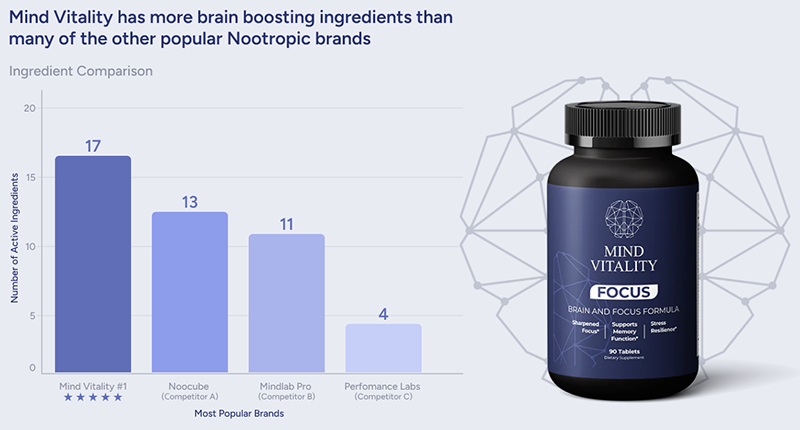
In today’s fast-paced world, maintaining optimal brain function is more important than ever. One key aspect of brain health is the Brain-Derived Neurotrophic Factor (BDNF), a protein that plays a critical role in the growth, maintenance, and survival of neurons. Here we delve into the world of BDNF, its significance for neural health, and practical ways to increase BDNF levels through diet, supplements, and fasting practices. By implementing these strategies, you can promote cognitive function, memory, and learning, ultimately enhancing your brain’s overall health and well-being.
What Is BDNF?
Brain-Derived Neurotrophic Factor (BDNF) is a protein that plays a vital role in the growth, maintenance, and survival of neurons in the human brain. It is one of several neurotrophins, which are proteins that support the development and functioning of the nervous system. BDNF is particularly important for the regulation of synaptic plasticity, a process that allows neurons to adapt and form new connections in response to learning and experiences.
Brief Explanation of Brain-Derived Neurotrophic Factor (BDNF)
BDNF is produced in various regions of the brain, including the hippocampus, cortex, and cerebellum. It supports the survival of existing neurons and encourages the growth and differentiation of new neurons and synapses. The protein also plays a role in the maintenance of synaptic connections, helping to ensure efficient communication between neurons.
Importance of BDNF for Neural Health
BDNF is crucial for maintaining neural health, as it supports the adaptability and resilience of the nervous system. Low levels of BDNF have been linked to various neurological and psychiatric disorders, such as depression, Alzheimer’s disease, and schizophrenia. On the other hand, increased BDNF levels have been associated with improved memory, learning, and overall cognitive function. As such, boosting BDNF levels is an area of interest for promoting brain health and preventing cognitive decline.
Overview of Methods to Increase BDNF Levels
There are several ways to increase BDNF levels naturally, which can be beneficial for maintaining and improving neural health. Some of these methods include consuming certain foods, taking nutritional supplements, and practicing fasting. Each of these approaches will be explored in more detail in the subsequent sections of this article.
Best BDNF Foods
The foods we consume can have a significant impact on our brain health and BDNF levels. Incorporating certain nutrient-rich foods into your diet can help increase BDNF levels and promote overall neural health.
Introduction to Dietary Impact on BDNF Levels
Dietary choices play a crucial role in influencing BDNF levels in the brain [1]. Consuming foods rich in specific nutrients can help promote the production of BDNF and support neural health. Let’s explore some of the most effective BDNF-boosting foods and their associated benefits.
Omega-3 Fatty Acids
Omega-3 fatty acids are essential for brain health and have been shown to increase BDNF levels. They are polyunsaturated fats that cannot be synthesized by the human body and must be obtained through diet.
Fish and Seafood
Fatty fish, such as salmon, mackerel, sardines, and trout, are rich sources of omega-3 fatty acids. Including these types of fish in your diet can help promote brain health and support BDNF production.
Nuts and Seeds
In addition to fish, nuts and seeds are another excellent source of omega-3 fatty acids. Walnuts, flaxseeds, and chia seeds are particularly rich in these essential fats and can be easily incorporated into your daily meals.
Antioxidant-Rich Foods
Antioxidants help protect the brain from oxidative stress, which can negatively impact BDNF levels [2]. Consuming foods high in antioxidants can help maintain and increase BDNF levels in the brain.
Berries and Fruits
Berries, such as blueberries, strawberries, and raspberries, are packed with antioxidants that support brain health. Other antioxidant-rich fruits include oranges, kiwis, and grapes. Incorporating these fruits into your diet can contribute to increased BDNF levels.
Dark Leafy Greens
Dark leafy greens, like spinach, kale, and Swiss chard, are also rich in antioxidants. Including these vegetables in your meals can help promote BDNF production and support overall brain health.
Flavonoids
Flavonoids are a group of plant compounds with antioxidant properties that have been shown to increase BDNF levels [3].
Dark Chocolate
Dark chocolate, especially with a high cocoa content (70% or higher), is a delicious source of flavonoids. Consuming moderate amounts of dark chocolate can help boost BDNF levels and support cognitive function.
Tea (Green and Black)
Green and black tea are also rich in flavonoids and have been linked to increased BDNF levels. Regular tea consumption can provide brain health benefits and contribute to overall well-being.

Best BDNF Supplements
While a healthy diet is essential for promoting BDNF production, some individuals may benefit from incorporating specific supplements to further support neural health.
Why Nutritional Supplements Can Be Beneficial for Increasing BDNF Levels
Nutritional supplements can be of benefit for increasing BDNF levels for several reasons. In some cases, individuals may not receive an adequate amount of specific nutrients through their diet alone, leading to suboptimal BDNF production. Supplements can help bridge these nutritional gaps and ensure the body has the necessary building blocks to produce BDNF efficiently. Here are some reasons why nutritional supplements can be beneficial for increasing BDNF levels.
Enhanced Nutrient Availability
Some people may have difficulty consuming a balanced diet that includes all the necessary nutrients for optimal BDNF production due to various factors such as dietary restrictions, allergies, or personal preferences [4]. In these cases, supplements can provide concentrated sources of the required nutrients and help support BDNF levels.
Improved Absorption
Certain individuals may have impaired nutrient absorption due to factors like age, genetics, or underlying health conditions. Nutritional supplements can sometimes be formulated with enhanced bioavailability, allowing for better absorption of the active compounds and, consequently, a more significant impact on BDNF levels.
Convenience and Consistency
Maintaining a balanced diet that consistently provides all the necessary nutrients for BDNF production can be challenging. Supplements offer a convenient way to ensure that individuals consistently receive the required nutrients to support BDNF levels, even on days when their diet may be less than ideal.
Targeted Support
Some supplements, like specific herbal extracts or compounds, can directly influence BDNF production through various mechanisms. For example, curcumin has been shown to increase BDNF levels by reducing inflammation and oxidative stress, while ashwagandha can enhance BDNF production through its adaptogenic and neuroprotective effects. These targeted supplements can be especially helpful for individuals looking to improve their brain health and cognitive function.
Synergistic Effects
Some nutrients may have a synergistic effect when taken together, meaning that their combined impact on BDNF levels is greater than the sum of their individual effects [5]. For example, omega-3 fatty acids and antioxidants can work together to reduce inflammation, protect neurons from oxidative stress, and promote BDNF production. By combining specific supplements, individuals may be able to maximize their potential benefits for brain health.
Omega-3 Fatty Acid Supplements
Omega-3 fatty acid supplements may increase a person’s BDNF levels through several mechanisms related to their anti-inflammatory, antioxidant, and neuroprotective properties [6]. Here are some ways in which omega-3 fatty acid supplements might contribute to increased BDNF levels:
- Anti-inflammatory effects: Omega-3 fatty acids, particularly EPA (eicosapentaenoic acid) and DHA (docosahexaenoic acid), have been shown to reduce inflammation in the body. Chronic inflammation can negatively impact brain function and suppress BDNF production. By reducing inflammation, omega-3 fatty acids may help create a more favorable environment for BDNF synthesis and release.
- Antioxidant properties: Oxidative stress, caused by an imbalance between free radicals and antioxidants, can damage neurons and hinder BDNF production. Omega-3 fatty acids have been found to possess antioxidant properties that can help neutralize free radicals, protect neurons from oxidative damage, and support BDNF production.
- Neuroprotective effects: DHA, a major component of omega-3 fatty acids, is an essential structural component of the brain’s cell membranes. Adequate DHA levels help maintain the integrity of cell membranes, support neuronal function, and promote neuroplasticity. This, in turn, can lead to increased BDNF levels and overall brain health.
- Modulation of BDNF signaling pathways: Omega-3 fatty acids have been shown to influence BDNF signaling pathways, which are crucial for neuronal survival, growth, and differentiation. By modulating these pathways, omega-3 fatty acids may directly contribute to increased BDNF levels and improved cognitive function.
- Improved mood and stress resilience: Omega-3 fatty acids have been linked to better mood regulation and stress resilience. As stress and mood disturbances can negatively impact BDNF levels, the mood-enhancing effects of omega-3 fatty acids may indirectly contribute to increased BDNF production.
Resveratrol
Resveratrol, a naturally occurring polyphenol found in red wine, grapes, and berries, has been shown to positively influence BDNF levels through several mechanisms related to its antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, and neuroprotective properties [7]. Here are some ways in which resveratrol might contribute to increased BDNF levels:
- Antioxidant properties: Oxidative stress, caused by an imbalance between free radicals and antioxidants, can damage neurons and hinder BDNF production. Resveratrol has potent antioxidant properties that can help neutralize free radicals, protect neurons from oxidative damage, and ultimately support BDNF production.
- Anti-inflammatory effects: Chronic inflammation in the body can negatively impact brain function and suppress BDNF production. Resveratrol has been shown to reduce inflammation by modulating inflammatory pathways and inhibiting the production of pro-inflammatory molecules. By mitigating inflammation, resveratrol may help create a more favorable environment for BDNF synthesis and release.
- Activation of SIRT1: Resveratrol has been found to activate the SIRT1 (Sirtuin 1) enzyme, which plays a crucial role in regulating cellular health, including processes related to aging, inflammation, and metabolism. Activation of SIRT1 has been linked to increased BDNF levels and improved cognitive function, suggesting that resveratrol’s impact on SIRT1 may contribute to its BDNF-boosting effects.
- Enhanced neurogenesis: Resveratrol has been shown to promote neurogenesis, the process by which new neurons are generated in the brain. BDNF is a critical factor in neurogenesis, supporting the survival, growth, and differentiation of new neurons. By stimulating neurogenesis, resveratrol may indirectly contribute to increased BDNF levels.
- Improved cerebral blood flow: Resveratrol has been found to enhance cerebral blood flow, which is essential for delivering oxygen and nutrients to brain cells. Improved blood flow can support overall brain health, including the production and release of BDNF.
Ashwagandha
Ashwagandha (Withania somnifera) is an adaptogenic herb with a long history of use in Ayurvedic medicine, known for its stress-reducing and neuroprotective effects. It may increase a person’s BDNF levels through several mechanisms, including [8]:
- Adaptogenic properties: As an adaptogen, ashwagandha helps the body better adapt to stress, which can have a negative impact on BDNF levels. By promoting a healthy stress response and enhancing stress resilience, ashwagandha may indirectly contribute to increased BDNF production.
- Antioxidant effects: Ashwagandha has been shown to possess antioxidant properties that can help neutralize free radicals and protect neurons from oxidative damage. By reducing oxidative stress, ashwagandha may support BDNF production and overall brain health.
- Anti-inflammatory properties: Chronic inflammation can suppress BDNF production and negatively affect brain function. Ashwagandha has been found to reduce inflammation by modulating inflammatory pathways and inhibiting the production of pro-inflammatory molecules. By mitigating inflammation, ashwagandha may help create a more favorable environment for BDNF synthesis and release.
- Neuroprotective effects: Ashwagandha has been shown to exert neuroprotective effects, including the promotion of neuronal survival, growth, and differentiation. These effects are partly mediated through the modulation of various signaling pathways, including those related to BDNF. By promoting neuroprotection, ashwagandha may directly contribute to increased BDNF levels.
- Regulation of neurotransmitters: Ashwagandha has been found to influence the levels of various neurotransmitters, such as serotonin, dopamine, and GABA, which are crucial for mood regulation and cognitive function. By modulating neurotransmitter levels, ashwagandha may indirectly support BDNF production and overall brain health.
Curcumin
Curcumin, the primary bioactive compound found in turmeric, has been shown to have multiple health benefits, including the potential to increase BDNF levels. The mechanisms through which curcumin may contribute to increased BDNF levels include:
- Anti-inflammatory effects: Chronic inflammation can negatively impact brain function and suppress BDNF production. Curcumin has been shown to exhibit potent anti-inflammatory properties by modulating inflammatory pathways and inhibiting the production of pro-inflammatory molecules. By reducing inflammation, curcumin may help create a more favorable environment for BDNF synthesis and release.
- Antioxidant properties: Oxidative stress, caused by an imbalance between free radicals and antioxidants, can damage neurons and hinder BDNF production. Curcumin has strong antioxidant properties that can help neutralize free radicals, protect neurons from oxidative damage, and support BDNF production.
- Neuroprotective effects: Curcumin has been found to exert neuroprotective effects, including the promotion of neuronal survival, growth, and differentiation. These effects are partly mediated through the modulation of various signaling pathways, including those related to BDNF. By promoting neuroprotection, curcumin may directly contribute to increased BDNF levels.
- Modulation of neurotransmitters: Curcumin has been shown to influence the levels of various neurotransmitters, such as serotonin and dopamine, which are crucial for mood regulation and cognitive function. By modulating neurotransmitter levels, curcumin may indirectly support BDNF production and overall brain health.
- Activation of the CREB/BDNF signaling pathway: Curcumin has been found to activate the cAMP response element-binding protein (CREB) and subsequently upregulate BDNF levels. CREB is a transcription factor that binds to the BDNF gene, promoting its expression. By activating the CREB/BDNF signaling pathway, curcumin may directly contribute to increased BDNF production.
Fasting and BDNF
Fasting, the practice of abstaining from food for a specific period, has been shown to have numerous health benefits, including the potential to increase BDNF levels.
Introduction to Fasting’s Impact on BDNF Levels
Research has shown that fasting can increase BDNF levels, which in turn supports neural health and cognitive function. Fasting has been found to trigger a process called autophagy, which is the natural recycling of damaged cellular components. This process can lead to increased BDNF production and improved brain health. Several fasting methods can be adopted to achieve these benefits.
Intermittent Fasting
Intermittent fasting is a popular method of fasting that involves alternating periods of eating and fasting. There are various intermittent fasting protocols, each with its unique eating and fasting window durations.
16:8 Method
The 16:8 method is a popular form of intermittent fasting that involves fasting for 16 hours followed by an 8-hour eating window. This approach can be relatively easy to implement and has been shown to increase BDNF levels, promoting overall brain health.
5:2 Method
The 5:2 method is another form of intermittent fasting that involves eating normally for five days a week and restricting caloric intake to approximately 500-600 calories on the remaining two non-consecutive days. This method has also been associated with increased BDNF levels and improved cognitive function.
Prolonged Fasting
Prolonged fasting involves abstaining from food for an extended period, typically ranging from 24 to 72 hours. This type of fasting can have a more significant impact on BDNF levels but may be more challenging to implement. It’s essential to consult with a healthcare professional before attempting prolonged fasting, especially for individuals with underlying health conditions.
Fasting-Mimicking Diet
The fasting-mimicking diet (FMD) is a specific dietary protocol that mimics the effects of fasting while still allowing for minimal caloric intake. This approach typically involves consuming a low-calorie, low-protein, and high-fat diet for five consecutive days, followed by a return to normal eating patterns. The fasting-mimicking diet has been shown to increase BDNF levels and support overall brain health. As with any dietary changes, it’s crucial to consult a healthcare professional before implementing the FMD.
References
[1] Effects of nutritional interventions on BDNF concentrations in humans
[2] Circulating Brain-Derived Neurotrophic Factor, Antioxidant Enzymes Activities, and Mitochondrial DNA in Bipolar Disorder
[3] Phytochemicals and cognitive health: Are flavonoids doing the trick?
[4] Suboptimal Nutrition and Low Physical Activity Are Observed Together with Reduced Plasma Brain-Derived Neurotrophic Factor (BDNF) Concentration
[5] Improved Neuroprotective Effects by Combining Bacopa monnieri and Rosmarinus officinalis
[6] The Gut-Brain Axis: How Your Microbiome Influences Cognitive Health
[7] Resveratrol Increases Serum BDNF Concentrations and Reduces Vascular Smooth Muscle Cells Contractility
[8] Ashwagandha: A Review of Clinical Use and Efficacy