
In today’s fast-paced world, finding ways to improve focus and cognitive function is more important than ever. One intriguing method that has recently gained popularity is the use of binaural beats. But what exactly are binaural beats, and can they genuinely enhance brain function and focus? Here we delve into the science behind binaural beats, explore their potential benefits, and provide practical guidance for those interested in harnessing the power of this auditory phenomenon to boost their cognitive performance.
Contents
Understanding Binaural Beats
Binaural beats are a unique auditory phenomenon that can potentially influence the brain’s activity and cognitive processes. To understand how they work and their potential effects on brain function and focus, let’s first define binaural beats and then explore the different types of brainwaves and their associated frequencies.
Definition of Binaural Beats
Binaural beats are an auditory illusion created when two slightly different frequencies are presented to each ear separately through headphones. The brain perceives a third, unique frequency as the difference between these two frequencies. For example, if a 300 Hz tone is played in the left ear and a 310 Hz tone is played in the right ear, the brain will perceive a 10 Hz binaural beat.
How Binaural Beats Are Created: Difference in Frequency Between Two Auditory Inputs
Binaural beats are created through a process known as frequency following response (FFR). When the brain detects the frequency difference between the two sounds, it tries to synchronize its internal brainwaves to match the perceived binaural beat frequency. This process can potentially lead to changes in cognitive states or mental processes.
The Four Types of Brainwaves and Associated Frequencies
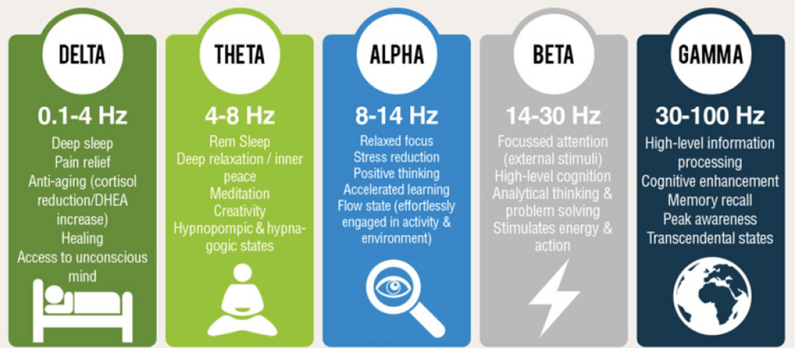
The human brain produces various types of electrical activity, which can be categorized into four primary brainwave states based on their frequency range [1]:
- Delta (0.5-4 Hz): These slow brainwaves are associated with deep sleep, unconsciousness, and regeneration. They are vital for physical and mental restoration.
- Theta (4-8 Hz): Theta waves occur during deep relaxation, light sleep, and meditation. They play a role in creativity, intuition, and memory consolidation.
- Alpha (8-13 Hz): Alpha waves are present during relaxation, daydreaming, and light meditation. They are responsible for promoting calmness, relaxation, and a heightened sense of awareness.
- Beta (13-30 Hz): Beta waves are dominant during waking hours and are involved in active thinking, problem-solving, and focus. High levels of beta waves can also be associated with anxiety and stress.
The Role of Each Brainwave State in Cognitive Processes
Each brainwave state plays a unique role in cognitive processes and mental states. Delta waves are crucial for physical and mental restoration, while theta waves are linked to creativity, intuition, and memory consolidation. Alpha waves are associated with relaxation and heightened awareness, whereas beta waves are crucial for active thinking and focus. By influencing these brainwave states through binaural beats, it is believed that specific cognitive processes can be enhanced or altered.
How Binaural Beats Work
To comprehend the potential effects of binaural beats on brain function and focus, it’s essential to understand the underlying mechanisms through which they impact the brain. In this section, we will discuss the concept of brainwave entrainment, the process of synchronization between brainwaves and external auditory stimuli, and the role of headphones in experiencing binaural beats.
The Concept of Brainwave Entrainment
Brainwave entrainment is a technique that uses rhythmic stimuli, such as sound or light, to synchronize the brain’s electrical activity with a specific frequency. The brain naturally attempts to match its brainwaves with the frequency of the external stimulus, leading to a shift in cognitive state or mental processes. Binaural beats are an example of auditory brainwave entrainment, where the brain synchronizes its activity with the perceived beat frequency.
The Process of Synchronization Between Brainwaves and External Auditory Stimuli
When a person listens to binaural beats, their brain perceives the difference in frequency between the two tones presented to each ear. As a result, the brain generates a third frequency that corresponds to the difference between the two original tones. This perceived frequency influences the brain’s electrical activity, causing it to synchronize with the binaural beat frequency [2].
For example, if a person listens to a 200 Hz tone in the left ear and a 210 Hz tone in the right ear, the brain perceives a 10 Hz binaural beat. The brain’s electrical activity will then attempt to synchronize with this 10 Hz frequency, leading to a shift in the dominant brainwave state. In this case, the 10 Hz frequency falls within the alpha range, potentially promoting relaxation and heightened awareness.
The Role of Headphones in Experiencing Binaural Beats
Headphones play a crucial role in experiencing the effects of binaural beats. They ensure that each ear receives the correct frequency, without any mixing or interference from external sounds. Without headphones, the two tones would blend together in the air, nullifying the binaural beat effect. Therefore, using headphones is essential for isolating the frequencies and allowing the brain to perceive and synchronize with the intended binaural beat.
Scientific Evidence for Binaural Beats’ Effects on Brain Function and Focus
Over the years, numerous research studies have investigated the potential benefits of binaural beats on cognitive function and focus. Here we examine the findings of these studies, discuss their limitations, and address the potential criticisms.
Research Studies Supporting the Benefits of Binaural Beats
Several studies have suggested that binaural beats may positively influence various cognitive processes, including:
- Improved focus and concentration: Research has shown that binaural beats in the beta frequency range (13-30 Hz) can enhance focus, attention, and cognitive performance. In a study published in the Journal of Cognitive Neuroscience, participants who listened to beta-frequency binaural beats demonstrated improved attention and working memory compared to a control group [3].
- Enhanced memory and learning: Binaural beats in the theta frequency range (4-8 Hz) have been associated with improved memory consolidation and learning. A study published in the Journal of Neuroscience found that listening to theta-frequency binaural beats enhanced participants’ memory recall and recognition [4].
- Reduced stress and anxiety: Binaural beats in the alpha (8-13 Hz) and theta frequency ranges have been linked to reductions in stress and anxiety levels. A study published in the Journal of Alternative and Complementary Medicine reported that participants who listened to alpha-frequency binaural beats experienced reduced anxiety and an increase in overall relaxation [5].
Limitations and Criticism of Current Research
Despite the promising findings, it is essential to consider the limitations and criticisms of the current research on binaural beats:
- Small sample sizes: Many studies on binaural beats have used small sample sizes, which limits the generalizability of the findings. Larger, well-controlled studies are needed to confirm and expand upon the existing evidence.
- Lack of standardized methodologies: Research on binaural beats has often employed varying methodologies, making it difficult to compare results across studies. There is a need for more standardized approaches to studying the effects of binaural beats on cognitive function and focus.
- Potential placebo effect: Some critics argue that the observed benefits of binaural beats could be attributed to the placebo effect, meaning that participants experience improvements in cognition and focus simply because they expect to. More rigorous studies with appropriate control groups and blinding procedures are necessary to rule out the possibility of a placebo effect.

How to Use Binaural Beats for Enhanced Brain Function and Focus
If you’re interested in trying binaural beats to potentially improve your cognitive performance, it’s essential to know how to use them effectively. Here we discuss choosing the appropriate frequency range, determining the optimal duration and frequency of use, creating a conducive environment for listening, and combining binaural beats with other focus-enhancing techniques.
Choosing the Appropriate Frequency Range
To reap the potential benefits of binaural beats, you must select the appropriate frequency range based on your desired outcome:
- For improved focus and concentration, choose binaural beats in the beta frequency range (13-30 Hz).
- To enhance memory and learning, opt for binaural beats in the theta frequency range (4-8 Hz).
- If your goal is to reduce stress and anxiety, select binaural beats in the alpha frequency range (8-13 Hz).
Duration and Frequency of Use
The optimal duration and frequency of use for binaural beats can vary depending on individual factors and desired outcomes. However, some general guidelines to follow include:
- Begin by listening to binaural beats for 15-30 minutes per session.
- Gradually increase the session duration to a maximum of 60 minutes if desired.
- Aim for consistent use, such as daily or every other day, to maximize potential benefits.
- Experiment with different frequencies and durations to find what works best for your needs.
Creating a Conducive Environment for Listening
To ensure the effectiveness of binaural beats, it’s essential to create a comfortable and distraction-free environment:
- Use high-quality headphones to ensure proper delivery of the binaural beat frequencies.
- Find a quiet, comfortable space where you can relax and focus on the audio without interruptions.
- Consider incorporating other relaxation techniques, such as deep breathing or meditation, to enhance the overall experience.
Combining Binaural Beats with Other Focus-enhancing Techniques
To maximize the potential benefits of binaural beats, consider incorporating them into a broader cognitive enhancement strategy. Some complementary techniques include:
- Regular physical exercise: Exercise has been shown to improve cognitive function and reduce stress.
- Mindfulness meditation: Practicing mindfulness can help increase focus, attention, and emotional well-being.
- Proper nutrition: Consuming a balanced diet rich in brain-boosting nutrients, such as omega-3 fatty acids, can support cognitive function and overall health.
- Adequate sleep: Ensuring that you get enough restorative sleep is vital for maintaining optimal cognitive performance and focus.

Light and Sound Meditation vs Binaural Beats
When people discuss binaural beats as it relates to cognition, the topic of light and sound meditation often arises.
What Is Light and Sound Meditation?
Light and sound meditation, also known as audio-visual entrainment (AVE) or brainwave entrainment, is a technique that combines rhythmic light and sound stimuli to influence brain activity and promote relaxation, focus, and overall well-being. This form of meditation involves the use of specialized devices or machines that generate synchronized flashes of light, often through goggles or glasses, and corresponding tones or beats delivered through headphones [6].
The underlying principle of light and sound meditation is brainwave entrainment, which aims to synchronize the brain’s electrical activity with the frequencies of the external stimuli. By exposing the brain to specific light and sound patterns, users can potentially induce altered states of consciousness, similar to those achieved during traditional meditation practices. This technique has been associated with various cognitive benefits, including improved mood, enhanced focus, reduced stress, and increased relaxation.
How Light and Sound Meditation Cognitively Compares to Binaural Beats
Both light and sound meditation and binaural beats are techniques that aim to influence brain activity and cognitive health through external stimuli. While binaural beats focus solely on auditory stimuli, light and sound meditation (AVE) combines both auditory and visual stimulation to achieve the desired effects. Here’s a comparison of the two techniques in terms of their potential effects on cognitive health.
Mechanism of action
Both binaural beats and light and sound meditation rely on the concept of brainwave entrainment. Binaural beats use two slightly different frequencies presented to each ear, while light and sound meditation employs rhythmic flashes of light and synchronized tones or beats. In both cases, the brain attempts to synchronize its electrical activity with the external stimuli, potentially leading to changes in cognitive states or mental processes.
Research evidence
Studies have shown that both binaural beats and light and sound meditation can potentially influence cognitive health. Binaural beats have been associated with improved focus, memory, and stress reduction, as discussed earlier. Similarly, light and sound meditation has been found to positively impact mood, attention, and relaxation. However, it’s essential to note that the research on both techniques is still in its early stages, and more studies are needed to fully understand their effects and potential applications.
Practical considerations
While both techniques can be used for enhancing cognitive health, there are some practical differences. Binaural beats require only a pair of headphones and can be easily accessed through various apps or online platforms. Light and sound meditation, on the other hand, may necessitate the use of specialized devices that combine synchronized light and sound stimulation, which can be more expensive and less accessible.
Personal preference
The choice between binaural beats and light and sound meditation may ultimately come down to individual preference. Some people may find the combined visual and auditory stimulation of light and sound meditation more engaging and effective, while others might prefer the simplicity and ease of use associated with binaural beats.
References
[1] What is the function of the various brainwaves?
[2] Binaural Beats
[3] The Effect of Binaural Beats on Visuospatial Working Memory and Cortical Connectivity
[4] The Role of Enriched Environments in Enhancing Cognitive Abilities and Brain Health
[5] The Power of Isochronic Tones: How Audio Stimulation Can Impact Brain Health and Focus
[6] Ganzframes and the Ganzfeld Effect for Light and Sound Meditation

