In recent years, nootropics have captured the attention of researchers and biohackers alike, promising enhanced cognitive abilities and improved brain health. Among the myriad of compounds being investigated for their potential nootropic effects, C60 Fullerene, a unique carbon molecule, stands out as an intriguing candidate. It has demonstrated remarkable properties, including antioxidant and anti-inflammatory effects.
Contents
Introduction to C60 Fullerene
Carbon, one of the most abundant elements on Earth, exhibits a wide range of properties and applications due to its unique ability to form various allotropes. From the hardness of diamond to the electrical conductivity of graphite, carbon’s versatile nature is the foundation of countless innovations in science and technology. One such allotrope that has captured the imagination of researchers is the C60 Fullerene, also known as the “Buckyball.”
Overview of Carbon Allotropes
Carbon allotropes are different structural forms of the same element, resulting in unique physical and chemical properties [1]. Some well-known carbon allotropes include diamond, graphite, amorphous carbon, and carbon nanotubes. The discovery of C60 Fullerene expanded the family of carbon allotropes, opening up new avenues of research and potential applications.
Discovery of C60 Fullerene
The C60 Fullerene was discovered in 1985 by researchers Robert Curl, Harold Kroto, and Richard Smalley [2]. Their groundbreaking work, which earned them the 1996 Nobel Prize in Chemistry, was based on the observation of a new form of carbon in the shape of a truncated icosahedron, resembling a soccer ball. Composed of 60 carbon atoms, the C60 molecule exhibits a unique structure, with each carbon atom bonded to three others, forming a pattern of hexagons and pentagons.
Unique Structure and Properties
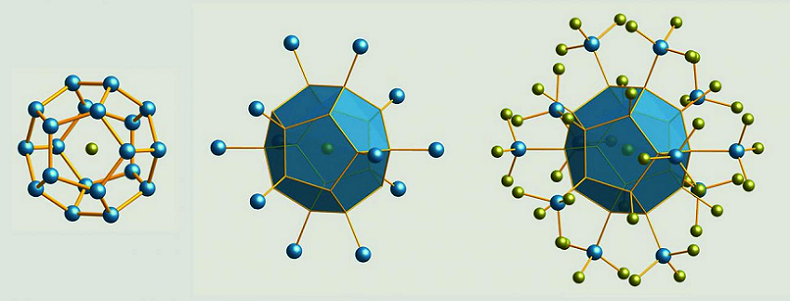
The C60 Fullerene’s distinctive structure endows it with a set of remarkable properties, distinguishing it from other carbon allotropes. It is highly stable, resistant to high temperatures and pressures, and can even withstand extreme chemical conditions.
Due to its electron-rich nature, C60 Fullerene acts as an efficient free radical scavenger, making it a potent antioxidant. Additionally, its unique geometry allows it to encapsulate various atoms and molecules, enabling potential applications in drug delivery and materials science.

Nootropics: A Brief Overview
Nootropics, also known as “smart drugs” or cognitive enhancers, have been steadily gaining popularity for their potential to improve cognitive function, memory, creativity, and motivation in healthy individuals. As the quest for optimal brain performance continues to gain traction, researchers have been investigating a wide variety of substances for their nootropic properties, including the C60 Fullerene.
Definition and Purpose of Nootropics
The term “nootropic” was coined by Romanian psychologist and chemist Dr. Corneliu E. Giurgea in 1972, derived from the Greek words “nous” (mind) and “trepein” (to bend or turn) [3]. Nootropics are substances that can enhance cognitive function, particularly executive functions such as memory, creativity, motivation, and attention, without causing significant side effects or toxicity. The primary goal of nootropics is to support and optimize brain function in healthy individuals, as well as mitigate age-related cognitive decline and protect the brain from injury or disease.
Common Types and Functions
Nootropics can be classified into various categories based on their chemical composition, source, and mechanism of action. Some common types of nootropics include:
- Natural Nootropics: These are substances derived from natural sources, such as herbs, plants, or fungi, and include compounds like ginkgo biloba, Bacopa monnieri, and lion’s mane mushroom. Natural nootropics often have a long history of traditional use and may exhibit antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, and neuroprotective properties.
- Synthetic Nootropics: These are man-made compounds, such as racetams (e.g., piracetam, aniracetam, and oxiracetam) and modafinil, that have been designed specifically for their cognitive-enhancing effects. Synthetic nootropics typically target specific neurotransmitter systems or cellular processes involved in learning, memory, and attention.
- Nutraceuticals: Nutraceuticals are dietary supplements that contain a combination of vitamins, minerals, amino acids, and other nutrients that support optimal brain function. Examples of nutraceuticals include omega-3 fatty acids, B vitamins, and choline.
C60 Fullerene as a Potential Nootropic
The unique properties of C60 Fullerene, including its stability, electron-rich nature, and ability to encapsulate other molecules, have led researchers to investigate its potential as a nootropic.
Antioxidant Properties
One of the most significant attributes of C60 Fullerene is its ability to act as a potent antioxidant, thanks to its electron-rich structure. This property allows C60 Fullerene to interact with free radicals and neutralize them, protecting cells from oxidative stress and damage.
Free Radical Scavenging
Free radicals are unstable molecules that can damage cellular structures, including proteins, lipids, and DNA. The brain, with its high metabolic activity and oxygen consumption, is particularly vulnerable to free radical damage. This damage can lead to a decline in cognitive function and contribute to the development of neurodegenerative diseases. C60 Fullerene’s ability to scavenge free radicals can help protect the brain from oxidative stress, potentially preventing or reducing cognitive decline [4].
Impact on Cellular Health
C60 Fullerene’s antioxidant effects can also benefit cellular health by reducing inflammation, promoting cellular repair mechanisms, and supporting the function of mitochondria, the cell’s energy-producing organelles [5]. Improved cellular health may translate into better cognitive function, as healthy brain cells are better equipped to communicate, process information, and adapt to new challenges.
Neuroprotective Effects
C60 Fullerene has also been investigated for its potential neuroprotective effects, which can contribute to its nootropic potential by preserving and enhancing the brain’s neural structures.
Prevention of Neurodegenerative Diseases
C60 Fullerene’s antioxidant and anti-inflammatory properties may help protect the brain from the damage associated with neurodegenerative diseases, such as Alzheimer’s and Parkinson’s [6]. By reducing oxidative stress and inflammation in the brain, C60 Fullerene could potentially slow the progression of these diseases and preserve cognitive function.
Promotion of Neuronal Growth and Repair
Emerging research suggests that C60 Fullerene may also promote neuronal growth and repair by supporting neurogenesis, the process by which new neurons are generated, and enhancing synaptic plasticity, the ability of neurons to form new connections [7]. These processes are critical for learning, memory, and overall cognitive function.
Cognitive Enhancement
The potential cognitive-enhancing effects of C60 Fullerene are a direct result of its antioxidant and neuroprotective properties. By protecting the brain from oxidative stress, inflammation, and damage, C60 Fullerene can help maintain optimal brain function and may even improve various aspects of cognition.
Memory and Learning
C60 Fullerene’s ability to promote neuronal growth and synaptic plasticity can potentially enhance memory and learning by supporting the formation and consolidation of new memories and improving the brain’s ability to adapt to new information and experiences [8].
Attention and Focus
C60 Fullerene may also improve attention and focus by reducing inflammation and oxidative stress in the brain, which can interfere with the efficient functioning of neural circuits responsible for attention and information processing [9]. Enhanced attention and focus can contribute to better overall cognitive performance and the ability to handle complex tasks effectively.

C60 Fullerene Bioavailability
For any nootropic to be effective, it must be bioavailable, meaning that it can be absorbed and utilized by the body. C60 Fullerene faces certain challenges in terms of bioavailability due to its inherent properties.
Solubility and Absorption Challenges
One of the primary challenges in utilizing C60 Fullerene as a nootropic is its poor solubility in water and most biological fluids. This property can limit its absorption into the bloodstream and its ability to cross the blood-brain barrier, a highly selective membrane that protects the brain from potentially harmful substances [10]. Consequently, researchers have been developing methods to improve C60 Fullerene’s solubility and absorption.
Liposomal and Nanoparticle Delivery Methods
One approach to enhance C60 Fullerene’s bioavailability is by using liposomal and nanoparticle delivery systems. Liposomes are tiny, spherical vesicles made up of phospholipid bilayers, which can encapsulate C60 Fullerene molecules, improving their solubility and facilitating their transport across cell membranes and the blood-brain barrier.
Nanoparticles are another promising delivery system, which can be engineered to improve C60 Fullerene’s solubility, stability, and targeted delivery to specific tissues, including the brain. By incorporating C60 Fullerene into these advanced delivery systems, researchers aim to overcome its bioavailability challenges and maximize its potential as a nootropic.
Potential Synergistic Effects with Other Nootropics
Another aspect of C60 Fullerene’s potential as a nootropic lies in its ability to interact with and enhance the effects of other cognitive enhancers. By combining C60 Fullerene with other nootropics that target different aspects of brain function, it may be possible to create synergistic effects that result in more pronounced cognitive benefits. This approach could also help to minimize the dosage and potential side effects of individual nootropics, making them safer and more effective.
Safety and Side Effects
As with any potential nootropic or therapeutic agent, it is crucial to consider the safety and possible side effects of C60 Fullerene. Despite its promising properties and potential benefits, there is still much to learn about the long-term safety and tolerability of C60 Fullerene, particularly in humans.
Reported Side Effects of C60 Fullerene
While C60 Fullerene has shown promise as a potent antioxidant and potential nootropic, there is limited information on its side effects, especially in humans. Most of the studies conducted to date have been in vitro or in animal models, making it difficult to extrapolate the findings to humans. However, some studies have reported mild side effects, such as gastrointestinal discomfort and skin irritation, particularly when C60 Fullerene is administered in high doses or through certain routes of administration.
Toxicity Concerns and Precautions
One of the primary concerns regarding C60 Fullerene’s safety is its potential toxicity. Some studies have suggested that, under certain conditions, C60 Fullerene can generate reactive oxygen species (ROS) and cause oxidative stress, leading to cellular damage. However, these findings have been inconsistent and may depend on factors such as the concentration and solubility of C60 Fullerene, as well as the specific biological context in which it is studied.
To minimize the potential risks associated with C60 Fullerene use, it is crucial to ensure that it is properly solubilized and administered at appropriate doses. Moreover, it is essential to conduct further research, including long-term studies and clinical trials in humans, to better understand the safety and tolerability of C60 Fullerene as a nootropic.
Recommended Dosage and Guidelines
Given the limited information on C60 Fullerene’s safety and side effects in humans, it is essential to approach its use with caution. Until more comprehensive research is available, it is advisable to follow the guidelines and dosages recommended by reputable sources, such as those provided by the manufacturer or based on peer-reviewed scientific studies.
Individuals considering C60 Fullerene as a nootropic should consult with a healthcare professional to ensure that its use is appropriate and safe, given their specific health status and medical history.
References
[1] C60 Fullerene – an overview
[2] This Nobel Prize-Winning Molecule Could Be The Best Thing For Anti-Aging
[3] Carbon 60 (C60) – Uses, Side Effects, and More
[4] What is C60 Oil (Fullerene)? + Risks
[5] Fullerene-C60
[6] C60 fullerene as promising therapeutic agent
[7] Dopamine’s Dual Role in Brain Health and Cognitive Function
[8] Effect of Long-Term Treatment with C60 Fullerenes
[9] Can [60]fullerene maintain good health and prolong lifespan?
[10] Biological Effects of C60 Fullerene Revealed with Bacterial Biosensor—Toxic or Rather Antioxidant?

