The intricate dance of hormones within our body influences everything from growth and metabolism to mood and cognition. Among these hormonal actors, somatostatin, often overshadowed by its counterparts, has begun to attract attention for its potential role in cognitive health. A peptide hormone primarily recognized for its influence on growth hormone and the digestive system, recent findings suggest that somatostatin may also play a pivotal role in the way our brain functions. But how deep is this connection? And what could it mean for the broader understanding of cognitive processes and disorders?
Contents
- Introduction to Somatostatin and Cognitive Health
- What is Somatostatin?
- The Role of Hormones in Cognitive Health
- Potential Implications of Somatostatin on Cognitive Decline
- The Controversies and Gaps in Current Knowledge of Somatostatin
- References
Introduction to Somatostatin and Cognitive Health
The intricate dance of hormones within our body influences everything from growth and metabolism to mood and cognition. Among these hormonal actors, somatostatin, often overshadowed by its counterparts, has begun to attract attention for its potential role in cognitive health.
Brief Description of Somatostatin
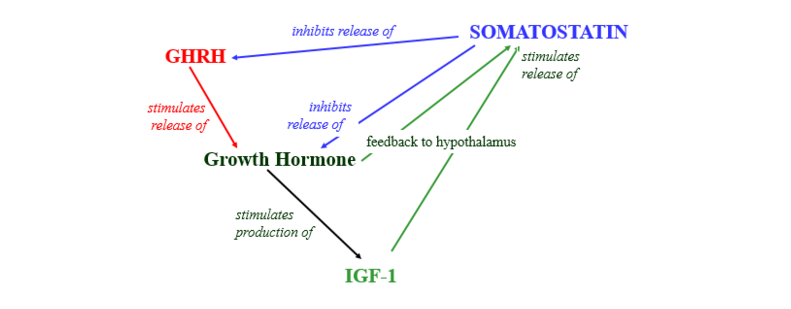
Somatostatin, sometimes referred to as growth hormone-inhibiting hormone (GHIH), is a peptide hormone produced in various parts of the human body, including the hypothalamus, pancreas, and the gastrointestinal tract. Its primary function has long been recognized as inhibiting the release of growth hormone, but its role goes far beyond this singular activity.
Somatostatin’s Primary Roles in the Human Body
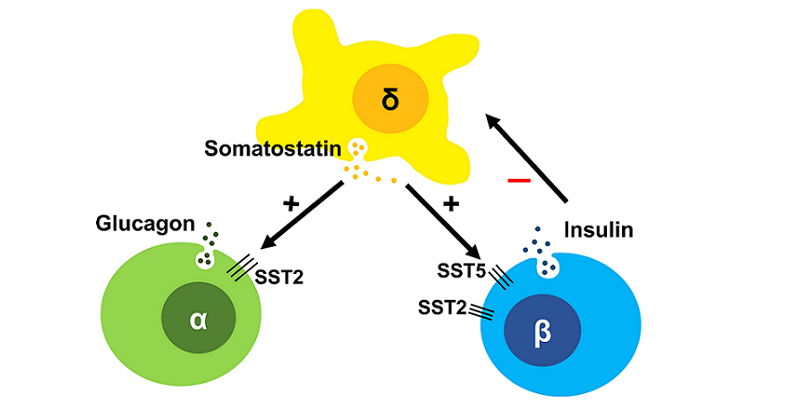
Within the human body, somatostatin has a myriad of responsibilities. In the pancreas, it plays a regulatory role in the secretion of other hormones such as insulin and glucagon, helping maintain glucose and lipid homeostasis. In the gastrointestinal system, it acts to slow down the digestive process by inhibiting the release of gastrin, secretin, and other digestive agents. Beyond these roles, the hormone is also implicated in neurotransmission and the modulation of cell proliferation.
The Potential Connection of Somatostatin to Cognitive Health
As scientists have delved deeper into the brain’s complex hormonal environment, somatostatin’s presence and potential influence on cognitive processes have come to the forefront. Preliminary studies and observations hint at a role in memory formation, synaptic plasticity, and even neuroprotection. As we peel back the layers of this multifaceted hormone, it becomes evident that its influence on cognitive health might have been underestimated and warrants further exploration [1].
What is Somatostatin?
Diving deeper into the world of hormones and their intricate functions within our system, somatostatin emerges as a significant player with diverse roles. To truly appreciate its potential influence on cognitive processes, it’s essential first to understand its chemical nature, origin, and primary functions in our body.
Chemical and Biological Overview
Somatostatin is a cyclic peptide hormone composed of two peptide sequences: one containing 14 amino acids and the other containing 28. These peptides are produced and released by neuroendocrine, inflammatory, and immune cells. While its structure may seem complex to those unfamiliar with biochemistry, it’s this very complexity that allows somatostatin to interact with a variety of receptors and mediate a multitude of physiological responses.
Key Functions and Signaling Pathways
Somatostatin’s name itself, derived from the Greek “soma” (body) and “statin” (to stop), provides a hint towards its primary function: inhibition. This hormone is well-known for its inhibitory effects on various bodily processes. Here are some of its primary functions.
Growth Hormone Regulation
Perhaps its most recognized role, somatostatin inhibits the release of growth hormone from the anterior pituitary gland, thereby regulating overall growth and development.
Digestive System Regulation
In the digestive tract, somatostatin slows down the release of various hormones and enzymes, modulating the digestive process and ensuring that nutrients are absorbed efficiently [2].
Neurotransmitter Modulation
In the nervous system, somatostatin acts as a neurotransmitter, influencing neuronal activity. This particular function hints at its potential role in cognitive processes, which we’ll explore further in subsequent sections.
In terms of signaling, somatostatin primarily interacts with five types of somatostatin receptors (termed sst1 to sst5). Each receptor has its unique distribution and function within the body, further adding to the hormone’s multifaceted nature.
The Role of Hormones in Cognitive Health
The labyrinthine realm of our cognitive processes, encompassing memory, attention, reasoning, and countless other functions, is astonishingly influenced by the hormones coursing through our body. While many tend to associate hormones solely with growth, metabolism, or mood regulation, the subtle underpinnings of these chemical messengers on our brain’s functioning are profound.
Overview of Hormonal Impact on the Brain
Hormones, in essence, are signaling molecules that regulate specific organs and tissues’ functions. When it comes to the brain, these molecules often modulate neuronal activity, influencing neurotransmitter release, synaptic plasticity, and neural network formations. Their roles can range from the immediate, like adrenaline sharpening our focus during a moment of crisis, to the long-term, such as thyroid hormones influencing neural development during early childhood.
Moreover, the influence of hormones isn’t just limited to specific periods or developmental stages. Throughout our lives, from the womb to old age, they continually shape our cognitive capabilities, responses to stimuli, and even susceptibility to various neurological conditions.
Notable Hormones and Their Impact on Cognitive Function
Several hormones have gained notable attention for their roles in shaping cognitive processes.
Cortisol
Often labeled the ‘stress hormone,’ cortisol impacts memory, attention, and decision-making processes. Chronic elevated cortisol levels, often resulting from prolonged stress, can lead to cognitive impairments and increased vulnerability to mental health disorders.
Thyroid Hormones (T3 and T4)
Crucial for neural differentiation and synaptic development in early life, imbalances in these hormones can lead to cognitive and motor function impairments [3].
Insulin
Beyond its metabolic roles, insulin has a neuroprotective function. It’s implicated in learning and memory, and its dysregulation can increase the risk of neurodegenerative diseases like Alzheimer’s.
Estrogen and Testosterone
Both of these sex hormones play roles in cognitive health. For instance, estrogen has been linked to verbal fluency and memory, while testosterone appears to influence spatial abilities and mood regulation.
Oxytocin
Known as the ‘love hormone’ or ‘bonding hormone’, oxytocin has roles in social recognition, emotional processing, and even the modulation of stress and anxiety.
Potential Implications of Somatostatin on Cognitive Decline
The journey of human cognition is as mesmerizing as it is fragile. As we age, certain cognitive abilities can decline, resulting in diminished memory, problem-solving capacities, or attention spans. Neurodegenerative diseases further exacerbate this decline, casting a shadow over the golden years of many individuals. Delving deeper into the relationship between hormones and cognitive health, somatostatin emerges as a potential player in either protecting against or contributing to this decline.
Alzheimer’s Disease and Somatostatin
Alzheimer’s Disease, the leading cause of dementia worldwide, is characterized by memory loss and cognitive impairment. Research has shown a puzzling connection between somatostatin levels and the progression of Alzheimer’s.
Somatostatin and Amyloid-β Plaques
One of the hallmarks of Alzheimer’s Disease is the accumulation of amyloid-β plaques in the brain. Studies have indicated that somatostatin might play a role in modulating the formation or clearance of these plaques, although the exact mechanisms remain to be fully understood [4].
Neuroprotective Effects
In certain experimental settings, somatostatin has demonstrated neuroprotective effects, potentially safeguarding neurons from degenerative processes.
Somatostatin Levels in Alzheimer’s Patients
Intriguingly, some studies have observed reduced somatostatin levels in the cerebrospinal fluid of Alzheimer’s patients, suggesting a potential role in disease pathology or as a biomarker.
Cognitive Aging and Potential Protective Effects
Beyond specific diseases, the normal process of aging can bring about cognitive changes. Here’s where somatostatin might have a role to play.
Memory Preservation
Preliminary studies suggest that somatostatin might support memory functions, especially spatial memory, potentially shielding it from age-related decline.
Synaptic Plasticity
Somatostatin has been implicated in modulating synaptic plasticity, the ability of synapses to strengthen or weaken over time, a crucial process for learning and memory.
Interaction with Other Neurotransmitters
By influencing other neurotransmitters like GABA, somatostatin might indirectly affect cognitive functions and their preservation during the aging process.
Role in Memory Formation and Recall
Memory, one of the most treasured cognitive faculties, is a complex process involving multiple stages like formation, consolidation, and recall. Somatostatin, with its presence in the brain and interaction with neurotransmission, has potential implications.
Influencing Memory Encoding
The initial step of creating a new memory might be influenced by somatostatin levels, with some studies hinting at improved memory encoding in the presence of optimal somatostatin concentrations.
Impact on Long-Term Potentiation (LTP)
LTP is a vital process where synaptic connections become stronger with repeated activation, crucial for memory consolidation. Somatostatin might modulate LTP, thereby influencing how memories are solidified in the brain [5].
The Controversies and Gaps in Current Knowledge of Somatostatin
In the ever-evolving landscape of scientific inquiry, somatostatin’s role in cognitive health stands as a testament to the complexities and nuances of understanding biological processes. While emerging research has provided tantalizing glimpses into its potential significance, it has also given rise to controversies and highlighted the gaps in our current comprehension.
Divergent Research Outcomes
Like many areas of study in neuroscience, research into somatostatin has produced divergent outcomes, some of which appear contradictory.
Neuroprotective vs. Neurodegenerative Roles
While certain studies laud somatostatin for its neuroprotective properties, others point towards potential neurodegenerative effects, leading to questions about the circumstances under which the hormone exerts its influence.
Somatostatin Levels and Cognitive Function
Some investigations have linked decreased somatostatin levels with cognitive impairments, whereas others suggest that elevated levels might be problematic. This disparity raises queries about the optimal concentration for cognitive health and whether it varies among individuals.
Interactions with Other Hormones
Somatostatin’s interplay with other hormones, such as growth hormone or insulin, and their collective impact on cognitive health remains an area of contention, with inconsistent findings across studies.
The Limitations of Current Methodologies
Science is only as reliable as the methods it employs. Several factors could be influencing our current understanding of somatostatin.
Animal Models vs. Human Studies
Much of our knowledge stems from animal models, which, while informative, don’t always translate seamlessly to human physiology and cognitive processes.
Short-term vs. Long-term Effects
Some studies focus on the immediate impact of somatostatin manipulation, while others investigate long-term changes. This temporal difference can result in varied outcomes and interpretations.
Variability in Study Populations
Factors such as age, genetic background, and overall health can influence how somatostatin affects cognitive processes, leading to varied results across different study groups.
Unanswered Questions and Future Research Directions
The world of somatostatin research is vast, with many territories still uncharted.
Mechanisms of Action
How exactly does somatostatin interact with neural circuits to influence cognition? The intricate pathways remain to be fully delineated.
Therapeutic Potential
Could somatostatin, or its modulators, be harnessed for therapeutic interventions in cognitive disorders? The potential is exciting but requires thorough exploration.
Lifespan Changes
How does somatostatin’s role in cognition change throughout an individual’s lifespan? From development to aging, there are many facets yet to be uncovered.
References
[1] The role of neuropeptide somatostatin in the brain
[2] Somatostatin and cognitive function in neurodegenerative disorders
[3] Study confirms that neuropeptide somatostatin can improve the brain’s cognitive function
[4] Somatostatin Neurons Cooperate in the Cerebral Cortex
[5] Uncovering the role of somatostatin signaling in the brain

