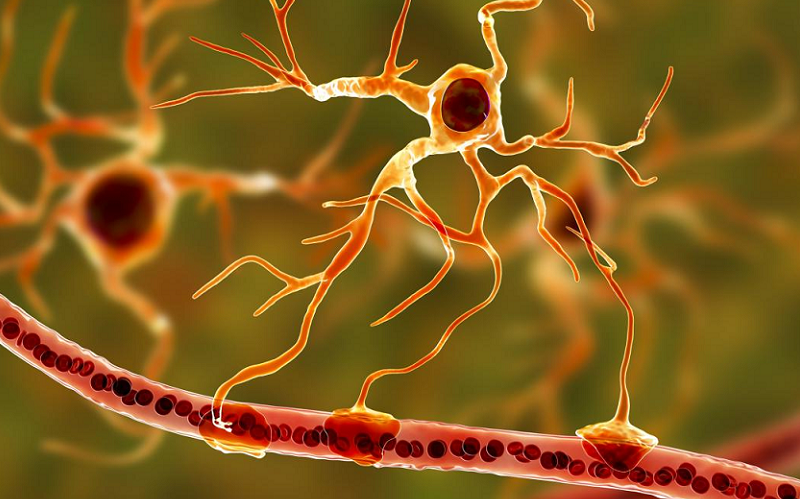
We all understand the importance of keeping our living spaces clean. Dusting, sweeping, and washing are regular tasks we undertake to maintain a clean and healthy environment. But have you ever wondered how your body, specifically your brain, keeps itself clean? Just like a well-oiled machine, the brain has its own unique cleaning service that works around the clock. This marvel of biology is known as the glymphatic system, and it plays a crucial role in maintaining not only cleanliness but also optimal brain function.
Contents
Introduction to the Glymphatic System and Brain Cleaning
Imagine living in a house filled with clutter, dirt, and dust—definitely not an inviting picture, right? Cleaning is vital not just for aesthetics but also for our well-being. A clean space is associated with better mental health, fewer allergies, and overall improved quality of life.
Just like your home, your body also requires regular maintenance and cleaning to function optimally. Our biological systems have built-in mechanisms for detoxification, waste removal, and cellular repair. However, when it comes to an organ as complex as the brain, traditional cleaning methods like those used by the rest of the body won’t suffice.
Meet the glymphatic system — your brain’s specialized cleaning crew that works tirelessly behind the scenes to keep things spick and span. It’s like the cleaning service you didn’t know you had, but one you couldn’t do without. This little-known yet vital system is responsible for flushing out waste and distributing essential nutrients, all to ensure that your brain stays in top-notch condition.
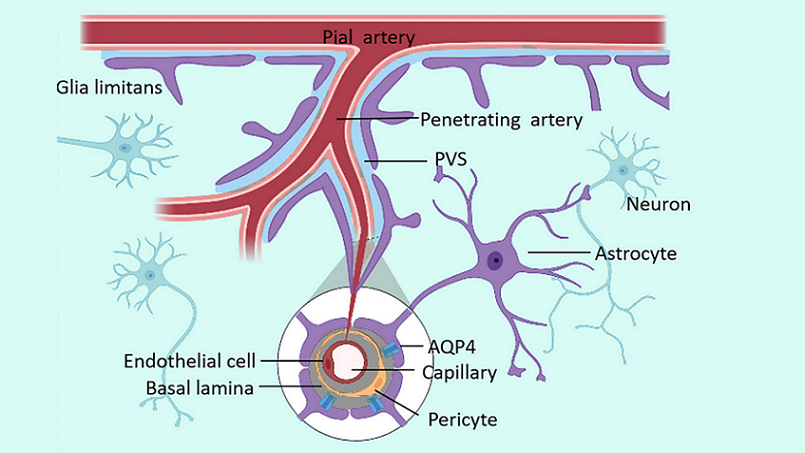
What Is the Glymphatic System?
The glymphatic system is a complex network of channels that runs alongside blood vessels in the brain. Its primary function is to clear out waste products and distribute essential nutrients to the brain cells. Think of it as the brain’s sewer and delivery system combined into one. Unlike the rest of the body, which relies on the lymphatic system for waste removal, the brain has its own specialized mechanism in the form of the glymphatic system.
Brief History and Discovery of the Glymphatic System
While the lymphatic system has been studied for centuries, the glymphatic system is a relatively new discovery. It was only in 2012 that neuroscientists first described this unique system. Researchers at the University of Rochester Medical Center coined the term “glymphatic system,” blending ‘glial cells,’ which are essential in its function, and ‘lymphatic system,’ to which it’s somewhat comparable. Despite its recent discovery, its significance in neuroscience and medical research has grown rapidly.
Glymphatic System Comparison with the Lymphatic System
You may be familiar with the lymphatic system, a network of tissues and organs that help to detoxify the body and fight off infections. While the lymphatic system serves the entire body, the glymphatic system is specialized for the brain. Unlike the lymphatic system, which uses lymphatic vessels and nodes, the glymphatic system relies on a different set of structures, including astrocytes and perivascular space, to perform its functions. It is an adaptation that meets the brain’s specific needs, and in some ways, it can be considered more efficient given the brain’s sensitivity and complexity [1].
Glymphatic System Role in Brain Health
So, why should you care about the glymphatic system? For starters, it plays a pivotal role in maintaining homeostasis in the brain. By clearing out waste like beta-amyloid plaques and excess neurotransmitters, it helps to prevent diseases like Alzheimer’s and Parkinson’s. Moreover, it regulates the distribution of essential nutrients that support cognitive functions, emotional regulation, and even sleep quality.

Anatomy of the Glymphatic System
Understanding the components that make up this system will provide a clearer picture of how it operates to keep our brain healthy.
Glymphatic System Components and Structure
The glymphatic system is a finely orchestrated network with its own set of unique structures and components. Knowing these key elements is akin to understanding the cast of characters in a play, each with a specific role that contributes to the larger story.
Astrocytes
Astrocytes are star-shaped glial cells that are foundational to the glymphatic system. They form end-feet that wrap around the blood vessels in the brain, essentially forming a channel for cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) and interstitial fluid to flow through. The integrity of these end-feet is crucial for the system to function effectively [2].
Perivascular Space
This refers to the small, fluid-filled space surrounding the blood vessels within the brain. This space serves as a pathway for the flow of CSF, which is essential for waste removal and nutrient distribution.
Aquaporin-4 Channels
These are specialized water channels located on the astrocytes that facilitate the movement of fluid within the glymphatic system. The presence of Aquaporin-4 channels greatly influences the rate at which waste is cleared and nutrients are delivered.
Glymphatic System Location within the Brain
The glymphatic system’s channels run alongside the brain’s blood vessels, providing a network that reaches into the brain’s deepest recesses. This strategic positioning allows the system to work effectively, ensuring that no part of the brain is too far away to be cleaned or nourished [3].
How the Glymphatic System Interacts with Other Systems
The glymphatic system does not operate in isolation. It closely interacts with the circulatory system, as it runs alongside blood vessels. It also has some level of interaction with the nervous system, given that its effective functioning is vital for optimal cognitive and neurological health.
Functions of the Glymphatic System
Having explored the anatomy of the glymphatic system, it’s time to turn our attention to its roles and responsibilities. What tasks does it perform, and why are these functions so essential to our well-being?
Waste Removal
Perhaps one of the most vital functions of the glymphatic system is waste removal. The brain is a highly active organ, and like any busy factory, it produces waste that needs to be efficiently managed and removed.
Types of Waste
Among the waste products that the glymphatic system helps to clear are beta-amyloid plaques, which are often implicated in Alzheimer’s disease. Other waste includes excess neurotransmitters, toxins, and metabolic byproducts [4].
Mechanism of Action
The glymphatic system uses the cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) as a medium to flush out these waste materials. The Aquaporin-4 channels and astrocytes facilitate the flow of CSF through the brain’s perivascular spaces, effectively ‘washing’ the brain and removing waste into the bloodstream, which eventually eliminates it from the body.
Distribution of Nutrients
But the glymphatic system isn’t just about taking out the trash; it’s also essential for bringing in the ‘groceries.’ In other words, it helps distribute nutrients to the brain.
Types of Nutrients
These include glucose, which is the brain’s primary source of energy, as well as various ions and amino acids that are essential for neural function.
Mechanism of Action
Much like its role in waste removal, the glymphatic system utilizes the cerebrospinal fluid to circulate these nutrients throughout the brain, ensuring that all cells receive what they need for optimal function.
Regulation of Cerebrospinal Fluid (CSF)
Beyond cleaning and nourishing, the glymphatic system also plays a role in maintaining the balance and composition of the cerebrospinal fluid, which is crucial for overall brain health [5].
Role in Sleep
Research has shown that the glymphatic system is more active during sleep. This increased activity may explain why sleep is so essential for cognitive function and why lack of sleep often leads to cognitive impairments; the system is essentially ‘cleaning up’ while you rest.
Relevance to Cognitive Functions
By ensuring that waste is removed and nutrients are evenly distributed, the glymphatic system has a direct impact on cognitive functions such as memory, attention, and problem-solving skills. In essence, a well-functioning glymphatic system sets the stage for a healthy, well-functioning brain.
References
[1] The Glymphatic System – A Beginner’s Guide
[2] Glymphatic System
[3] The Glymphatic System: A Novel Component of Fundamental Neurobiology
[4] Understanding the Glymphatic System
[5] The Brain’s Glymphatic System: Current Controversies

