In recent years, nootropics have gained significant attention for their potential to improve cognitive function, memory, and overall brain health. Among the myriad of compounds that have emerged in the field of cognitive enhancement, methylene blue stands out due to its unique mechanism of action and promising benefits. Here we delve into the nootropic potential of methylene blue, exploring its ability to enhance mitochondrial function and cognition.
Contents
Introduction to Nootropics and Methylene Blue
Nootropics, often referred to as “smart drugs” or “cognitive enhancers,” are compounds that aim to improve cognitive function, memory, creativity, or motivation in healthy individuals. As our understanding of the human brain continues to advance, the quest for novel nootropics has led researchers to explore a wide range of compounds, including natural substances, pharmaceutical drugs, and dietary supplements. One such compound that has gained traction in recent years is methylene blue, a synthetic molecule with a rich history in various medical applications.
Definition of Nootropics
Nootropics are substances that can enhance cognitive function without causing significant side effects or toxicity [1]. These compounds often work by modulating neurotransmitter levels, improving blood flow to the brain, or optimizing cellular energy production. Nootropics can be found in various forms, including natural plant extracts, amino acids, vitamins, and synthetic compounds.
Overview of Methylene Blue
Methylene blue, also known as methylthioninium chloride, is a synthetic dye that has been used for over a century in various medical applications, including as an antidote for cyanide poisoning, a treatment for methemoglobinemia, and as a diagnostic tool in medical imaging [2]. More recently, methylene blue has gained interest in the field of nootropics due to its unique properties that have the potential to enhance brain function.

The Role of Mitochondria in Brain Function
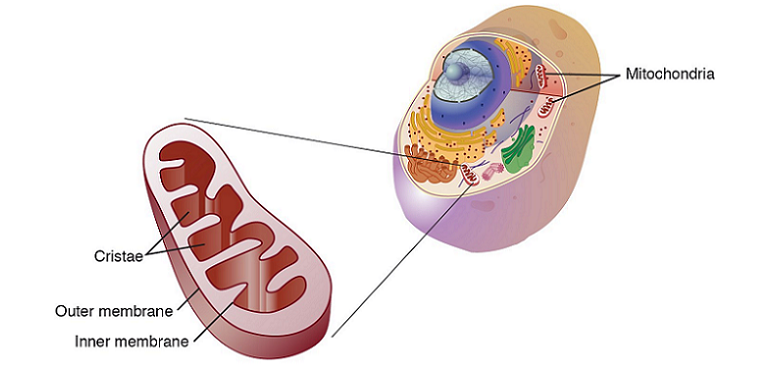
Mitochondria play a crucial role in maintaining optimal brain function. These small organelles are often referred to as the “powerhouses” of the cell, responsible for generating the energy required for cellular processes.
Overview of Mitochondria
Mitochondria are double-membraned organelles found in the cells of most eukaryotic organisms. Their primary function is to generate adenosine triphosphate (ATP), the primary energy currency of cells, through a process known as oxidative phosphorylation. In addition to energy production, mitochondria also play a critical role in other cellular processes, such as regulating the cell cycle, maintaining calcium homeostasis, and mediating apoptosis [3].
Importance of Mitochondria in Neuronal Function
Neurons are highly dependent on mitochondria for their function, as they require a significant amount of energy to maintain their specialized processes, including neurotransmitter synthesis, ion transport, and synaptic plasticity. Mitochondria are strategically distributed within neurons to provide localized energy support for various cellular compartments, such as synapses, axons, and dendrites. This efficient energy supply is essential for the proper functioning of neuronal networks and overall cognitive performance.
Mitochondrial Dysfunction and Cognitive Decline
Mitochondrial dysfunction has been implicated in various neurodegenerative diseases and age-related cognitive decline. [4] Impaired mitochondrial function can lead to a decrease in ATP production, increased production of reactive oxygen species (ROS), and a subsequent cascade of events that can damage neuronal structures and disrupt neural communication.
Mitochondrial dysfunction has been linked to the development of Alzheimer’s disease, Parkinson’s disease, and other cognitive disorders. Therefore, maintaining optimal mitochondrial function is crucial for preserving cognitive health and preventing age-related cognitive decline.

Methylene Blue as a Mitochondrial Enhancer
Methylene blue has emerged as a potential mitochondrial enhancer due to its unique mechanism of action that can improve mitochondrial function and, consequently, cellular energy production.
Mechanism of Action
Methylene blue acts on the mitochondria through two primary mechanisms: redox cycling and Complex IV activation [5]. Both of these mechanisms contribute to improved mitochondrial function and enhanced cellular energy production.
Redox Cycling
Methylene blue can undergo redox cycling within the mitochondria, accepting and donating electrons in the electron transport chain (ETC). This redox cycling property enables methylene blue to act as an electron carrier, facilitating the transfer of electrons between different ETC complexes, ultimately leading to increased ATP production.
Complex IV Activation
Methylene blue also directly stimulates Complex IV, also known as cytochrome c oxidase, within the ETC. Complex IV plays a crucial role in the final step of oxidative phosphorylation, where it catalyzes the transfer of electrons to molecular oxygen, generating water as a byproduct. Activation of Complex IV by methylene blue enhances the efficiency of the ETC, resulting in increased ATP production.
Methylene Blue’s Impact on Mitochondrial Function
The combined effects of redox cycling and Complex IV activation contribute to the overall improvement of mitochondrial function by methylene blue.
Increased ATP Production
By facilitating electron transfer and activating Complex IV, methylene blue enhances the overall efficiency of the ETC, leading to increased ATP production [6]. This increase in cellular energy can support various energy-demanding processes within neurons, such as ion transport, synaptic plasticity, and neurotransmitter synthesis, ultimately promoting optimal brain function.
Improved Mitochondrial Respiration
Methylene blue’s influence on mitochondrial function extends beyond ATP production. Its redox cycling properties can also help maintain the balance between the production and removal of ROS, which are generated as byproducts of mitochondrial respiration [7]. By reducing ROS levels, methylene blue can protect neuronal structures from oxidative damage and support the overall health of the mitochondrial network.
Cognitive Benefits of Methylene Blue
Given its ability to enhance mitochondrial function, methylene blue has shown promise as a nootropic agent, with potential cognitive benefits in various domains, including memory and executive function.
Memory Enhancement
Methylene blue has been shown to improve memory in both preclinical and human studies, likely due to its positive effects on mitochondrial function and overall neuronal health.
Preclinical Studies
In animal studies, methylene blue has demonstrated the ability to improve memory consolidation and retrieval in various memory tasks [8]. For instance, rodent studies have shown that methylene blue administration can enhance long-term memory in contextual and spatial memory tasks, as well as in object recognition tasks. These improvements have been attributed to the compound’s ability to boost mitochondrial function and reduce oxidative stress in the brain.
Human Studies
Preliminary human studies also suggest that methylene blue may have memory-enhancing properties [9]. In a small clinical trial involving healthy adults, a single dose of methylene blue improved short-term memory and increased functional magnetic resonance imaging (fMRI) activity in brain regions associated with memory processing. While these findings are promising, more extensive clinical trials are needed to further investigate the memory-enhancing effects of methylene blue in humans.
Improved Executive Function
Methylene blue has also shown potential in improving executive functions, such as attention, focus, and cognitive flexibility.
Attention and Focus
While there is limited direct evidence on methylene blue’s effects on attention and focus, its ability to enhance mitochondrial function and increase neuronal energy production may indirectly support these cognitive domains. Improved energy availability in the brain could contribute to better attentional control and sustained focus.
Cognitive Flexibility
Cognitive flexibility, the ability to adapt and switch between tasks or mental processes, may also benefit from methylene blue supplementation. Animal studies have demonstrated that methylene blue can improve cognitive flexibility in tasks that require strategy-switching and adaptation to new rules. While human studies in this area are currently limited, the preclinical evidence suggests that methylene blue may hold promise in enhancing this aspect of executive function.
Potential Benefits in Neurodegenerative Diseases
Methylene blue’s ability to improve mitochondrial function and reduce oxidative stress has led researchers to investigate its potential benefits in neurodegenerative diseases, such as Alzheimer’s and Parkinson’s disease.
Alzheimer’s Disease
Preclinical studies have shown that methylene blue can reduce amyloid-beta and tau protein accumulation, two hallmarks of Alzheimer’s disease pathology [10]. In animal models of Alzheimer’s disease, methylene blue treatment has been associated with improved memory and reduced neuroinflammation. While these findings are promising, clinical trials in humans have yielded mixed results, and further research is needed to determine the efficacy of methylene blue in Alzheimer’s disease treatment.
Parkinson’s Disease
In animal models of Parkinson’s disease, methylene blue has demonstrated neuroprotective effects, reducing dopaminergic neuron loss and improving motor function [11]. These effects are thought to be mediated by methylene blue’s impact on mitochondrial function and antioxidant properties. Although preliminary, these findings suggest that methylene blue may have potential therapeutic benefits in Parkinson’s disease, warranting further investigation in human trials.
Comparing Methylene Blue to Other Nootropics
As interest in nootropics continues to grow, it is essential to evaluate the advantages and limitations of methylene blue in comparison to other cognitive enhancers. In this section, we will discuss the unique benefits of methylene blue, potential limitations and considerations, and the possibility of combining it with other nootropics for synergistic effects.
Advantages of Methylene Blue
Methylene blue possesses several unique advantages compared to other nootropics:
- Mitochondrial Enhancement: Methylene blue’s primary mechanism of action, enhancing mitochondrial function through redox cycling and Complex IV activation, sets it apart from many other nootropics, which often work through modulating neurotransmitter levels or improving blood flow.
- Antioxidant Properties: Methylene blue’s ability to reduce oxidative stress in the brain may offer additional neuroprotective benefits beyond its impact on cognition.
- Established Safety Profile: With its long history of medical use, methylene blue has an established safety profile, making it a relatively safe option for cognitive enhancement.
Limitations and Considerations
Despite its advantages, there are some limitations and considerations to be aware of when evaluating methylene blue as a nootropic:
- Limited Human Studies: While preclinical research on methylene blue is promising, human studies exploring its cognitive benefits are still limited, and more extensive trials are needed to determine its efficacy in healthy individuals and those with cognitive impairments.
- Dosing and Absorption: The optimal dose of methylene blue for cognitive enhancement is not yet well-established, and individual responses may vary. Additionally, the compound’s bioavailability may be affected by factors such as stomach acidity, food intake, and individual metabolism.
- Potential Side Effects: Although generally well-tolerated, methylene blue can cause some side effects, such as dizziness, headache, and gastrointestinal disturbances. At higher doses, it may cause more severe side effects, including serotonin syndrome, when combined with certain medications.
Synergistic Effects with Other Nootropics
Methylene blue may be combined with other nootropics for potential synergistic effects, enhancing the benefits of each compound. For instance, pairing methylene blue with nootropics that improve blood flow, such as vinpocetine or ginkgo biloba, could provide additional support for brain health.
Likewise, combining methylene blue with substances that modulate neurotransmitter levels, like racetams or citicoline, may lead to a more comprehensive approach to cognitive enhancement. However, when combining nootropics, it is essential to consider possible interactions and consult with a healthcare professional to ensure safety and efficacy.
References
[1] Do nootropics and brain boosters work, and are they safe?
[2] Cellular and Molecular Actions of Methylene Blue in the Nervous System
[3] Mitochondria
[4] The role of mitochondria in neurodegenerative diseases
[5] Mitochondria as a target for neuroprotection: role of methylene blue and photobiomodulation
[6] The Potentials of Methylene Blue as an Anti-Aging Drug
[7] Methylene blue and its importance in medicine
[8] Methylene blue alters retention of inhibitory
avoidance responses
[9] Huperzine A: A Natural Nootropic for Memory, Focus, and Neuroprotection
[10] Alzheimer’s disease beyond amyloid: strategies for future therapeutic interventions
[11] Neuroprotective Actions of Methylene Blue and Its Derivatives

