
In the vast world of nootropics, where each compound promises a host of cognitive benefits, there stands L-theanine, a naturally occurring amino acid predominantly found in tea leaves. Revered for centuries in tea-drinking cultures for its serene and soothing effects, modern science is beginning to understand why. At the intersection of ancient practices and contemporary research lies the fascinating realm of alpha brain waves, the “frequency bridge” between our conscious and subconscious. Here we examine the calm focus promoted by L-theanine, exploring its unique ability to enhance alpha brain waves, balancing relaxation with alertness.
Contents
What is L-theanine?
L-theanine, a name often whispered in health circles and increasingly spotlighted in scientific studies, has found itself at the forefront of discussions about cognitive health and relaxation. But what exactly is this compound, and where does it come from? Let’s dive deeper to unravel the essence of L-theanine.
Natural Sources of L-theanine: Tea Leaves and Fungi
One of the most delightful ways to start a morning or wind down an evening is with a cup of tea. Beyond its comforting warmth and diverse flavors, tea, especially green tea, has long been associated with relaxation and focus. The secret to this calm alertness? L-theanine.
Predominantly found in tea leaves, especially Camellia sinensis – the plant behind green, black, and oolong teas – L-theanine is a major reason behind the unique mental state often induced by tea consumption. Interestingly, while tea is its most famous source, L-theanine is also naturally present in certain fungi, though in much smaller quantities.
Chemical Structure and Properties of L-theanine
L-theanine, chemically known as gamma-glutamylethylamide or N-ethyl-L-glutamine, is a non-essential amino acid, meaning our bodies don’t naturally produce it, and we must obtain it from dietary sources. Unlike many amino acids, L-theanine doesn’t contribute to protein building; instead, its primary role in the body is neurological.
Its structure is similar to glutamate, a neurotransmitter in the brain. This resemblance allows L-theanine to bind to the same brain receptors, playing a role in modulating neurotransmitter activity. However, despite its potential to influence brain chemistry, L-theanine doesn’t cause drowsiness. Instead, it’s best known for promoting relaxation without sedation, leading to a state of calm alertness [1].
Understanding Alpha Brain Waves
As we traverse the vast landscape of cognitive health, certain terms frequently emerge as markers of mental states and processes. Among these, ‘brain waves’ stand prominent, acting as a testament to the electrical activity that underpins every thought, emotion, and reaction. Specifically, alpha brain waves have captured the attention of neuroscientists and mindfulness practitioners alike. But what are these waves, and why are they so crucial to our mental well-being?
Definition and Significance of Alpha Brain Waves
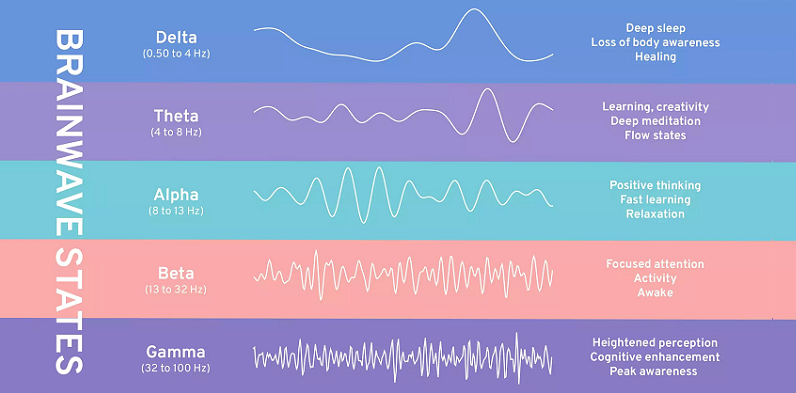
Brain waves, in essence, are patterns of electrical activity produced by neurons as they communicate with each other. These patterns vary in frequency and amplitude, with each type corresponding to different states of consciousness and cognitive activities. Alpha brain waves, typically ranging from 8 to 14 Hz, are one of the most well-recognized of these patterns.
Historically, alpha waves have been associated with a state of relaxed alertness. When you close your eyes, meditate, or simply drift into a peaceful yet attentive daydream, you’re likely riding on a tide of alpha activity. They’re neither the rapid waves of active, analytical thinking (that’s the beta range) nor the deep, slow waves of deep sleep (delta waves). Instead, they hold a middle ground, representing a bridge between the conscious and the subconscious.
Alpha Brain Waves Role in Relaxation and Alertness
Imagine that serene moment when, amidst the cacophony of daily life, you find a pocket of tranquillity. It might be during a gentle morning stretch, a meditation session, or even during those moments of “flow” when you’re deeply engrossed in a hobby. Here, alertness and relaxation aren’t at odds; they’re in harmony. This harmonious state is largely underpinned by alpha brain waves.
Alpha waves dominate when our minds are in a wakeful state but free from processing sensory inputs. This might sound counterintuitive, but think about how you feel when engrossed in a captivating book or when your gaze softens, focusing on nothing in particular, yet absorbing everything around you. This isn’t passive inactivity; it’s an active form of relaxation, a quiet readiness [2].
Distinction of Alpha Brain Waves from Other Brain Waves (e.g., Beta, Theta, Delta)
To truly appreciate the significance of alpha waves, one must understand them in the context of the broader spectrum of brain waves.
Beta Waves (14-30 Hz)
These are the “busy” waves. They dominate our normal waking state when we are alert, attentive, and engaged in problem-solving or decision-making. However, prolonged beta activity, especially in the higher ranges, can be linked to anxiety, stress, and restlessness.
Theta Waves (4-8 Hz)
Theta waves are more dominant during deep meditation, light sleep, or when we’re in a state of daydreaming. They’re linked to creativity, intuition, and emotional connection.
Delta Waves (0.1-4 Hz)
The deepest sleep stages are ruled by delta waves. They play a pivotal role in bodily restoration and healing. These waves are rarely active when we’re awake.
With this spectrum in mind, alpha waves’ role becomes clearer. They act as a transitionary phase, a bridge between the alertness of beta and the deep introspection of theta. Their significance is not just in relaxation but in facilitating the shifts between different cognitive states.
The Connection: How L-theanine Influences Alpha Brain Waves
Having traversed the landscapes of L-theanine’s origins and delved into the realm of alpha brain waves, an intriguing question emerges: How do these two seemingly disparate entities intertwine? The relationship between L-theanine and alpha brain waves is not merely coincidental; it’s a dance of chemistry and electricity, culminating in a state of calm focus.
Scientific Studies and Findings
The curiosity surrounding L-theanine’s effects on the brain has spurred a wealth of scientific research. Studies spanning decades have delved into the profound connection between this amino acid and our brain’s electrical rhythms.
Enhanced Alpha Brain Wave Activity
One of the most consistent findings across multiple studies is L-theanine’s ability to promote alpha brain wave activity. Participants, even those without any prior meditation or relaxation training, often exhibit an increase in alpha waves after consuming L-theanine [3].
A landmark study conducted in 1998 showcased this effect. Participants were given either L-theanine or a placebo, and their brain wave patterns were monitored. Those who consumed L-theanine demonstrated a significant increase in alpha brain wave activity, particularly in the occipital and parietal regions of the brain. This was observed as early as 30 minutes post-consumption, underscoring L-theanine’s swift and noticeable impact.
Reduced Anxiety and Stress
Beyond its influence on alpha waves, L-theanine has been associated with a reduction in psychological and physiological stress responses. In experiments where subjects were exposed to stressors, L-theanine intake often led to a reduction in the heart rate and salivary immunoglobulin A response. This points towards not just a subjective feeling of relaxation, but a tangible, physiological relaxation response.
Mechanism of Action
While the outcomes of L-theanine consumption are consistently reported, understanding the underpinnings of these effects requires a deeper dive into the realms of neurochemistry.
Influence on Neurotransmitters
At the heart of L-theanine’s effects is its impact on neurotransmitters, the brain’s chemical messengers. L-theanine has been shown to affect several key neurotransmitters, including:
- GABA (Gamma-Aminobutyric Acid): L-theanine increases the levels of GABA in the brain. GABA is an inhibitory neurotransmitter, meaning it reduces neural activity. Elevated GABA levels are often associated with feelings of calm and relaxation.
- Dopamine and Serotonin: Both of these neurotransmitters play roles in mood regulation, pleasure, and reward. L-theanine can influence the levels and activity of these neurotransmitters, potentially contributing to its anxiety-reducing effects.
Impact on Nerve Signals and Brain Function
Beyond neurotransmitters, L-theanine might influence brain function more directly. Its chemical structure allows it to cross the blood-brain barrier easily. Once in the brain, it can affect nerve signals and neural connectivity, thus playing a direct role in modulating brain wave activity, particularly in the promotion of alpha waves [4].

Benefits of Enhanced Alpha Brain Waves through L-theanine
Having journeyed through the intricate relationship between L-theanine and alpha brain waves, it’s essential to understand the tangible benefits one can derive from this connection. Enhancing alpha brain wave activity isn’t merely a scientific curiosity; it translates into real-world advantages that can profoundly impact our daily lives, productivity, and overall well-being.
Improved Cognitive Performance
In the symphony of our brain’s electrical rhythms, the prominence of alpha waves often coincides with heightened cognitive faculties.
Studies have consistently shown that when individuals experience an increase in alpha wave activity—such as after consuming L-theanine—they often exhibit better attention, sharper memory recall, and faster reaction times. This isn’t about hyper-charging the brain, but rather tuning it to a state where it operates at an optimal balance of alertness and relaxation, a sweet spot for many cognitive tasks.
Increased Creativity and Problem-Solving Ability
Creativity often blossoms in moments of quiet reflection, when the conscious mind takes a step back, allowing the subconscious to come forward. Enhanced alpha activity, fostered by L-theanine, sets the stage for such moments.
Researchers have found that tasks requiring divergent thinking—an essential component of creativity—often see improved performance under heightened alpha wave conditions. This means that when seeking solutions outside the box or looking for innovative approaches, an alpha-dominant brain state, like that encouraged by L-theanine, can be a valuable ally [5].
Reduced Stress and Anxiety
Stress and anxiety are, unfortunately, common companions in modern life. The fast-paced nature of today’s world, with its incessant demands, can take a toll on mental health. Here, L-theanine steps in as a soothing balm.
As discussed earlier, L-theanine’s impact on neurotransmitters, particularly GABA, contributes to a state of calm. By enhancing alpha brain wave activity, L-theanine provides a two-fold defense against stress: a direct neurochemical response and the promotion of a brain wave state synonymous with relaxation. This dual action can lead to a notable reduction in feelings of stress and anxiety, making challenges more manageable and daunting tasks less overwhelming.
Enhanced Meditation and Mindfulness Practices
For those who practice meditation or mindfulness, L-theanine can serve as a potent aid. The core of many such practices is to achieve a state of present-moment awareness, where the mind is neither agitated nor lethargic.
This state of equilibrium aligns beautifully with the calm focus of enhanced alpha brain waves. Consuming L-theanine prior to meditation or mindfulness exercises can help practitioners achieve deeper states of focus more quickly, making sessions more fruitful and insights more profound.
References
[1] What You Need to Know About L-theanine
[2] Effects of l-theanine on attention and reaction time response
[3] L-theanine, a natural constituent in tea, and its effect on mental state
[4] The 5 Best L-Theanine Supplements of 2023, According to Experts
[5] L-Theanine for Sleep

