds have emerged as potential modulators of septal nuclei activity or their associated pathways.
Cholinergic Enhancers
Given the close relationship between the septal nuclei and cholinergic systems, compounds that enhance acetylcholine function might impact the septal nuclei’s performance. Drugs like Donepezil or supplements like Alpha GPC could be of interest in this context.
Dopaminergic Modulators
Considering the septal nuclei’s involvement in dopamine regulation, substances like Modafinil, which influence dopaminergic transmission, might interact with septal functions, particularly those related to pleasure, reward, and motivation.
Neuroprotective Agents
Compounds like Noopept, with their potential neuroprotective qualities, could indirectly benefit the septal nuclei by maintaining overall brain health and integrity.
Considerations and Limitations of Nootropics and the Septal Nuclei
While the potential of nootropics in modulating septal nuclei functions is intriguing, it’s essential to approach the topic with caution and a discerning lens.
Holistic Brain Functioning
The brain is an intricate web of interconnected regions. Targeting the septal nuclei might influence other areas, leading to unexpected outcomes. It’s crucial to view nootropic interventions in the context of the brain’s holistic functioning.
Research Gaps
The field of nootropics is still evolving, and comprehensive research on their interactions with specific brain regions, including the septal nuclei, may be limited. It’s vital to rely on evidence-based findings and be wary of exaggerated claims.
Individual Variation
The efficacy and impact of nootropics can vary among individuals, influenced by genetics, overall health, and other factors. Personalized approaches, taking into account individual needs and responses, are crucial.
References
[1] Septal Nuclei
[2] Know Your Brain: Septum
[3] Evolution of Septal Nuclei
[4] Human septal nuclei
[5] Development and neural diversity of septal nuclei

