
In today’s fast-paced world, stress has become an inevitable part of our daily lives. But have you ever considered how stress affects your memory and learning? At the center of this impact is cortisol, a hormone produced by the adrenal glands in response to stress. Often dubbed the “stress hormone,” cortisol plays a crucial role in regulating our body’s response to stress. Here we delve into the intricate relationship between cortisol, memory, and learning, examining how this hormone can both enhance and impair cognitive processes.
Contents
The Role of Cortisol in the Stress Response
Cortisol plays a vital role in our body’s response to stress, helping us adapt to challenging situations. To better understand its impact on memory and learning, it’s essential to first explore the biological mechanisms behind cortisol release and its subsequent effects.
The Hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal (HPA) Axis
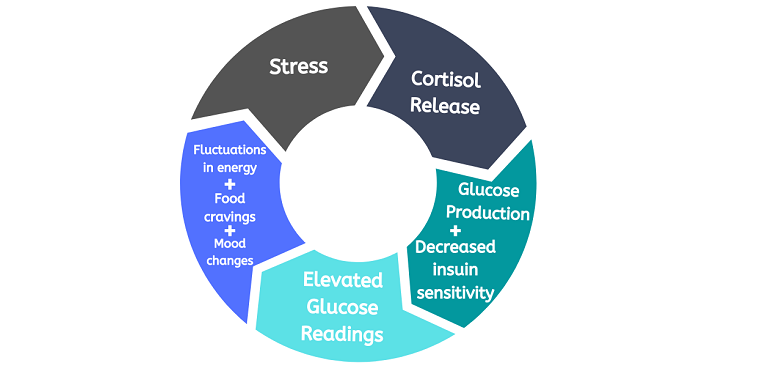
When we encounter a stressor, our body activates a complex physiological response known as the hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal (HPA) axis. This system is responsible for coordinating our body’s response to stress, initiating a series of hormonal and neural signals that ultimately lead to the release of cortisol [1].
As part of the HPA axis response, the hypothalamus releases corticotropin-releasing hormone (CRH), which then stimulates the pituitary gland to produce adrenocorticotropic hormone (ACTH). ACTH travels through the bloodstream to the adrenal glands, which respond by producing and releasing cortisol into the bloodstream.
Effects of Cortisol Release
Cortisol helps our body prepare for a “fight or flight” response by mobilizing energy stores. It increases the availability of glucose in the bloodstream, ensuring that our muscles and brain have access to the energy they need to respond to the stressor [2].
In addition to mobilizing energy, cortisol also suppresses the immune system’s response to inflammation, allowing our body to focus on addressing the immediate threat posed by the stressor. While this is beneficial in acute stress situations, chronic exposure to cortisol can lead to a weakened immune system and an increased risk of illness.
Cortisol plays a role in regulating blood pressure by constricting blood vessels, increasing the amount of blood pumped by the heart, and helping to maintain adequate blood flow to vital organs. This ensures that our body can effectively respond to stress and maintain homeostasis.
Cortisol and Memory
Cortisol has a complex relationship with memory formation and retrieval, exhibiting both beneficial and detrimental effects depending on the duration and intensity of stress.
Short-term Effects
In the short-term, moderate cortisol release can actually enhance memory consolidation — the process of converting short-term memories into long-term ones [3]. This effect is particularly prominent for emotionally-charged memories, helping us to remember important or threatening events that may be crucial for our survival.
Cortisol’s impact on emotionally-charged memories is mediated by its interaction with the amygdala, a brain region involved in processing emotional information. This interaction helps to strengthen the neural connections associated with these memories, making them more resistant to forgetting and easier to recall in the future.
Long-term Effects
While short-term cortisol exposure can have positive effects on memory, chronic stress and prolonged cortisol exposure can lead to detrimental outcomes [4]. High cortisol levels over an extended period can impair memory formation and retrieval, making it more difficult to learn and remember new information.
One of the primary reasons for the negative impact of chronic stress on memory is the effect of cortisol on the hippocampus, a brain region critical for learning and memory. Sustained exposure to high cortisol levels can result in a reduction in hippocampal volume, leading to long-lasting memory impairments.
Individual Differences
Individual differences in cortisol response and its effects on memory can be partly attributed to genetic factors. Certain genetic variations can influence an individual’s sensitivity to cortisol and its effects on memory processes, making some people more vulnerable to the negative consequences of stress.
Environmental factors also play a role in determining the impact of cortisol on memory. Factors such as early life experiences, social support, and coping strategies can all influence an individual’s stress response and, consequently, their memory performance.
Cortisol and Learning
Cortisol’s impact on learning is similarly complex, with both positive and negative effects depending on the nature of the stressor and the individual’s stress response.
Acute Stress and Learning
In the context of acute stress, cortisol release can actually facilitate learning by heightening attention and focus [5]. This heightened state allows us to concentrate on the task at hand and process information more efficiently, potentially leading to better learning outcomes.
Acute stress can also promote adaptive learning by strengthening the neural connections associated with relevant information. This effect is particularly evident when learning about threats or challenges in the environment, allowing us to better anticipate and respond to similar situations in the future.
Chronic Stress and Learning
While acute stress can have positive effects on learning, chronic stress and prolonged cortisol exposure can lead to a range of negative consequences for cognitive function [6]. High cortisol levels over an extended period can impair learning by disrupting the neural processes involved in encoding, consolidating, and retrieving new information.
Chronic stress can also affect our ability to solve problems and make decisions, both of which are essential components of the learning process. Prolonged cortisol exposure can lead to cognitive rigidity and reduced cognitive flexibility, making it more difficult for us to adapt to new situations and learn from our experiences.
Strategies for Managing Cortisol and Enhancing Memory and Learning
Given the complex relationship between cortisol, memory, and learning, it is essential to develop strategies that help manage stress levels and optimize cognitive performance.
Stress Management Techniques
A crucial aspect of mitigating the effects of cortisol on memory and learning is effectively managing stress. Stress management techniques can help lower cortisol levels, promote relaxation, and enhance cognitive performance.
Mindfulness practices
Mindfulness practices, such as meditation, deep breathing, and progressive muscle relaxation, can help reduce cortisol levels by promoting relaxation and emotional regulation. Incorporating these practices into daily routines can help mitigate the negative effects of stress on memory and learning.
Exercise
Regular physical activity is an effective way to manage stress and maintain healthy cortisol levels. Exercise has been shown to improve cognitive function, enhance memory, and promote the growth of new neurons in the hippocampus, which can counteract the negative effects of cortisol on memory and learning.
Proper sleep
Getting adequate sleep is crucial for managing cortisol levels and maintaining optimal cognitive function. Sleep deprivation can lead to increased cortisol levels and impaired memory and learning processes. Prioritizing sleep and establishing a consistent sleep schedule can help minimize the negative effects of stress on cognitive performance.
Environmental Modifications
Establishing a learning environment that fosters a sense of safety, support, and encouragement can help reduce stress levels and promote better memory and learning outcomes. This may involve cultivating positive relationships with peers and educators, setting realistic expectations, and providing access to necessary resources.
Identifying and addressing sources of stress in the learning environment can help minimize cortisol’s impact on memory and learning. This may involve time management strategies, breaking down tasks into manageable steps, and seeking support when necessary.
Individual Approaches
Each individual responds to stress differently, so it is important to find stress management techniques that work best for you. Experiment with various methods to identify which practices are most effective in helping you manage cortisol levels and maintain optimal memory and learning performance.
Becoming aware of the specific situations or factors that trigger your stress response can help you develop targeted strategies for managing cortisol levels. By understanding your unique stress triggers, you can proactively address them and minimize their impact on your memory and learning processes.
Nutritional Supplements That Help Manage Cortisol Levels
Nutritional supplements can also play a role in managing cortisol levels and supporting a healthy stress response. Some supplements that have been researched for their potential impact on cortisol levels include:
Ashwagandha
Ashwagandha (Withania somnifera) is an adaptogenic herb that has been traditionally used in Ayurvedic medicine to help the body manage stress and improve overall well-being. It is believed to have several mechanisms through which it may help manage cortisol levels [7]:
- Modulating stress response: As an adaptogen, ashwagandha helps the body adapt to stress by modulating the stress response. It is believed to regulate the production and release of cortisol and other stress hormones by influencing the hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal (HPA) axis. By helping to balance the HPA axis, ashwagandha can prevent excessive cortisol production in response to stress.
- Reducing inflammation: Chronic stress and elevated cortisol levels can lead to increased inflammation in the body. Ashwagandha has been shown to possess anti-inflammatory properties, which may help reduce inflammation and, consequently, decrease cortisol levels.
- Antioxidant properties: Oxidative stress can contribute to an imbalanced stress response and increased cortisol levels. Ashwagandha contains antioxidant compounds that can help neutralize free radicals and reduce oxidative stress, thereby promoting a healthier stress response.
- Anxiolytic effects: Ashwagandha has been found to possess anxiolytic (anxiety-reducing) properties, which can help alleviate stress and anxiety symptoms. By reducing anxiety, ashwagandha may indirectly help manage cortisol levels and improve the body’s overall stress response.
- Neuroprotective effects: Some research suggests that ashwagandha has neuroprotective effects, helping to protect the brain from the detrimental effects of chronic stress and elevated cortisol levels. By promoting brain health, ashwagandha may contribute to more balanced cortisol production and stress management.
Phosphatidylserine
Phosphatidylserine is a phospholipid found in cell membranes and is involved in various cellular functions, including cell signaling and cell-to-cell communication. Research suggests that phosphatidylserine supplementation may help manage cortisol levels and improve the body’s response to stress through several mechanisms [8]:
- Modulating the HPA axis: Phosphatidylserine is believed to influence the hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal (HPA) axis, which regulates the body’s stress response and cortisol production. By modulating the HPA axis, phosphatidylserine may help maintain a healthy stress response and prevent excessive cortisol release.
- Reducing stress-induced cortisol spikes: Some studies have shown that phosphatidylserine supplementation can help reduce the cortisol spike in response to stress, particularly exercise-induced stress. By mitigating these cortisol spikes, phosphatidylserine may help maintain balanced cortisol levels and improve stress resilience.
- Supporting brain health: Phosphatidylserine plays a critical role in maintaining healthy brain function, including supporting memory, learning, and overall cognitive performance. A healthy brain is better equipped to manage stress and regulate cortisol levels effectively. By promoting brain health, phosphatidylserine may indirectly contribute to a more balanced stress response and cortisol production.
- Enhancing mood: Some research suggests that phosphatidylserine may have a positive impact on mood and may help reduce symptoms of depression and anxiety. By improving mood, phosphatidylserine may help alleviate stress, which can contribute to more balanced cortisol levels.
L-theanine
L-theanine is an amino acid predominantly found in green tea and some other plant sources. It has been well-studied for its potential to promote relaxation without causing drowsiness and may help manage cortisol levels through several mechanisms [9]:
- Modulating stress response: L-theanine is thought to influence the body’s stress response by affecting the levels of certain neurotransmitters, such as dopamine, serotonin, and GABA (gamma-aminobutyric acid), which are involved in regulating mood, relaxation, and anxiety. By modulating these neurotransmitters, L-theanine may help reduce the physiological stress response and, consequently, manage cortisol levels.
- Reducing anxiety: L-theanine has been shown to possess anxiolytic (anxiety-reducing) properties, which can help alleviate stress and anxiety symptoms. By reducing anxiety, L-theanine may indirectly help manage cortisol levels and improve the body’s overall stress response.
- Enhancing alpha brain waves: L-theanine has been found to increase alpha brain wave activity, which is associated with a relaxed but alert mental state. By promoting this relaxed state, L-theanine may help reduce stress and cortisol levels without causing sedation or drowsiness.
- Protecting against stress-related damage: L-theanine has been shown to possess antioxidant properties and may help protect the brain and body from the detrimental effects of stress and elevated cortisol levels, including oxidative stress and inflammation. By providing this protection, L-theanine may contribute to more balanced cortisol production and stress management.
References
[1] Understanding the stress response
[2] Stress effects on the body
[3] Sleep, dreams, and memory consolidation: The role of the stress hormone cortisol
[4] Chronic stress puts your health at risk
[5] Neuroplasticity and the Importance of Learning New Skills Throughout Life
[6] How chronic stress changes the brain – and what you can do to reverse the damage
[7] Does Ashwagandha Actually Relieve Stress?
[8] The Effects Of Phosphatidylserine On Reaction Time And Cognitive Function Following Exercise Stress
[9] How does the tea L-theanine buffer stress and anxiety

